BCA PART I semester-wise scheme: 2007-2008 ... - Vikram University
BCA PART I semester-wise scheme: 2007-2008 ... - Vikram University
BCA PART I semester-wise scheme: 2007-2008 ... - Vikram University
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
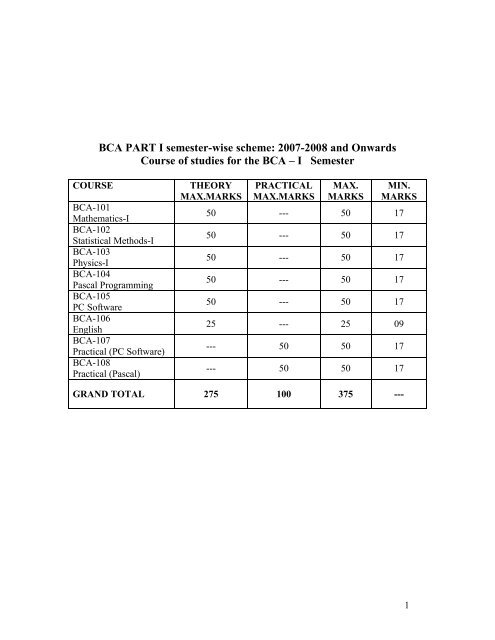
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> I <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: <strong>2007</strong>-<strong>2008</strong> and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – I SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-101Mathematics-I<strong>BCA</strong>-102Statistical Methods-I<strong>BCA</strong>-103Physics-I<strong>BCA</strong>-104Pascal Programming<strong>BCA</strong>-105PC Software<strong>BCA</strong>-106English<strong>BCA</strong>-107Practical (PC Software)<strong>BCA</strong>-108Practical (Pascal)THEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMIN.MARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1725 --- 25 09--- 50 50 17--- 50 50 17GRAND TOTAL 275 100 375 ---1
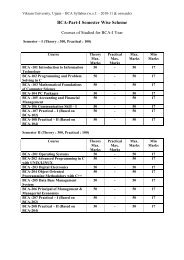
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> I <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: <strong>2007</strong>-<strong>2008</strong> and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – II SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-201Mathematics-II<strong>BCA</strong>-202Statistical Methods-II<strong>BCA</strong>-203Physics-II<strong>BCA</strong>-204‘C’ Programming<strong>BCA</strong>-205Introduction to Internet<strong>BCA</strong>-206Hindi<strong>BCA</strong>-207‘C’ Programming Lab<strong>BCA</strong>-208Practical (Internet)THEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMIN.MARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1725 --- 25 09--- 50 50 17--- 50 50 17GRAND TOTAL 275 100 375 ---2
SEMESTER-I<strong>BCA</strong>-101: MATHEMATICS-IMax.Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to familiarize the studentswith calculus.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IReview of concepts of function of one variable: define a function. types offunction;Limits: define, working rule for finding out the limit, fundamental propertyof limit, problems based on limits,Continuity: define, point of discontinuity, classification of discontinuity,problems based on continuity & discontinuity;Differentiability: condition for derivability and problemsUNIT - IISuccessive differentiation, Rolles theorem, Mean value theorem, Taylor'stheorem, Taylor’s & Maclaurin’s series, Intermediate forms.UNIT - IIITangents, Normals, Curvature, asymptotes, integration of HyperbolicFunction and Reduction Formula.UNIT - IVDifferentiation of vector function, gradient, directional derivatives,Divergence and curl, vector function of several scalar variables and theirpartial derivative, level surface gradient in Cartesian and polar coordinates,divergences of vector and curl of vector.UNIT - VMatrix - definition, types of matrix, special matrix, elementarytransformation of matrix, inverse of matrix - adjoint methods and gaussian3
elimination, normal form of matrix, rank of matrix, nullity of matrix (theirapplications) consistency and solution of linear simultaneous equations.BOOKS:1.A text book of calculus by Dr. H. S. Sharma, Ratan Prakashan .2.A Text Book of Calculus by Dr. H. K. Pathak & D.C. Agrawal (TEXT)3.Vector Calculus & Geometric by Dr. H. K. Pathak & D.C. Agrawal(TEXT)4.Discrete Mathematics by Dr. H. K. Pathak & D.C. Agrawal- (ShikhaSahitya Prakashan)<strong>BCA</strong> –102: STATISTICAL METHODS – IMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to familiarize the studentswith statistics .EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IVariables & graphs: Statistics, population & sample, discrete & continuousvariables, graphs, equations, inequalities, logarithms. Frequencydistributions: frequency distribution, histograms, frequency polygons.frequency curve. Cumulative frequency distribution. ogives.UNIT -IIMeasures of central tendency: The arithmetic mean, weighted arithmeticmean, geometric mean, harmonic mean, mean power of numbers, root meansquare, median, mode, quartiles, deciles & percentiles.Measures of dispersion: The range, mean deviation, semi inter quartilerange for quartile deviation, absolute & related dispersion, coefficient ofvariation.4
UNIT -IIIMoments Skewness & kurtosis: Moments of various types, relation betweenmoments, sheppard’s correction to moments, skewness & kurtosis, momentgenerating function.Elementary probability theory: Sample space, events, classical definition ofportability, relative frequency definition, theorems of total & compoundportability, Independent & dependent event, mutually exclusive events,mathematical expectation.UNIT- IVTheoretical distributions: Discrete & continuous probability distribution,Basic concepts & applications of degenerate. Bernoulli, Binomial,geometric, negative binomial. Hyper geometric & poisson distributions,normal distribution.Curve fitting & the method of least squares: Curve fitting, the method ofleast square, the least square lines, the least square parabola, Regression.UNIT - VCorrelation theory: Linear correlation, Measures of correlation, the leastsquare regression lines, expected & unexpected variation, coefficient ofcorrelation, rank correlation, correlation index, multiple & partialcorrelation for three variables.Theory of attributes: Consistency of data, association of attributes,coefficient of association, contingency tables.BOOKS:1. Spiegel, M.R.: Statistics Schaum’s outline series, McGraw HillPublishing Company.2. Kapoor & Saxena: Mathematical statistics- S. Chand & sons.5
<strong>BCA</strong> -103 : PHYSICS - IMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to familiarize the studentswith basic concept of electricityEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IFrictional electricity, Charges & their conservation, Coulomb’s law, Electricfield & Potential due to a point charge & Dipole. Dielectric Potential- Anatomic view, dielectric Polarization, Dielectric Susceptibility; Forces on thesurface of a charged conductor, energy stored in a dielectric medium.Capacity, units of capacity, Potential energy of a charged conductor,Principle of condenser or Capacitor.UNIT - IIMagnetic Properties of Materials & Magnetic Circuits: Para, Dia &Ferromagnetic substances, Magnetic circuit, Magnetomotive force,Reluctance, Permeance, Ohm’s Law and comparison with electric circuits,Relation between M & H, Hysterisis loop, Energy loss, Determination ofSusceptibility & Permeability.UNIT - IIIA. C. Circuits: Definitions, Different forms of e.m.f. equations, Effective,virtual or rms value, Mean and Average value of AC quantities, Formsfactor, AC circuits containing Resistance, Capacitance, Inductance,Separately & simultaneously, Series and Parallel Resonance Circuit (Phasordiagram treatment).UNIT - IVOhm's Law, factors affecting resistance, -color code, variable resistors,power and energy, D.C series and parallel circuits, Kirchoff's voltage andcurrent laws, voltage and current divider rules, Network Theorems:6
