Composite dry sliding bearings â maintenance-free and space-saving
Composite dry sliding bearings â maintenance-free and space-saving
Composite dry sliding bearings â maintenance-free and space-saving
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
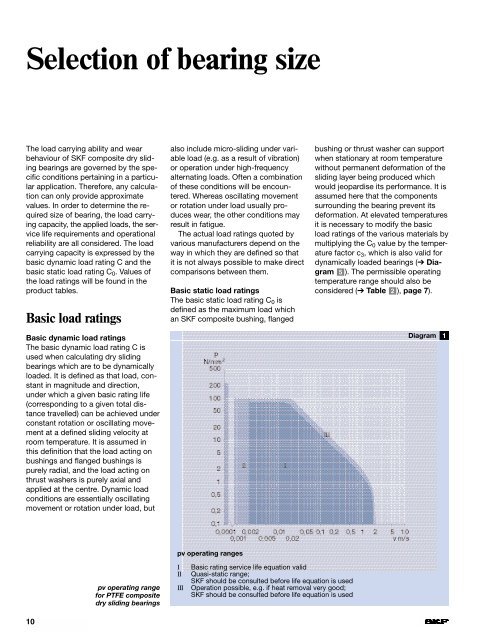
Selection of bearing sizeThe load carrying ability <strong>and</strong> wearbehaviour of SKF composite <strong>dry</strong> <strong>sliding</strong><strong>bearings</strong> are governed by the specificconditions pertaining in a particularapplication. Therefore, any calculationcan only provide approximatevalues. In order to determine the requiredsize of bearing, the load carryingcapacity, the applied loads, the servicelife requirements <strong>and</strong> operationalreliability are all considered. The loadcarrying capacity is expressed by thebasic dynamic load rating C <strong>and</strong> thebasic static load rating C 0 . Values ofthe load ratings will be found in theproduct tables.Basic load ratingsBasic dynamic load ratingsThe basic dynamic load rating C isused when calculating <strong>dry</strong> <strong>sliding</strong><strong>bearings</strong> which are to be dynamicallyloaded. It is defined as that load, constantin magnitude <strong>and</strong> direction,under which a given basic rating life(corresponding to a given total distancetravelled) can be achieved underconstant rotation or oscillating movementat a defined <strong>sliding</strong> velocity atroom temperature. It is assumed inthis definition that the load acting onbushings <strong>and</strong> flanged bushings ispurely radial, <strong>and</strong> the load acting onthrust washers is purely axial <strong>and</strong>applied at the centre. Dynamic loadconditions are essentially oscillatingmovement or rotation under load, butalso include micro-<strong>sliding</strong> under variableload (e.g. as a result of vibration)or operation under high-frequencyalternating loads. Often a combinationof these conditions will be encountered.Whereas oscillating movementor rotation under load usually produceswear, the other conditions mayresult in fatigue.The actual load ratings quoted byvarious manufacturers depend on theway in which they are defined so thatit is not always possible to make directcomparisons between them.Basic static load ratingsThe basic static load rating C 0 isdefined as the maximum load whichan SKF composite bushing, flangedbushing or thrust washer can supportwhen stationary at room temperaturewithout permanent deformation of the<strong>sliding</strong> layer being produced whichwould jeopardise its performance. It isassumed here that the componentssurrounding the bearing prevent itsdeformation. At elevated temperaturesit is necessary to modify the basicload ratings of the various materials bymultiplying the C 0 value by the temperaturefactor c 3 , which is also valid fordynamically loaded <strong>bearings</strong> (➔ Diagram5 ). The permissible operatingtemperature range should also beconsidered (➔ Table 2 ), page 7).Diagram1pv operating rangespv operating rangefor PTFE composite<strong>dry</strong> <strong>sliding</strong> <strong>bearings</strong>IIIIIIBasic rating service life equation validQuasi-static range;SKF should be consulted before life equation is usedOperation possible, e.g. if heat removal very good;SKF should be consulted before life equation is used10