Tool for the Assessment of Patient Education in Diabetes in Scotland ...
Tool for the Assessment of Patient Education in Diabetes in Scotland ...
Tool for the Assessment of Patient Education in Diabetes in Scotland ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong><strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong><strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>&<strong>Tool</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong><strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong> <strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>
Contents<strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong> <strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>Introduction............................................................................................................... 1NICE criteria <strong>for</strong> structured education...................................................................... 2Philosophy............................................................................................................... 2Written curriculum.................................................................................................... 2Aims and Learn<strong>in</strong>g Outcomes.................................................................................. 3Tra<strong>in</strong>ed Educator...................................................................................................... 3Quality Assurance.................................................................................................... 4Audit........................................................................................................................ 5<strong>Tool</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong> <strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>Introduction............................................................................................................... 7Philosophy................................................................................................................. 7Curriculum, Aims and Learn<strong>in</strong>g Outcomes.............................................................. 7Tra<strong>in</strong>ed Educator....................................................................................................... 7Quality Assurance..................................................................................................... 8Audit.......................................................................................................................... 8References.............................................................................................................. 10Appendix................................................................................................................. 11Acknowledgements................................................................................................ 12A P E D S T A P E D S© NHS <strong>Education</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong> 2012. You can copy or reproduce <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation <strong>in</strong> thisdocument <strong>for</strong> use with<strong>in</strong> NHS<strong>Scotland</strong> and <strong>for</strong> non‐commercial educational purposes.Use <strong>of</strong> this document <strong>for</strong> commercial purposes is permitted only with <strong>the</strong> writtenpermission <strong>of</strong> NES.
<strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong><strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong><strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND
IntroductionThe Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Action Plan 1 endorsed<strong>the</strong> recommendations <strong>of</strong> SIGN 116 2 regard<strong>in</strong>gstructured patient education with<strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>.Structured education is central to diabetescare and to <strong>the</strong> self management <strong>of</strong> long termconditions. Moreover, people liv<strong>in</strong>g with diabeteshave stated that structured education was <strong>the</strong>most valued type <strong>of</strong> education. It is <strong>the</strong> aim <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Action Plan that peoplewith diabetes receive a structured educationprogramme that fulfils <strong>the</strong> nationally agreed criteriafrom <strong>the</strong> time <strong>of</strong> diagnosis with annual review andhave access to ongo<strong>in</strong>g education result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> an<strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> percentage <strong>of</strong> people participat<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong> self management programmes that will berecorded on SCI-<strong>Diabetes</strong> and reported <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong>Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Survey.The def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>of</strong> a structured patient educationprogramme accord<strong>in</strong>g to NICE 3 is:“a planned and graded programmethat is comprehensive <strong>in</strong> scope,flexible <strong>in</strong> content, responsive to an<strong>in</strong>dividual’s cl<strong>in</strong>ical and psychologicalneeds and adaptable to his or hereducational and cultural background.The aim <strong>of</strong> patient education is <strong>for</strong> people withdiabetes to improve <strong>the</strong>ir knowledge, skills andconfidence, enabl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>m to take <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>gcontrol <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir own condition and <strong>in</strong>tegrateeffective self-management <strong>in</strong>to <strong>the</strong>ir daily lives.Moreover, NICE recommend that:“structured patient education ismade available to all people withdiabetes at <strong>the</strong> time <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>itialdiagnosis and <strong>the</strong>n as requiredon an ongo<strong>in</strong>g basis, based on a<strong>for</strong>mal, regular assessment <strong>of</strong> need.””The current document aims to def<strong>in</strong>e <strong>the</strong> processadopted with<strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong> to assess patienteducation provision accord<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong>Action Plan 1 thus ensur<strong>in</strong>g that people withdiabetes, and/or <strong>the</strong>ir carers, receive a structurededucation programme that fulfils <strong>the</strong> nationallyagreed criteria. The document is written <strong>for</strong>pr<strong>of</strong>essional health care workers deliver<strong>in</strong>g patienteducation. It is acknowledged that patientscan also deliver patient education and <strong>the</strong>follow<strong>in</strong>g criteria would also apply to patient ledstructured education.The criteria that def<strong>in</strong>e a structured educationprogramme are:1. A philosophy2. An evidence based curriculum3. Aims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes4. Delivered by a tra<strong>in</strong>ed educator5. Quality Assured6. AuditedEach Health Board should have a Managed Cl<strong>in</strong>icalNetwork (MCN) responsible <strong>for</strong> diabetes care.Each MCN is charged with ensur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> provision<strong>of</strong> a range <strong>of</strong> educational solutions that should<strong>in</strong>clude quality assured structured education<strong>for</strong> people with diabetes. Each MCN ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>srecords <strong>of</strong> educational provision and reports <strong>the</strong>irprogress towards meet<strong>in</strong>g this standard to <strong>the</strong>Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Group.1REVIEWERS’ HANDBOOK FOR ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND (APEDS)
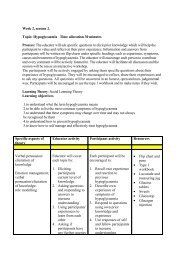
NICE 3 criteria <strong>for</strong> structured education1. Philosophy2. Written curriculumThe structured education programme has aclearly stated philosophy that reflects <strong>the</strong> beliefs,attitudes and values <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> people with diabetes <strong>for</strong>which <strong>the</strong> course is aimed, and <strong>the</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>essionalsdeliver<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> course.In <strong>Scotland</strong>, a strong philosophy <strong>of</strong> selfmanagement and life long learn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>for</strong> peopleliv<strong>in</strong>g with a long term condition, like diabetes, isdevelop<strong>in</strong>g 4 . <strong>Patient</strong> education should promoteperson centered care, self management and activebehaviour change.The philosophy <strong>of</strong> an education programme shouldbe developed <strong>in</strong> conjunction with <strong>the</strong> people <strong>for</strong>whom <strong>the</strong> course is aimed and will adopt an equaland diverse approach that is appropriate to <strong>the</strong>patient regardless <strong>of</strong> geographical location, age,gender, race, religion, creed, disability, social class,sexuality, culture and life circumstances.The philosophy should be type specific andappropriate <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> age group and educationalabilities <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> persons attend<strong>in</strong>g. Partners andcarers should be <strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> education processwhere appropriate.To engage with patients <strong>in</strong> writ<strong>in</strong>g a philosophy,pr<strong>of</strong>essionals are encouraged to hold focus groupsor directed discussions with patients and <strong>the</strong>ircarers. <strong>Patient</strong>s may even lead <strong>the</strong> development <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> educational philosophy if asked so to do.Any diabetes education programme requires awritten curriculum encompass<strong>in</strong>g:• <strong>the</strong> philosophy• evidence based course content• aims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes• lesson plans <strong>for</strong> each session• <strong>in</strong>tended