Litigator's Guide to Metadata - Codemantra.net
Litigator's Guide to Metadata - Codemantra.net
Litigator's Guide to Metadata - Codemantra.net
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
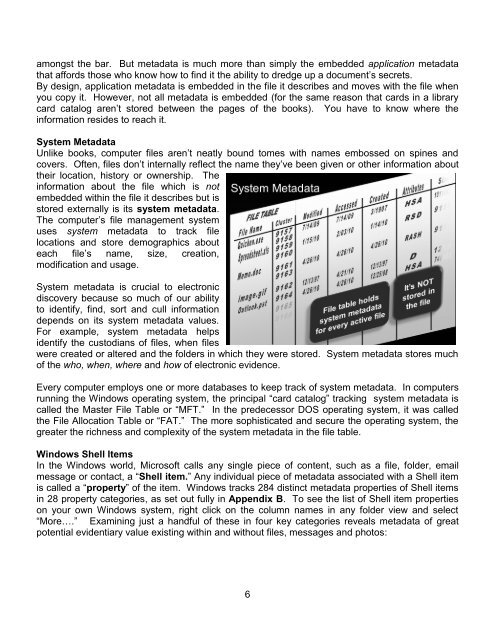
amongst the bar. But metadata is much more than simply the embedded application metadatathat affords those who know how <strong>to</strong> find it the ability <strong>to</strong> dredge up a document’s secrets.By design, application metadata is embedded in the file it describes and moves with the file whenyou copy it. However, not all metadata is embedded (for the same reason that cards in a librarycard catalog aren’t s<strong>to</strong>red between the pages of the books). You have <strong>to</strong> know where theinformation resides <strong>to</strong> reach it.System <strong>Metadata</strong>Unlike books, computer files aren’t neatly bound <strong>to</strong>mes with names embossed on spines andcovers. Often, files don’t internally reflect the name they’ve been given or other information abouttheir location, his<strong>to</strong>ry or ownership. Theinformation about the file which is notembedded within the file it describes but iss<strong>to</strong>red externally is its system metadata.The computer’s file management systemuses system metadata <strong>to</strong> track filelocations and s<strong>to</strong>re demographics abouteach file’s name, size, creation,modification and usage.System metadata is crucial <strong>to</strong> electronicdiscovery because so much of our ability<strong>to</strong> identify, find, sort and cull informationdepends on its system metadata values.For example, system metadata helpsidentify the cus<strong>to</strong>dians of files, when fileswere created or altered and the folders in which they were s<strong>to</strong>red. System metadata s<strong>to</strong>res muchof the who, when, where and how of electronic evidence.Every computer employs one or more databases <strong>to</strong> keep track of system metadata. In computersrunning the Windows operating system, the principal ―card catalog‖ tracking system metadata iscalled the Master File Table or ―MFT.‖ In the predecessor DOS operating system, it was calledthe File Allocation Table or ―FAT.‖ The more sophisticated and secure the operating system, thegreater the richness and complexity of the system metadata in the file table.Windows Shell ItemsIn the Windows world, Microsoft calls any single piece of content, such as a file, folder, emailmessage or contact, a ―Shell item.‖ Any individual piece of metadata associated with a Shell itemis called a ―property‖ of the item. Windows tracks 284 distinct metadata properties of Shell itemsin 28 property categories, as set out fully in Appendix B. To see the list of Shell item propertieson your own Windows system, right click on the column names in any folder view and select―More….‖ Examining just a handful of these in four key categories reveals metadata of greatpotential evidentiary value existing within and without files, messages and pho<strong>to</strong>s:6