Marginally lubricated
Marginally lubricated
Marginally lubricated
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
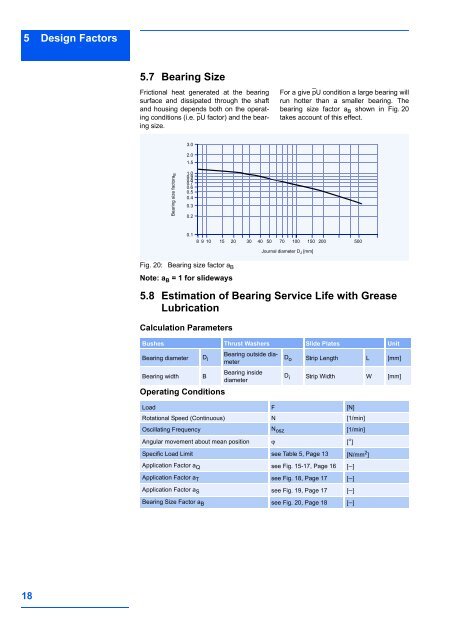
5 Design Factors5.7 Bearing SizeFrictional heat generated at the bearingsurface and dissipated through the shaftand housing depends both on the operatingconditions (i.e. pU factor) and the bearingsize.For a give pU condition a large bearing willrun hotter than a smaller bearing. Thebearing size factor a B shown in Fig. 20takes account of this effect.3.02.01.5Bearing size factora B1.00.90.80.70.60.50.40.30.20.18 91015 20 30 40 50 70 100 150 200 500Journal diameter D J [mm]Fig. 20:Bearing size factor a BNote: a B = 1 for slideways5.8 Estimation of Bearing Service Life with GreaseLubricationCalculation ParametersBushes Thrust Washers Slide Plates UnitBearing diameter DBearing outside diameteriBearing insideBearing width BdiameterOperating ConditionsD o Strip Length L [mm]D i Strip Width W [mm]Load F [N]Rotational Speed (Continuous) N [1/min]Oscillating Frequency N osz [1/min]Angular movement about mean position ϕ [°]Specific Load Limit see Table 5, Page 13 [N/mm 2 ]Application Factor a Q see Fig. 15-17, Page 16 [−]Application Factor a T see Fig. 18, Page 17 [−]Application Factor a S see Fig. 19, Page 17 [−]Bearing Size Factor a B see Fig. 20, Page 18 [−]18