Magazine – PDF - Cal Lab Magazine
Magazine – PDF - Cal Lab Magazine
Magazine – PDF - Cal Lab Magazine
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
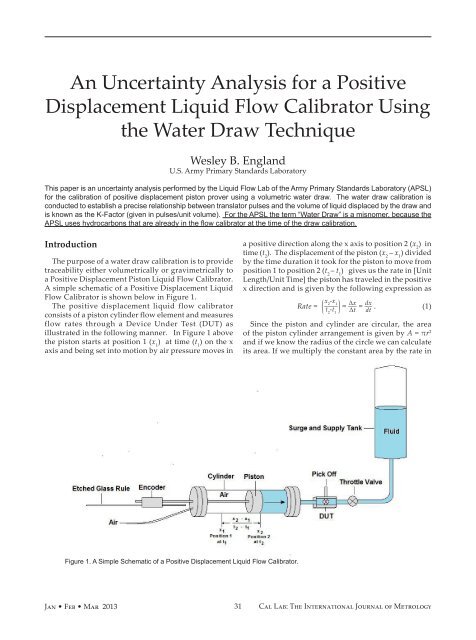
An Uncertainty Analysis for a PositiveDisplacement Liquid Flow <strong>Cal</strong>ibrator Usingthe Water Draw TechniqueWesley B. EnglandU.S. Army Primary Standards <strong>Lab</strong>oratoryThis paper is an uncertainty analysis performed by the Liquid Flow <strong>Lab</strong> of the Army Primary Standards <strong>Lab</strong>oratory (APSL)for the calibration of positive displacement piston prover using a volumetric water draw. The water draw calibration isconducted to establish a precise relationship between translator pulses and the volume of liquid displaced by the draw andis known as the K-Factor (given in pulses/unit volume). For the APSL the term “Water Draw” is a misnomer, because theAPSL uses hydrocarbons that are already in the flow calibrator at the time of the draw calibration.IntroductionThe purpose of a water draw calibration is to providetraceability either volumetrically or gravimetrically toa Positive Displacement Piston Liquid Flow <strong>Cal</strong>ibrator.A simple schematic of a Positive Displacement LiquidFlow <strong>Cal</strong>ibrator is shown below in Figure 1.The positive displacement liquid flow calibratorconsists of a piston cylinder flow element and measuresflow rates through a Device Under Test (DUT) asillustrated in the following manner. In Figure 1 abovethe piston starts at position 1 (x 1) at time (t 1) on the xaxis and being set into motion by air pressure moves ina positive direction along the x axis to position 2 (x 2) intime (t 2). The displacement of the piston (x 2<strong>–</strong> x 1) dividedby the time duration it took for the piston to move fromposition 1 to position 2 (t 2<strong>–</strong> t 1) gives us the rate in [UnitLength/Unit Time] the piston has traveled in the positivex direction and is given by the following expression asRate =____( x -x 2 1t 2-t 1) = ___ ΔxΔt = __ dxdt . (1)Since the piston and cylinder are circular, the areaof the piston cylinder arrangement is given by A = πr 2and if we know the radius of the circle we can calculateits area. If we multiply the constant area by the rate inFigure 1. A Simple Schematic of a Positive Displacement Liquid Flow <strong>Cal</strong>ibrator.Jan • Feb • Mar 201331<strong>Cal</strong> <strong>Lab</strong>: The International Journal of Metrology