Maximum power transfer theorem, Thevenin's theorem, Norton's theorem,Super position theorem, Millman's Theorem, Reciprocity theorem. .UNIT- VClassification of Solids : Energy bands in solids, Conductor, Semiconductor& Insulator, Chemical bands in Gerrmanium & Silicon, Intrinsic &Extrinsic Semiconductors, Conductivity Diode & The Transistor, Superconductivity.BOOKS:1. Physics Part II : Resnick & Halliday.2. Engineering Physics: R. K. Gaur & S. L. Gupta. Dhanpat Rai Publication<strong>BCA</strong>-I04: PASCAL PROGRAMMINGMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to familiarize withprogramming concepts using PSCALEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IBasic steps in programming, program Development characteristics, ProgramDevelopment Tool- Algorithms, Efficiency of Algorithms, Flow Charts,Decision Table.Concepts of Structure Programming, Modular Programming.Language Processor - Compiler, Assembler, Interpreter, Linker, Loader.Lcvel of language - High Level Language, Assembly Level language, LowLevel language.UNIT - IIStructure of a pascal program, Identifier, Reserve word, Standard Identifier,Data types, Operators, Operators precedence, User Defined Data types.Control Structure - Decision Making, Loop control, Unconditional with7
examples.UNIT - IIISub program - User Defined sub program, features of subprogram - Call ByValue, Call By Reference, Recursion with example.Standard sub Program - Round, Trunc , sqrt, Sqr, Exponent, naturallogarithms, ord, chr, pred, succ, int, frac, read, write.String handling functions - I/O functions, concate, insline, decline, chreoletc.UNIT -IVRecord - declaration, accessing of records, with statement, nested record,variant record, array with record.Array concepts and types of array, bubble sort, linear search, function toarray with examples.UNIT -VFiles – physical, logical files, declaring and assigning files, creating, copy,merging and appending files using binary and text routines.BOOKS:1. Programming in Pascal - B.J. HOLEMS.2. Pascal Programming – Gottfried, Tata McGraw Hill.3. Pascal Programming - B. Vennugopal.<strong>BCA</strong>-I05: PC - SOFTWAREMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to give knowledge about thebasics of computer and it’s applications.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.8
UNIT -IBasic computer organization - Von Numann M/c, Types of computers,block diagram of modern Digital Computer, types of memory devices,printers.Number system - representation of number system, integer representation,floating point representation, binary number, octal number, hexadecimalnumber, system and their conversion.Character coding - BCD, ASCII, and EBCDIC.UNIT - IIOperating system - types of operating system. DOS- booting, external andinternal commands,filters, pipes, comparison between COM, EXE and BATfiles. simple batch processing creating and execution.UNIT -IIIWindows - 98 - Features of Win 98, startup screen, desktop screenmanagement (Display Properties), utility of recycling bin, networkneighbourhood and dialup settings.Control panel- Installation of S/W, addition of new hardware. Installation ofmodern sound card, printers.UNIT -IVMS Word: types of word processor, creating documents in MS-Word,formatting features of MS-word, Word standard tool bar, word drawingtoolbar, text formatting, header and footer, autotext, table handling features,insertion files, pictures, clipboard, graphs, mail merge, macros.UNIT – VMS Powerpoint: Different presentation styles, editing slides, insertingslides, inserting menu facility, slide sorter, Slide Miniature, Slide show,inserting chart, slide transition, formatting slides, tool menu, presentanimation of slides, animation preview.BOOKS:1. Computer fundamentals : P.K. Sinha, BPB Publication2. DOS: Peter Norton DOS guide, BPB Publication3. Windows 98: Sam Publication4. Microsoft Office: Ron Mansfield, BPB Publication9