participants• evidence <strong>of</strong> educational <strong>the</strong>ory appropriateto <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>tended participants• evidence <strong>of</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g activities appropriateto <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>tended participants• method <strong>of</strong> assessment• resources to deliver <strong>the</strong> courseIt is best practice to have one named person,an <strong>Education</strong>al Lead, who is overall responsible<strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> programme while work<strong>in</strong>g with<strong>in</strong> a team.All educational resources should be kept up todate, collated and easily accessible by all members<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> educator team. The curriculum content is<strong>in</strong>dicative ra<strong>the</strong>r than prescriptive and <strong>the</strong>re shouldbe a system to <strong>of</strong>fer follow up topics not covered<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> programme but requested by <strong>in</strong>dividuals,hence accord<strong>in</strong>g to need. This may take <strong>the</strong> <strong>for</strong>m<strong>of</strong> a signpost<strong>in</strong>g system to leaflets, resources,o<strong>the</strong>r educational sessions, o<strong>the</strong>r services or<strong>the</strong> person may require one to one support <strong>for</strong> aparticular issue.NICE CRITERIA FOR STRUCTURED EDUCATION 2
3. Aims and learn<strong>in</strong>goutcomesThe programme should have an overall aim andobjectives that are expanded and developedthrough each session <strong>for</strong> which fur<strong>the</strong>r aimsand learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes should be written. Thelevel <strong>of</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong>tended outcomes should<strong>in</strong>corporate <strong>the</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g needs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> participantsand should build on previous knowledge, skills andexperiences <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> participants.4. Tra<strong>in</strong>ed EducatorAll normal Human Resource issues apply around<strong>the</strong> employment and deployment <strong>of</strong> staff. All staffhave a job description that meets <strong>the</strong> Knowledgeand Skills Framework. All staff have a Pr<strong>of</strong>essionalDevelopment Plan through which <strong>the</strong>ir ownlearn<strong>in</strong>g and developmental needs are identifiedand <strong>the</strong> meet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se facilitated. Records arereta<strong>in</strong>ed by staff and l<strong>in</strong>e managers <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se and, ifappropriate, Human Resources Departments.There are nationally agreed competencyframeworks <strong>for</strong> nurses, dietitians and podiatristswork<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> diabetes care 5, 6, 7 . The Scottish<strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>Education</strong> Advisory Group recommendsthat <strong>the</strong>se documents are used <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> appropriaterecruitment <strong>of</strong> staff. Prior to deliver<strong>in</strong>g any patienteducation, it is essential that <strong>the</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>essionalmust have knowledge <strong>of</strong> diabetes, experience<strong>of</strong> work<strong>in</strong>g with people with diabetes as well asmeet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> requirements <strong>of</strong> a tra<strong>in</strong>ed educator.It is recommended that pr<strong>of</strong>essionals are mentoredby a more experienced practitioner <strong>the</strong> first timethat <strong>the</strong>y provide an educational programme.Where mentor<strong>in</strong>g is not possible, pr<strong>of</strong>essionals areencouraged to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> a written reflective log <strong>of</strong>each session.The knowledge and skills <strong>of</strong> a tra<strong>in</strong>ed educator aredetailed below:1. Write a philosophy <strong>of</strong> education2. Write aims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes3. Identify tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and educationalopportunities4. Identify patient and carers learn<strong>in</strong>g anddevelopment needs5. Develop an educational session thatengages and supports patients <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>irlearn<strong>in</strong>g and development6. Deliver an educational session that engagesand supports patients <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir learn<strong>in</strong>g anddevelopment – <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g presentation skills,facilitation <strong>of</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g and development,question<strong>in</strong>g skills7. Prepare and use PowerPo<strong>in</strong>t slides/slides/overhead/visual resources as part <strong>of</strong> aneducational