Viscous Flow in Pipes.pdf
Viscous Flow in Pipes.pdf
Viscous Flow in Pipes.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
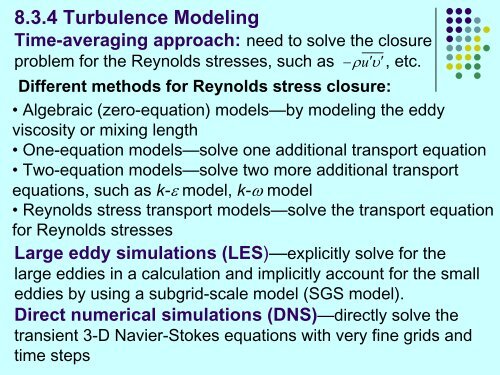
8.3.4 Turbulence Model<strong>in</strong>gTime-averag<strong>in</strong>g approach: need to solve the closureproblem for the Reynolds stresses, such as −ρuυ′ ′, etc.Different methods for Reynolds stress closure:• Algebraic (zero-equation) models—by model<strong>in</strong>g the eddyviscosity or mix<strong>in</strong>g length• One-equation models—solve one additional transport equation• Two-equation models—solve two more additional transportequations, such as k-ε model, k-ω model• Reynolds stress transport models—solve the transport equationfor Reynolds stressesLarge eddy simulations (LES)—explicitly solve for thelarge eddies <strong>in</strong> a calculation and implicitly account for the smalleddies by us<strong>in</strong>g a subgrid-scale model (SGS model).Direct numerical simulations (DNS)—directly solve thetransient 3-D Navier-Stokes equations with very f<strong>in</strong>e grids andtime steps