<strong>BCA</strong>- 106: ENGLISHMax. Marks: 25OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to give knowledge about thebasics of English Language.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.Scheme for ExaminationUNIT – IUNIT – IIUNIT – IIIUNIT – IVUNIT – V: Short answer type question: Reading Comprehensive and vocabulary: Paragraph writing: Letter writing (both Formal & Informal): Grammar (20 items from the prescribed text book to be askedand 15 to be attempted)Structural Items:1. Simple Compound and Complex sentences2. Co-ordinate clauses (with, but, or, either-or, neither-nor, other<strong>wise</strong> orelse).3. Subordinate clauses – noun clauses – as subject, object and compliment:Relative clauses (restrictive and non-restrictive clauses); Adverb Clauses(Open and Hypothetical conditional with because, though, here, so that, aslong as, as soon as).4. Comparative clauses (as + = adjective/adverb + as-no sooner….than)10
Tenses:i) Simple present, progressive and present perfect.j) Simple past, progressive and past perfect.k) Indication of futurity.The Passive (Simple present and past, presennt and past perfect and toinfinitive structure). Reported Speech: i) Declarative Sentences, ii)Imperatives, iii) Interrogativc-wh-questions, Exclamatory sentences.l) Modals (will, shall, should, would, ought to. have to/have got to, cancould,may-might and need).Verb Structures (infinitives and gerundials). Linking Devices.NOTE: The above language items will be introduced to express thefollowingcommunicative functions:a. Seeking and impartinginformation.b. Expressing attitudes-intellectualand emotional.c. Persuasion and dissuasion etc.Questions on all the units shall be asked from the prescribed text, which willcomprise specimens of popular creative writing and the following items:i) Indian ArtMeaning of Art, Features of Indian ArtElementary Knowledge of Paintings, Music, dancing, Sculpture,Archaeology, Iconography and other Social Arts.ii) Indian LiteratureAncient Indian LiteratureElementary Knowledge of Vedic Literature, Mahabharata, Ramayanand Olher Main Granthas.iii) Indian Freedom StruggleFreedom Struggle of 1857, National Consciousness, Non cooperationMovement, Civil Disobedient Movement. Contribution ofRevolutionaries in freedom struggle.iv) Indian ConstitutionIntroduction, Main features ofconstitution, fundamental rights,fundamental duties.BOOKS:11
English Language and:Published by M.P.HindiIndian CultureGranth Academy, Bhopal12
<strong>BCA</strong> -107: PRACTlCALS (PC SOFTWARE)Max. Marks: 50PRACTICALS BASED ONDOS:Introduction to PCs with related Hardware, Software. DOS and itsvariations. Starting DOS. DOS Commands: Internal & External commands.Common commands notation, files & file commands, Disk Commands.Batch files: Introduction to batch processing, creation of batch files.Special batch file: Autoexec.bat Hard disk setup. configuring a system,creation of subdirectories, Pipelines, filters and miscellaneous.WINDOWS 98:Desktop setting - new folder, rename. Recycle bin operations, briefcasefunction, control panel utility. Display properties: Screen saver, backgroundsettings.MS - WORD:Creating file: save, save as , save as HTML, save as Text, template, RTFformat.Page setup utility: Margin settings, paper size setting, paper source, layout.Editing: cut, paste, paste special, undo, redo, find, replace, goto etc.View tile: Page layout, Normal outline, master document, ruler, header,footer, footnote, full screen.Insert: break, page number, symbol, date & time, auto text, caption file,object, hyperlink, picture etc.Format: font, paragraph, bullets & numbering, borders & shading, changecase, columns.Tools: Spelling, merge documents, protect document, mail merge, macro.Table: Draw label, insert table, cell handling, table auto format, sortformula.MS-POWERPOINT:Creating new slide, formatting slide. slide layout, slide show & sorter,Inserting new slide. slide no., date, time, chart, formatting slide, tooloperation.NOTE:13
