Connective Tissue Table - Faculty.rmc.edu
Connective Tissue Table - Faculty.rmc.edu
Connective Tissue Table - Faculty.rmc.edu
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
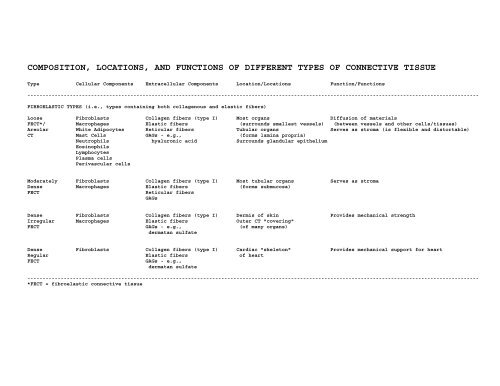
COMPOSITION, LOCATIONS, AND FUNCTIONS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE<br />
Type Cellular Components Extracellular Components Location/Locations Function/Functions<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
FIBROELASTIC TYPES (i.e., types containing both collagenous and elastic fibers)<br />
Loose Fibroblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Most organs Diffusion of materials<br />
FECT*/ Macrophages Elastic fibers (surrounds smallest vessels) (between vessels and other cells/tissues)<br />
Areolar White Adipocytes Reticular fibers Tubular organs Serves as stroma (is flexible and distortable)<br />
CT Mast Cells GAGs - e.g., (forms lamina propria)<br />
Neutrophils hyaluronic acid Surrounds glandular epithelium<br />
Eosinophils<br />
Lymphocytes<br />
Plasma cells<br />
Perivascular cells<br />
Moderately Fibroblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Most tubular organs Serves as stroma<br />
Dense Macrophages Elastic fibers (forms submucosa)<br />
FECT Reticular fibers<br />
GAGs<br />
Dense Fibroblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Dermis of skin Provides mechanical strength<br />
Irregular Macrophages Elastic fibers Outer CT "covering"<br />
FECT GAGs - e.g., (of many organs)<br />
dermatan sulfate<br />
Dense Fibroblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Cardiac "skeleton" Provides mechanical support for heart<br />
Regular Elastic fibers of heart<br />
FECT GAGs - e.g.,<br />
dermatan sulfate<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
*FECT = fibroelastic connective tissue
Type Cellular Components Extracellular Components Location/Locations Function/Functions<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
"SPECIALIZED" FIBROUS TYPES* (i.e., types with predominant fiber type)<br />
Dense Fibroblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Tendons Attachment - muscle to bone (tendon)<br />
Regular Tendinocytes GAGs - e.g., Some ligaments Attachment - bone to bone (ligament)<br />
Collagenous chondroitin sulfate Transmit forces from muscle to bone<br />
CT dermatan sulfate (thus facilitating body movements)<br />
Dense Fibroblasts Elastic fibers Intervertebral ligaments Attachment - bone to bone<br />
Regular Collagen fibers (type I) (yellow elastic ligaments)<br />
Elastic GAGs - e.g., True vocal cords<br />
CT dermatan sulfate Middle ear<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
*Specialized due to predominance of single fiber type and highly regular fiber orientation
Type Cellular Components Extracellular Components Location/Locations Function/Functions<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
"SPECIALlZED" SKELETAL TYPES (i.e., types with abundant amorphous ECM)<br />
Hyaline Cartilage Chondroblasts Collagen fibers (type II) Nasal septum Provides flexible support<br />
(hyaline type of Chondrocytes GAGs - e.g., Larynx<br />
chondrogenic CT) chondroitin sulfate Trachea<br />
keratan sulfate Bronchi<br />
hyaluronic acid Articulating surfaces of most "bones"<br />
Proteoglycans<br />
Elastic Cartilage Chondroblasts Elastic fibers Pinna/external ear Provides very flexible support<br />
(elastic type of Chondrocytes Collagen fibers (type II) Eustachian tube<br />
chondrogenic CT) GAGs - e.g., Epiglottis<br />
chondroitin sulfate Larynx<br />
keratan sulfate<br />
hyaluronic acid<br />
Fibrocartilage Chondrocytes Collagen fibers (types I, II) Intervertebral discs Provides resistance to<br />
(fibrous type of GAGs - e.g., Pubic symphysis compression and<br />
chondrogenic CT) chondroitin sulfate Knee joint shearing forces<br />
keratan sulfate Shoulder joint<br />
hyaluronic acid Mandibular joint<br />
Bone-tendon junctions<br />
Compact Bone Osteoblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Diaphysis/shaft of long "bones" Provides structural support<br />
(compact type of Osteocytes GAGs - e.g., Outer covering of all "bones" for body (especially in<br />
osseous CT) Osteoclasts chondroitin sulfate extremities)<br />
keratan sulfate<br />
Proteoglycans<br />
Glycoproteins<br />
Calcium phosphate<br />
Calcium carbonate<br />
Cancellous/Spongy Bone Osteoblasts Collagen fibers (type I) Inside skull bones, facial bones, Provides support for body<br />
(spongy type of Osteocytes GAGs - e.g., vertebrae. ribs<br />
osseous CT) Osteoclasts chondroitin sulfate Inside epiphyses of long "bones"<br />
keratan sulfate<br />
Proteoglycans<br />
Glycoproteins<br />
Calcium phosphate<br />
Calcium carbonate<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type Cellular Components Extracellular Components Location/Locations Function/Functions<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
"SPECIALIZED" CELLULAR TYPES* (i.e., types with more extensive cellular compartment)<br />
White White Adipocytes Reticular fibers Subcutaneous Provides padding<br />
Adipose Fibroblasts GAGs Around internal organs Fat storage<br />
CT<br />
Brown Brown Adipocytes Reticular fibers Subcutaneous Heat production<br />
Adipose White Adipocytes GAGs Around internal organs Fat storage<br />
CT Fibroblasts<br />
Reticular Reticular cells Reticular fibers Lymph nodes Provides supporting framework<br />
CT Lymphocytes GAGs Spleen for lymphoid organs<br />
Plasma cells Bone marrow<br />
Macrophages<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
*Specialized due to increase in cellular compartment and decrease in the extracellular compartment<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
EMBRYONIC TYPES (i.e., types found only in embryos/prenatal vertebrates)<br />
Mesenchyme/ Mesenchyme cells GAGs - e.g., Embryo Differentiates into all types of connective tissue<br />
Mesenchymal hyaluronic acid<br />
CT<br />
Mucous Differentiating Collagen fibers Embryo Differentiates into loose connective tissue<br />
CT Fibroblasts GAGs - e.g., Umbilical cord Serves as stroma<br />
hyaluronic acid<br />
chondroitin sulfate<br />
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------