session8. Teach a skill e.g. blood glucose monitor<strong>in</strong>g9. Manage learn<strong>in</strong>g and development <strong>in</strong>groups10. Evaluate <strong>the</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> patients after aneducational session11. Improve learn<strong>in</strong>g and developmentprovision12. Reflect on, develop and ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> own skillsand practice <strong>in</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g and development.It is recommended that <strong>the</strong> <strong>Education</strong>al Lead, whohas overall responsibility <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> programme, isable to demonstrate all <strong>the</strong> above knowledge andskills (1-12). Those who are <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>gpatient education, but not necessarily <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong>1-5 above, are required to demonstrate 6-12 aswell as <strong>the</strong>ir understand<strong>in</strong>g and application <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>philosophy to <strong>the</strong>ir teach<strong>in</strong>g and adapt<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>irown teach<strong>in</strong>g styles to meet <strong>the</strong> philosophy. It is<strong>the</strong> responsibility <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Education</strong>al Lead to ensurethat only people with <strong>the</strong> necessary knowledge andskills are <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>g patient education.3REVIEWERS’ HANDBOOK FOR ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND (APEDS)
It is acknowledged that pr<strong>of</strong>essionals are requiredto have many skills <strong>in</strong> car<strong>in</strong>g <strong>for</strong> people withdiabetes. The cl<strong>in</strong>ical and educational skillsrequired will vary accord<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> patient’sjourney and <strong>the</strong>ir stage on this journey utiliz<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>educational framework <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> short life work<strong>in</strong>ggroup on type 1 diabetes 8 (Appendix 1).All staff who are <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> support<strong>in</strong>g people withdiabetes and also <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>g patient educationare encouraged to develop <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g skillsus<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>ir annual Per<strong>for</strong>mance and DevelopmentPlan as a tool towards acquir<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>m:• robust consultative communication skills• skills <strong>in</strong> promot<strong>in</strong>g behaviour change• <strong>the</strong> ability to conduct peer review• facilitation skills• motivational <strong>in</strong>terview<strong>in</strong>g• skills <strong>in</strong> promot<strong>in</strong>g decision mak<strong>in</strong>g• skills <strong>in</strong> promot<strong>in</strong>g self care andmanagement5. Quality AssuranceThe purpose <strong>of</strong> quality assurance is to ensure <strong>the</strong>highest standard <strong>of</strong> delivery <strong>for</strong> all educationalprogrammes to meet <strong>the</strong>ir <strong>in</strong>tended audience<strong>in</strong> relation to its philosophy, aims and learn<strong>in</strong>goutcomes. Specific aspects <strong>of</strong> each educationalprogramme or session will be evaluated and <strong>the</strong>detail is def<strong>in</strong>ed under <strong>the</strong> head<strong>in</strong>g ‘Audit’.Ultimately it is <strong>the</strong> responsibility <strong>of</strong> each HealthBoard to ensure that patient care is qualityassured. The outcomes <strong>of</strong> quality assur<strong>in</strong>geducational programmes and educational sessionswill be reported to <strong>the</strong> relevant MCN who will reportto <strong>the</strong> Health Board and, on behalf <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> HealthBoard, to <strong>the</strong> Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Group. Actionplans will be derived as required.Specific cl<strong>in</strong>ical outcomes are currently recordedon SCI-<strong>Diabetes</strong> and <strong>the</strong> <strong>of</strong>fer to attend aneducational course, participation or o<strong>the</strong>rwisewill also be recorded. This data will be reportedannually <strong>in</strong> an anonymous manner through <strong>the</strong>National <strong>Diabetes</strong> Survey 9 .Written records (paper or electronic) <strong>of</strong> all aspectsidentified <strong>for</strong> quality assurance purposes willnormally be reta<strong>in</strong>ed accord<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> NHS Code<strong>of</strong> Practice 10 .TRAINED EDUCATOR 4
