Logic Model Sample and Definitions - Mile High United Way
Logic Model Sample and Definitions - Mile High United Way
Logic Model Sample and Definitions - Mile High United Way
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
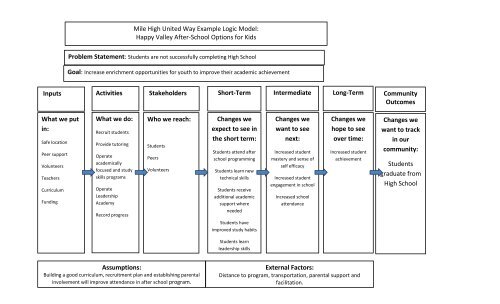
<strong>Mile</strong> <strong>High</strong> <strong>United</strong> <strong>Way</strong> Example <strong>Logic</strong> <strong>Model</strong>:Happy Valley After-School Options for KidsProblem Statement: Students are not successfully completing <strong>High</strong> SchoolGoal: Increase enrichment opportunities for youth to improve their academic achievementInputs Activities Stakeholders Short-TermIntermediateLong-TermCommunityOutcomesWhat we putin:Safe locationPeer supportVolunteersTeachersCurriculumFundingTheWhat we do:Recruit studentsProvide tutoringOperateacademicallyfocused <strong>and</strong> studyskills programsOperateLeadershipAcademyRecord progressWho we reach:StudentsPeersVolunteersChanges weexpect to see inthe short term:Students attend afterschool programmingStudents learn newtechnical skillsStudents receiveadditional academicsupport whereneededStudents haveimproved study habitsChanges wewant to seenext:Increased studentmastery <strong>and</strong> sense ofself efficacyIncreased studentengagement in schoolIncreased schoolattendanceChanges wehope to seeover time:Increased studentachievementChanges wewant to trackin ourcommunity:Studentsgraduate from<strong>High</strong> SchoolStudents learnleadership skillsAssumptions:Building a good curriculum, recruitment plan <strong>and</strong> establishing parentalinvolvement will improve attendance in after school program.External Factors:Distance to program, transportation, parental support <strong>and</strong>facilitation.
<strong>Logic</strong> <strong>Model</strong> Guidance:• Inputs: Include specifics such as how many volunteers you intend to use, how many staff, which partnerships are critical, specifics on technology if that iscritical to the success of your program, etc. Provide numbers if you are able, <strong>and</strong> describe how certain resources are critical to your success.• Activities: Describe the services, training, convening, meetings, etc. that you will do <strong>and</strong> the frequency or number of those activities.• Participation: Those noted in this column are the target of activities you described in the Activities column. Provide the number ofchildren/volunteers/parents etc. that will be reached by the activities you are engaging in. Also describe the population you intend to serve –Whatgeography <strong>and</strong> demographics? Will you serve a population with demographics that require programmatic consideration such as language or specialneeds?• Outcomes: In these columns you will describe the outcomes you hope to see as a result of the activities you are doing. Be explicit about the outcomesyou hope for – think of them as changes in knowledge, skills, abilities, behavior or circumstances. Short-term outcomes are those you expect will happenfirst <strong>and</strong> may contribute to or enable longer term outcomes. For example, you may engage in training <strong>and</strong> coaching of volunteers with the short-termoutcome of competent volunteers who will foster the longer-term outcome of improvement in child or adult outcomes for those who participate in yourprogram.• Assumptions <strong>and</strong> External Factors: If there are any assumptions you have or external factors you know will impact your program, its good to state themexplicitly there. Those might be policy issues, the assumption of continued funding, organizational considerations you may have that may impact yourprogram.• Goal: The ultimate goal, also known as the long-term outcome, of your logic model reflects the overall purpose of the program or intervention <strong>and</strong> istypically described at the population level. For example, a long-term goal could be that all children or adults with a specific identified need receivequality services through your program or intervention. This long-term goal should be logically connected temporally to the short-term <strong>and</strong> intermediateoutcomes you describe, so that the “logic” of you plan proceeds from short-term to intermediate to long-term outcomes.Generally, assume your audience knows nothing about what you do <strong>and</strong> describe it in detail so they have an underst<strong>and</strong>ing of what you will do, how much youwill do, with who, <strong>and</strong> what results that will bring about.