1. Every student will be given 6 periods/week laboratory (1 period = 45minutes)2.Every student will work on independent Computer (Student: Computer =1: 1)<strong>BCA</strong> -108: PRACTICALS (PASCAL)Max. Marks : 50SIMPLE PASCAL PROGRAMME FOR• Exchanging value of two variables, summation of a set of numbers,factorial computation.PASCAL PROGRAMME FOR• Sine function computation, generation of fibonacci sequence.• Reversing the digits of an integer.• Finding of square root of a number, G.C.D computation, Generation ofprime number.• Computing the prime factors of an integer, generation of pseudo-randomnumbers.• Computing the Nth fibonacci number: (illustrate efficiency aspect byshowing two – three methods forth is problem)• Array order reversal, array counting, removal of duplicates in a orderedarray.• Partitioning of an array with reference to a given clement. Finding thekth smallest element.• String handling functions - trunc, round, frac, int, abs, insline, deline,concate etc.• Linear search14
• Bubble sort• Keyword searching in text, text lines editing, linerar pattern search.• Multiple record handeling.• File creation, File merging, File copying.• Summation of n numbers, variable exchange, use of for structure, use ofif-then structures.• Factorial computation, reversing the digit of an integer.• Comparison of three numbers.NOTE:• Every student will be given 6 periods/week laboratory (1 period = 45minutes)• Every student will work on independent Computer (Student: Computer =1: 1)15
SEMESTER - II<strong>BCA</strong> - 201 : MATHEMATICS-IIMax.Mark: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to help students gainknowledge about advanced Calculus.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - ICurve tracing: Tracing of curves with equations in Cartesian & polar forms.Improper Integrals: Convergence of improper integrals, Evaluation ofconvergent improper integrals.UNIT – IIGamma and Beta functions and their properties, some important deductions(duplication formula), Rectification: length curve, intrinsic equation.UNIT-IIIMultiple integrals: Integration of functions of two & three variables, Double& triple integrals, Dirichlet integral use of double and triple integrals infinding areas and volumes. Vector integration: Indefinite and definite, Line,surface and volume integrals, Gauss and stokes theorems and someapplications.UNIT - IVPartial differential: Function of several variables, Limits, continuity anddifferentiability, Partial derivatives, Eulers Theorem, Mean Theorem, Meanvalue theorem & Taylor’s theorem.UNIT -VMaxima & Minima, functions of two and three variables, convergence anddivergence of series: Definition and various tests.16
BOOKS:1. A text book of higher calculus for B.Sc II by Dr. H. S. Sharma. RatanPrakashan2. A text book of Higher calculus for B.Sc II by Dr. H. K. Pathak & D.C.Agrawal.Shikha Sahitya Prakashan. .<strong>BCA</strong> - 202 : STATISTICAL METHODS - IIMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to give knowledge about theadvanced statistics to the studentsEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IEstimation Theory, Unbiasedness, consistency, efficiency and sufficiency ofestimators, Maximum likelihood estimates and their properties (withoutproof). Cramer Rao inequality and Minimum variance estimates.UNIT - IITesting of Hypotheses: Simple and composite hypothesis, errors of kind- Iand kind - II, critical region, level of significance, size and power of a test,Neymann Pearson's fundamental, lemma and its application (with proof).UNIT - IIITests of significance: Test of simple hypothesis, Beta, gamma distributionsand their properties, Chi-square, T, F, Z distribution and tests based onthem.UNIT - IVNon - parametric Tests: Sign test, Median test, Wilcoxon’s run test,Wilcoxon’s signed rank test, contingency tables.17