6. AuditThe outcomes from an educational programmeshould be regularly audited. It is acknowledgedthat specific cl<strong>in</strong>ical parameters are capturedon SCI-<strong>Diabetes</strong>. It is our <strong>in</strong>tention that patienteducation <strong>of</strong>fered, attended and completed wouldalso be recorded on SCI-<strong>Diabetes</strong>. At this stage,it is acknowledged that data cannot normally becollected regularly <strong>for</strong> people who attend a ‘one<strong>of</strong>f’ teach<strong>in</strong>g session.It is recommended that <strong>the</strong> written curriculumis reviewed at a m<strong>in</strong>imum <strong>of</strong> every secondyear <strong>for</strong> its reliability, validity, relevance andcomprehensiveness although it is expected to beresponsive to new research or <strong>in</strong>novations andadapted accord<strong>in</strong>gly.Each MCN should reta<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation on thoseprovid<strong>in</strong>g patient education <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g: name, jobtitle, qualifications that meet <strong>the</strong> skills identified <strong>for</strong><strong>the</strong> role <strong>of</strong> a tra<strong>in</strong>ed educator, date <strong>of</strong> peer reviewor when self reflection was undertaken.<strong>Patient</strong> education will be undertaken <strong>in</strong> a variety<strong>of</strong> sett<strong>in</strong>gs and through different media e.g. telemedic<strong>in</strong>e.For each venue utilized, <strong>the</strong>re should beprocedures <strong>for</strong> deal<strong>in</strong>g with emergencies dur<strong>in</strong>gprogramme delivery where possible.For each educational programme that a patientattends, specific data should be collected that isexpanded <strong>in</strong> The <strong>Tool</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong><strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong> (TAPEDS).5 TOOL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND
<strong>Tool</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong><strong>of</strong> <strong>Patient</strong> <strong>Education</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>TOOL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND 6
IntroductionThe follow<strong>in</strong>g checklist has been derived to assesspatient education as meet<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> NICE criteria <strong>for</strong>structured patient education.The criteria that def<strong>in</strong>e a structured educationprogramme are:1. A written philosophy2. An evidence based written curriculum3. Written aims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes4. Delivered by a tra<strong>in</strong>ed educator5. Quality Assured6. Audited.For each Programme submitted <strong>for</strong> reviewplease provide written evidence on <strong>the</strong>follow<strong>in</strong>g programme structure:• The name <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Programme• The name <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Education</strong>al Lead whois also responsible <strong>for</strong> updat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>curriculum.• If this is a national programme (e.g. DAFNE,DESMOND, X-PERT <strong>Diabetes</strong>) has it beenmodified <strong>in</strong> any way?If yes, detail <strong>the</strong> modifications:e.g. duration, tim<strong>in</strong>g, content, resources• The <strong>in</strong>tended target patient group• How <strong>the</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g needs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> target patientgroup were identified• Names <strong>of</strong> all people participat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>deliver<strong>in</strong>g patient education: <strong>the</strong>irpr<strong>of</strong>essional qualification and job title• Where all educational resources arereta<strong>in</strong>ed and how accessible <strong>the</strong>y are to allmembers <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> health care team• Dates <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> educational programme• Venue <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> education: NHS site, privatesector, non-NHS, patient’s home, viatelemedic<strong>in</strong>ePlease provide written evidence <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>follow<strong>in</strong>g:Philosophy• The philosophy <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> programme• How patients were <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> develop<strong>in</strong>g<strong>the</strong> philosophy• How <strong>the</strong> philosophy is communicated toand understood by patients, pr<strong>of</strong>essionalsreferr<strong>in</strong>g and educationalists deliver<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>programme• How <strong>the</strong> philosophy supports selfmanagementCurriculum, Aims and Learn<strong>in</strong>gOutcomes• The educational <strong>the</strong>ory appropriate to <strong>the</strong><strong>in</strong>tended participants• The evidence based course content• Aims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomes <strong>for</strong> eachsession• Lesson plans <strong>for</strong> each session• The learn<strong>in</strong>g activities appropriate to <strong>the</strong><strong>in</strong>tended participants• The method <strong>of</strong> assessment <strong>of</strong> learn<strong>in</strong>g• The resources used to deliver <strong>the</strong> courseTra<strong>in</strong>ed Educator• How each pr<strong>of</strong>essional <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong>deliver<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> programme meets <strong>the</strong>requirements identified <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> APEDSdocument.7 TOOL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND
• Details <strong>of</strong> additional skills <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>pr<strong>of</strong>essionals <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>programme (APEDS page 4).• Details <strong>of</strong> mentorship provided to peoplewho are <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> first time• Records <strong>of</strong> any peer reviews, externalassessment or self reflection <strong>for</strong> allpr<strong>of</strong>essionals <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>gpatient education.Quality Assurance• Where and how written or electronicrecords are reta<strong>in</strong>ed regard<strong>in</strong>g patienteducation• <strong>Patient</strong> evaluation <strong>for</strong>ms• Evidence <strong>of</strong> peer review or self reflection onability to teach o<strong>the</strong>rs.Audit<strong>Patient</strong> aspectsHow are <strong>the</strong> views <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> participantsacquired <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> programme?What actions are taken as a consequence<strong>of</strong> participants responses?Pr<strong>of</strong>essional aspects• How each educator is evaluated by patients• How pr<strong>of</strong>essionals are facilitated to peerreview each o<strong>the</strong>r• Evidence <strong>of</strong> self reflection by all staff<strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> deliver<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> programme 11, 12 .Organisational aspects• <strong>Patient</strong> attendance rates at <strong>the</strong> educationalprogramme• <strong>Patient</strong> completion rates at <strong>the</strong> educationalprogramme• Any identified accessibility issues• Date <strong>of</strong> last review <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> written curriculum• How quality <strong>of</strong> life is assessed:Is quality <strong>of</strong> life assessed with youngpeople? If so, please state <strong>in</strong> what way itis assessed.Action taken as a result <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> outcomes<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> quality <strong>of</strong> life assessmentWhat attempts are made to cont<strong>in</strong>uallyassess patients’ knowledge and skills, preand post education?How patient confidence to changebehaviour is assessedHow patient behaviour change isassessedHow self management by patients isassessedINTRODUCTION 8
9 TOOL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND
References1. Scottish Government (2010) <strong>Diabetes</strong>Action Plan 2010. The ScottishGovernment, Ed<strong>in</strong>burgh2. SIGN (2010) SIGN 116: Management <strong>of</strong><strong>Diabetes</strong>. SIGN, Ed<strong>in</strong>burghwww.sign.ac.uk3. NICE (2003) Guidance on <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> patienteducation models <strong>for</strong> diabetes. TechnologyAppraisal 60. NICE, London4. The Scottish Government, Long TermConditions Alliance <strong>Scotland</strong> (2008) GaunYersl! The Scottish Government, Ed<strong>in</strong>burgh5. Trend UK (2011) An <strong>in</strong>tegrated careerand competency framework <strong>for</strong> diabetesnurs<strong>in</strong>g. 3rd edition SB Communications,Londonwww.trend-uk.org9. Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Group (2010) Scottish<strong>Diabetes</strong> Survey. Scottish Government,Ed<strong>in</strong>burghhttp://diabetes<strong>in</strong>scotland.org.uk/Publications.aspx10. Scottish Government (2010) ScottishGovernment Records Management: NHSCode <strong>of</strong> Practice (<strong>Scotland</strong>) Version 2.0March, Scottish Government, Ed<strong>in</strong>burgh11. NHS <strong>Education</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong> Fly<strong>in</strong>g Starthttp://www.fly<strong>in</strong>gstart.scot.nhs.uk12. NHS <strong>Education</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong> EffectivePractitionerhttp://www.effectivepractitioner.nes.scot.nhs.uk/learn<strong>in</strong>g-and-development/cl<strong>in</strong>icalpractice.aspx6. <strong>Diabetes</strong> UK (2011) An <strong>in</strong>tegrated careerand competency framework <strong>for</strong> dietitiansand frontl<strong>in</strong>e staff. <strong>Diabetes</strong> UK, Londonhttp://www.dmeg.org.uk/Doccuments/Dietetic%20Competency%20Framework%202011.pdf7. TRIEPodD-UK (2012) Podiatry CompetencyFramework <strong>for</strong> Integrated Diabetic FootCare – A User’s Guide TRIEPodD-UK,London8. Bath L (2009) Short Life work<strong>in</strong>g group <strong>of</strong>type 1 diabetes. Scottish <strong>Diabetes</strong> Group,Ed<strong>in</strong>burghhttp://diabetes<strong>in</strong>scotland.org.uk/Publications/F<strong>in</strong>al%20report%20<strong>of</strong>%20<strong>the</strong>%20Type%201%20<strong>Diabetes</strong>%20Short%20Life%20Work<strong>in</strong>g%20Group.pdfREFERENCES 10
