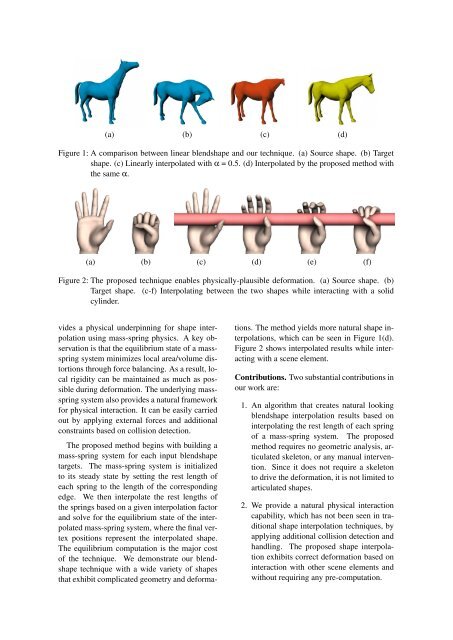
(a) (b) (c) (d)Figure 1: A comparison between linear blendshape and our technique. (a) Source shape. (b) Targetshape. (c) Linearly interpolated with α = 0.5. (d) Interpolated by the proposed method withthe same α.(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)Figure 2: The proposed technique enables physically-plausible deformation. (a) Source shape. (b)Target shape. (c-f) Interpolating between the two shapes while interacting with a solidcylinder.vides a physical underpinning for shape interpolationusing mass-spring physics. A key observationis <strong>that</strong> the equilibrium state of a massspringsystem minimizes local area/volume distortionsthrough force balancing. As a result, localrigidity can be maintained as much as possibleduring deformation. The underlying massspringsystem also provides a natural frameworkfor physical interaction. It can be easily carriedout by applying external forces and additionalconstraints based on collision detection.The proposed method begins with building amass-spring system for each input blendshapetargets. The mass-spring system is initializedto its steady state by setting the rest length ofeach spring to the length of the correspondingedge. We then interpolate the rest lengths ofthe springs based on a given interpolation factorand solve for the equilibrium state of the interpolatedmass-spring system, where the final vertexpositions represent the interpolated shape.The equilibrium computation is the major costof the technique. We demonstrate our blendshapetechnique with a wide variety of shapes<strong>that</strong> exhibit complicated geometry and deformations.The method yields more natural shape interpolations,which can be seen in Figure 1(d).Figure 2 shows interpolated results while interactingwith a scene element.Contributions. Two substantial contributions inour work are:1. An algorithm <strong>that</strong> creates natural lookingblendshape interpolation results based oninterpolating the rest length of each springof a mass-spring system. The proposedmethod requires no geometric analysis, articulatedskeleton, or any manual intervention.Since it does not require a skeletonto drive the deformation, it is not limited toarticulated shapes.2. We provide a natural physical interactioncapability, which has not been seen in traditionalshape interpolation techniques, byapplying additional collision detection andhandling. The proposed shape interpolationexhibits correct deformation based oninteraction with other scene elements andwithout requiring any pre-computation.
2 Related WorkOur technique relates to works for interpolatingbetween shapes in two or three dimensions,mass-spring systems, and rest length animation.Shape Interpolation and Deformation. Shapeinterpolation has been widely used for animatinggeometric deformation. The linear blendshapetechnique is the most common methodfor shape interpolation. Shape interpolationcan also be achieved using an articulated skeleton.The skeleton may be manually specified[15,35,37], or automatically determined byfinding near-rigid components of input shapes[11] or using the medial axis transform [6, 38].Rohmer et al. [27] proposed a skinning methodwhich exactly preserves (or controls) the volumeof an object.Other methods are free of using an articulatedskeleton. One effective research trend isbased on maintaining the rigidity criteria of localgeometrical elements, or so-called “as-rigidaspossible” principle. [1] and [16] are typicalexamples of this approach. Baxter et al. [4] proposeda solution for solving the rotation ambiguityarising from previous rigid as-rigid-as possibleapproaches. Winkler et al. [36] interpolatededge lengths and dihedral angles of the inputshapes, followed by a global multi-registrationmethod to determine the best rigid transformation.There are also methods <strong>that</strong> create shapeinterpolation <strong>that</strong> conforms to user manipulation.Barbič et al. [3] proposed a method forkey frame animation based on an underlyingphysically-based simulation, which, similar toour approach, can also be driven by a massspringsystem. Both their method and ours computean equilibrium state as the interpolated result.However, their method interpolates the deformationforces, which are either provided bya user or computed automatically based on keyposes. Our method simply interpolates springrest lengths. Kondo et al. [18] provided guidedanimations with dynamics. A user can have controlsover trajectory and deformation. Their targettrajectory is not obtained via proper shapeinterpolation, but just by pushing the object intonext key frame. Lewis and Anjyo [20] introduceda direct manipulation method for blendshapes.This approach constrains any desiredsubset of vertices based on manual manipulationsand automatically infers the remaining vertexpositions. However, the method only produceshapes <strong>that</strong> are within the convex space ofthe original blendshape poses and has no physicalmeaning.Other related works on shape interpolationor deformation include [12], which used exampleshapes to build a reduced deformable modelwhich controls with mesh-based inverse kinematics.Galoppo et al. [14] introduced the conceptof dynamic morph targets, to skeletally interpolateelastic forces, which allows controlover geometry and elastic properties of an animatedcharacter. Teran et al. [32] solved quasistaticstates of a finite element system for simulatingdeformations of nonlinear elastic materials.We also solve for quasi-static states andconsider interaction with other rigid bodies butwe only balance the mass-spring system with respectto varying the rest lengths.Lewis et al. [21] regards shape interpolationas a scattered data interpolation problemin an abstract parameter (pose) space. Ourmethod does not require high dimensional scattereddata interpolation, and it interpolates shapewith the support of physical simulation, presumablyrequiring fewer input shapes. Kilianet al. [17] presented an isometric deformationmethod based on Riemannian geometry,considering shape interpolation as a geodesiccurve in shape space. Both of these previoustechniques are unable to provide interaction capabilitiesbecause they lack an underlying physicalapproach.Mass-Spring Systems. Mass-spring systemsare commonly used for simulating physical behaviors.Generally, such systems are easy to implementand convenient to integrate with othertechniques, such as collision detection. Applications<strong>that</strong> make use of a mass-spring system includesurgical simulation [22], dynamics for animals[23], cloth [2,10,13], muscles [9,24], andother deformable objects. Lee et al. [19] appliedmass-spring systems to facial animation using athree-layered mesh to model the anatomy of humanfacial tissue. While finite element methods(FEM) can deliver more sophisticated andphysically accurate analysis, mass-spring sys-