UNIT - VAnalysis of Variance: one - way & Two - way classification with oneobservation per cell, basic designs of experiments: completely randomizeddesign, randomized block design & latin square design.BOOKS:1. Mathematical Statistics by J. N. Kapoor & H. C. Saxena, S. Chand &Co.2. Fundamentals of Statistics Vol. I By A. M. Goon, B. Dasgupta, M. K.Gupta, The World press pvt. Ltd.<strong>BCA</strong> - 203: PHYSICS - IIMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to familiarize the studentswith Optics and Magnetism.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT -IBasic concepts of Electromagnetic wave propagation, properties of planewave Propagation, guided and unguided media, ionospheric propagation:critical frequency, MUF, skip distance, drik propagation.Electromagnetic waves: Transmission line, coaxial cable, reflectioncoefficient, VSWR, Standing waves, impedance matching, wave guide,traveling waves and Maxwell’s equations.UNIT - IIInterference: Principle of Superposition, Interference of light, Analyticaltreatment of Interference, Theory of Interference fringes, Interference in thinfilms, wedge shaped film, Newton’s rings and determination of wavelength,Michelson’s interferometer and its uses.18
UNIT - IIIDiffraction: Two kinds of diffraction, Rectilinear Propagation of light, Zoneplate, Diffraction at straight edge, Diffraction at single slit, double slit,plane diffraction grating, Resolving power of a grating, Dispersive power ofa grating.UNIT - IVPolarization: Polarization of light waves, various types of light, doublerefraction, Nicol’s prism, Huygen’s theory of double refraction, Quarter andhalf wave plate, Production & analysis of polarized light of different kind,Optical activity, Fresnel’s theory of optical rotation.UNIT - VDoppler effect of light & its applications.Laser: concepts of coherence, spatial and temporal coherence, Spontaneousand stimulated emission, Population inversion, Ruby Laser, Gas Laser,Semiconductor Laser, Uses of Laser.BOOKS:1.Physics Part II : Resnick & Halliday.2. Engineering Physics: R. K. Gaur & S. L. Gupta., Dhanpat Rai Publication<strong>BCA</strong> - 204 : ‘C’ PROGRAMMINGMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to enhance theirprogramming capabilities using C.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IDifferent data types and sizes, variables names, constants, Declarations,type conversion, Arithmetic operators, Relational and logical operators,19
Increment and decrement operators, Bit <strong>wise</strong> and logical operators,Assignment operators and expressions, Precedence and order of evaluation.UNIT - IIStatement and blocks, if-else, else-if, switch, while, for, do-while loops,break, continue, goto and labels, Functions and program structures,Function arguments, External, Static, Register variables, scope rules, Blockstructure, Initialization, Recursion.UNIT - IIIPointer and Addresses, Pointers and Function Arguments, Pointers andArrays, Address arithmetic, character pointers and functions,Multidimensional arrays, Pointer arrays, Pointers to Pointers, Initializationof pointer arrays, Pointer vs Multidimensional arrays, command lineargument, Pointer to functions.UNIT - IVStructures and functions, Arrays of structures, pointer to structure, Self -Referential structures, Table lookup, Fields, Union, Typedef.UNIT - VStandard Input and output, Formatted input & output, in memory formatconversion, file access, Error handling, Line I/O.BOOKS:1. The C programming Language by Brain W. Kernigham and DennisM. Ritchie.2. Let us C by Y. Kanetkar.3. Working with C by Y. Kanetkar.20
