National Knowledge Commission Report to the Nation 2009: Baseline
National Knowledge Commission Report to the Nation 2009: Baseline
National Knowledge Commission Report to the Nation 2009: Baseline
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
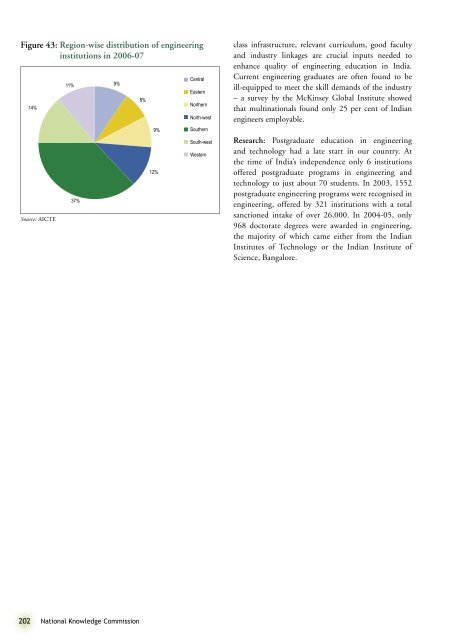
Figure 43: Region-wise distribution of engineeringinstitutions in 2006-0714%Source: AICTE11% 9%37%8%9%12%CentralEasternNor<strong>the</strong>rnNorth-westSou<strong>the</strong>rnSouth-westWesternclass infrastructure, relevant curriculum, good facultyand industry linkages are crucial inputs needed <strong>to</strong>enhance quality of engineering education in India.Current engineering graduates are often found <strong>to</strong> beill-equipped <strong>to</strong> meet <strong>the</strong> skill demands of <strong>the</strong> industry– a survey by <strong>the</strong> McKinsey Global Institute showedthat multinationals found only 25 per cent of Indianengineers employable.Research: Postgraduate education in engineeringand technology had a late start in our country. At<strong>the</strong> time of India’s independence only 6 institutionsoffered postgraduate programs in engineering andtechnology <strong>to</strong> just about 70 students. In 2003, 1552postgraduate engineering programs were recognised inengineering, offered by 321 institutions with a <strong>to</strong>talsanctioned intake of over 26,000. In 2004-05, only968 doc<strong>to</strong>rate degrees were awarded in engineering,<strong>the</strong> majority of which came ei<strong>the</strong>r from <strong>the</strong> IndianInstitutes of Technology or <strong>the</strong> Indian Institute ofScience, Bangalore.202 <strong><strong>Nation</strong>al</strong> <strong>Knowledge</strong> <strong>Commission</strong>