Onchocerciasis - An Overview - Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences ...
Onchocerciasis - An Overview - Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences ...
Onchocerciasis - An Overview - Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
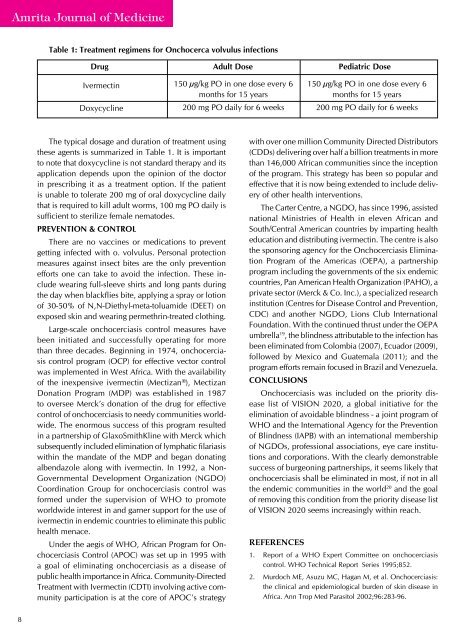
<strong>Amrita</strong> Journal <strong>of</strong> MedicineTable 1: Treatment regimens for Onchocerca volvulus infectionsDrug Adult Dose Pediatric DoseIvermectinDoxycycline150 μg/kg PO in one dose every 6months for 15 years200 mg PO daily for 6 weeks150 μg/kg PO in one dose every 6months for 15 years200 mg PO daily for 6 weeksThe typical dosage and duration <strong>of</strong> treatment usingthese agents is summarized in Table 1. It is importantto note that doxycycline is not standard therapy and itsapplication depends upon the opinion <strong>of</strong> the doctorin prescribing it as a treatment option. If the patientis unable to tolerate 200 mg <strong>of</strong> oral doxycycline dailythat is required to kill adult worms, 100 mg PO daily issufficient to sterilize female nematodes.PREVENTION & CONTROLThere are no vaccines or medications to preventgetting infected with o. volvulus. Personal protectionmeasures against insect bites are the only preventionefforts one can take to avoid the infection. These includewearing full-sleeve shirts and long pants duringthe day when blackflies bite, applying a spray or lotion<strong>of</strong> 30-50% <strong>of</strong> N,N-Diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) onexposed skin and wearing permethrin-treated clothing.Large-scale onchocerciasis control measures havebeen initiated and successfully operating for morethan three decades. Beginning in 1974, onchocerciasiscontrol program (OCP) for effective vector controlwas implemented in West Africa. With the availability<strong>of</strong> the inexpensive ivermectin (Mectizan®), MectizanDonation Program (MDP) was established in 1987to oversee Merck’s donation <strong>of</strong> the drug for effectivecontrol <strong>of</strong> onchocerciasis to needy communities worldwide.The enormous success <strong>of</strong> this program resultedin a partnership <strong>of</strong> GlaxoSmithKline with Merck whichsubsequently included elimination <strong>of</strong> lymphatic filariasiswithin the mandate <strong>of</strong> the MDP and began donatingalbendazole along with ivermectin. In 1992, a Non-Governmental Development Organization (NGDO)Coordination Group for onchocerciasis control wasformed under the supervision <strong>of</strong> WHO to promoteworldwide interest in and garner support for the use <strong>of</strong>ivermectin in endemic countries to eliminate this publichealth menace.Under the aegis <strong>of</strong> WHO, African Program for <strong>Onchocerciasis</strong>Control (APOC) was set up in 1995 witha goal <strong>of</strong> eliminating onchocerciasis as a disease <strong>of</strong>public health importance in Africa. Community-DirectedTreatment with Ivermectin (CDTI) involving active communityparticipation is at the core <strong>of</strong> APOC’s strategywith over one million Community Directed Distributors(CDDs) delivering over half a billion treatments in morethan 146,000 African communities since the inception<strong>of</strong> the program. This strategy has been so popular andeffective that it is now being extended to include delivery<strong>of</strong> other health interventions.The Carter Centre, a NGDO, has since 1996, assistednational Ministries <strong>of</strong> Health in eleven African andSouth/Central American countries by imparting healtheducation and distributing ivermectin. The centre is alsothe sponsoring agency for the <strong>Onchocerciasis</strong> EliminationProgram <strong>of</strong> the Americas (OEPA), a partnershipprogram including the governments <strong>of</strong> the six endemiccountries, Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), aprivate sector (Merck & Co. Inc.), a specialized researchinstitution (Centres for Disease Control and Prevention,CDC) and another NGDO, Lions Club InternationalFoundation. With the continued thrust under the OEPAumbrella 19 , the blindness attributable to the infection hasbeen eliminated from Colombia (2007), Ecuador (2009),followed by Mexico and Guatemala (2011); and theprogram efforts remain focused in Brazil and Venezuela.CONCLUSIONS<strong>Onchocerciasis</strong> was included on the priority diseaselist <strong>of</strong> VISION 2020, a global initiative for theelimination <strong>of</strong> avoidable blindness - a joint program <strong>of</strong>WHO and the International Agency for the Prevention<strong>of</strong> Blindness (IAPB) with an international membership<strong>of</strong> NGDOs, pr<strong>of</strong>essional associations, eye care institutionsand corporations. With the clearly demonstrablesuccess <strong>of</strong> burgeoning partnerships, it seems likely thatonchocerciasis shall be eliminated in most, if not in allthe endemic communities in the world 20 and the goal<strong>of</strong> removing this condition from the priority disease list<strong>of</strong> VISION 2020 seems increasingly within reach.REFERENCES1. Report <strong>of</strong> a WHO Expert Committee on onchocerciasiscontrol. WHO Technical Report Series 1995;852.2. Murdoch ME, Asuzu MC, Hagan M, et al. <strong>Onchocerciasis</strong>:the clinical and epidemiological burden <strong>of</strong> skin disease inAfrica. <strong>An</strong>n Trop Med Parasitol 2002;96:283-96.8