Appendix<strong>Diabetes</strong> Care: Mapp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> patient/pr<strong>of</strong>essional journey with <strong>the</strong> differ<strong>in</strong>groles <strong>of</strong> patients and pr<strong>of</strong>essionals throughout <strong>the</strong> journeyTime l<strong>in</strong>ePr<strong>of</strong>essionals<strong>Education</strong>al<strong>the</strong>orySkills requiredPr<strong>of</strong>essional Knowledge andUnderstand<strong>in</strong>g<strong>Patient</strong>supportDiagnosisGP/ConsultantDSN/PNAndragogy/DictateClear communicatorFacilitatorListen<strong>in</strong>g skillsEmpathyExpert diabetes cl<strong>in</strong>ical knowledgeKnowledge <strong>of</strong> how to teach<strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mationKnowledge <strong>of</strong> how to teach a skillBehavioural changeLevel 1Core SkillsGP/ConsultantDSN/PNDietitianPodiatristAndragogy/DictateAbility to:impart knowledge;pace <strong>the</strong> giv<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation;teach a skill;reassure.Expert diabetes cl<strong>in</strong>ical knowledgeKnowledge <strong>of</strong> how to teach<strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mationKnowledge <strong>of</strong> how to teach a skillBehavioural changePeer supportDiscuss changes to lifestylee.g. food, physical activity,smok<strong>in</strong>gLevel 2Liv<strong>in</strong>g withdiabetesCont<strong>in</strong>ualContactGP/ConsultantDSN/PNDietitianPodiatristPsychologist,SchoolsAndragogy/FacilitateAvailabilityDiscernmentListen<strong>in</strong>gAbility to:Empower;Motivate;Encourage;Praise where <strong>the</strong>re isevidence <strong>of</strong> self-managementMotivational <strong>in</strong>terview<strong>in</strong>gPsychological assessmentPsychological impact (HADS,PIDPAD)CHO count<strong>in</strong>gWeight management programmesSmok<strong>in</strong>g cessation cl<strong>in</strong>icsFacilitation skillsBehaviour changeCare plann<strong>in</strong>g around person’sgoals and problem solv<strong>in</strong>gPeer supportLevel 3Manag<strong>in</strong>gdiabetesTeamSelfmanagementresource/FacilitatorPhilosophy <strong>of</strong> careAims and learn<strong>in</strong>g outcomesNICE criteriaStructured patient educationPeer learn<strong>in</strong>gand emotionalsupportStructured<strong>Patient</strong>educationLevel 3Manag<strong>in</strong>gdiabetesTeamSelf-Management/FacilitatorAvailabilityDiscernmentListen<strong>in</strong>gStructured patient educationIntensive <strong>in</strong>sul<strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>rapyMotivational <strong>in</strong>terview<strong>in</strong>gPeer supportOngo<strong>in</strong>gstructurededucationAbility to:Empower;Motivate;Encourage;Praise where <strong>the</strong>re isevidence <strong>of</strong> self-managementMotivational <strong>in</strong>terview<strong>in</strong>gPsychological assessmentPromot<strong>in</strong>g behavioural changeCounsell<strong>in</strong>gEmpower<strong>in</strong>gSelf-managementLong term conditionsPeer review <strong>for</strong> o<strong>the</strong>rsQuality assuranceCHO and <strong>in</strong>sul<strong>in</strong> dose adjustment11 TOOL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF PATIENT EDUCATION IN DIABETES IN SCOTLAND
AcknowledgementsThis document was developed by a variety <strong>of</strong> people through consultations and workshops.Contributors were people with diabetes and pr<strong>of</strong>essionals from all Health Boards, <strong>Education</strong>al Leads<strong>in</strong> <strong>Diabetes</strong>, <strong>the</strong> Steer<strong>in</strong>g Group <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> National <strong>Education</strong> Co-Ord<strong>in</strong>ator and members <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Scottish<strong>Diabetes</strong> <strong>Education</strong> Advisory Group.APPENDIX 12
Different <strong>for</strong>mat required?This resource can be made available, <strong>in</strong> full or summary <strong>for</strong>m, <strong>in</strong> alternative<strong>for</strong>mats and community languages.Please contact us on 0131 313 8061 or email alt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.uk todiscuss how we can best meet your requirements.0131 313 8061alt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.uk0131 313 8061alt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.ukalt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.uk0131 313 8061alt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.uk0131 313 8061Ten material może być udostępniony jako streszczenie lub pelen tekst w <strong>in</strong>nych<strong>for</strong>matach i językach. Promisy o kontakt pod numerem telefonu 0131 313 8061 lubpocztą elektroniczną pod adresem alt<strong>for</strong>mats@nes.scot.nhs.uk by przedyskutowaćPaństwa konkretne wymagania.Published September 2012NHS <strong>Education</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Scotland</strong>Thistle House91 Haymarket TerraceEd<strong>in</strong>burghEH12 5HDTel: 0131 313 8000www.nes.scot.nhs.uk