<strong>BCA</strong> -205: INTRODUCTION TO INTERNETMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : The objective of this course is to give the concept ofnetworking and Internet to the students.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IConcepts of the point to point and Broadcast Networks, LAN and otherNetwork topologies, Development of the Internet. Introduction to TCP/IPand shell account Internet addressing. Concepts of Internet and ISP (InternetService Provider).UNIT - IIInternet Backbones, NAPs. Technologies of Interconnections between Userand ISP and within the ISPs through Backbones and NAPs., Concepts of theURL addresses and domain names for e-mails and web sites.UNIT - IIIHypertext concept and WORLD WIDE WEB, Services on Internet, HTTP.SMTP, FTP, NNTP, The e-mail Electronic post service, SMPT, Configuringa computer for an e-mail, Free e-mail sites & settings. The Rediff,Indiainfoline, zeenext, America On-line, yahoo, hotmail, mail city, e-mailwith additional features.UNIT - IVFile transfer, FTP, FTP server, Telnet, Web Sites, Gopher and its server,Usenet and News Servers, Internet chatting, Internet phone, WIAS.UNIT - VAll the features in Internet Explorer, Netscape Navigator, Netscapecommunication suite, Outlook Express and Frontpage.BOOKS:21
1. Internet Complete Reference by Sybex Pub.2. Any other suitable and latest reference.<strong>BCA</strong> – 206 : HINDI LANGUAGEMax.Marks : 25fgUnh Hkk"kkbdkà 1¼d½ ekud fgUnh Hkk"kk %1- ekud fgUnh ds y{k.k vkSj mnkgj.k]2- ekud fgUnh dk Lo:i]3- ekud fgUnh ds çdkj¼[k½ v’kqf);k¡ vkSj mudk la’kks/ku %1- v’kqf);ksa ds mnkgj.k] 2- v’kqf);ksa ds çdkj ¼mPpkj.kxr] orZuh xr]'kCn vkSj vFkZ xr]O;kdj.k xr½bdkà 2¼d½ fgUnh dk 'kCn HkaMkj %1- 'kCnksa ds çdkj]2- 'kCnksa dh jpuk]3- u;s ç;ksx¼[k½ fgUnh dh okD; jpuk %4- okD;ksa ds çdkj5-okD; foU;kl22
6- okD; xr lkekU; v’kqf);k¡]fojke fpUg7-bdkà 3i= ys[ku] lkj ys[ku] iYyou %1- i=ksa ds mnkgj.k]2- i=ksa ds çdkj]3- i= ys[ku dh fo’ks"krk,¡ ¼i= ys[ku] lacks/ku] var fnukad vkfn Mkyuk½]4- lkj ys[ku] 5-iYyoubdkà 4Hkkjrh; laL—fr] Hkkjr ns’k vkSj mlds fuoklh] Hkkjrh; lekt dh lajpuk] lkekftdxfr’khyrk & vn~;ru] dk;Z vkSj n’kZubdkà 5Hkkjrh; laL—fr dk fo’o ij çHkko] e/;çns’k dk lkaL—frd oSHkoIkkB~;iqLrd % Hkkjrh;rk ds vej Loj] çdk’kd % e-ç- fgUnh xzaFk vdkneh] HkksikyAvuqØef.kdk[k.M ,d % ikB~; lkexzhbdkà ,d 1- Hkkjr oUnuk lw;ZdkUr f=ikBh **fujkyk** 12- LorU=rk iqdkjrh t;’kadj **çlkn** 23- cM+s ?kj dh csVh çsepUn 3bdkà nks 4- ,d x/ks dh okilh —'upanj 125- VsyhQksu gfj’kadj ijlkà 156- vQlj 'kjn tks’kh 18bdkà rhu 7- LkkSUn;Z dh unh ueZnk ve`ryky csxM+ 218- cLrj esa ck?k 'kkuh 26bdkà pkj 9- cq) dh d:.kk MkW- l)k frLl 3223
10- lknxh egkRek xk¡/kh 37bdkà ik¡p 11- ;ksx dh 'kfDr gfjoa’kjk; **cPpu** 3912- f'kdkxks esa Lokeh foosdkuUn dk i= 43[k.M nks % fgUnh Hkk"kk] lEçs"k.k dkS’kybdkà ,d d- ekud fgUnh Hkk"kk 48[k- v'kqf);k¡ vkSj mudk la’kks/ku 67bdkà nks d- fgUnh dk 'kCn&HkaMkj 79[k- fgUnh dh okD;&jpuk vkSj fojke fpUg 91bdkà rhu d- i=&ys[ku] lkj&ys[ku vkSj iYyou 107[k.M rhu % Hkkjrh; laL—frbdkà pkj d- Hkkjr ns’k vkSj mlds fuoklh 126[k- Hkkjrh; lekt dh lajpuk 134x- Lkekftd xfr’khyrk 142?k- /keZ vkSj n’kZu 146bdkà ik¡p d- Hkkjrh; laL—fr dk fo’o ij çHkko 155[k- e/;çns’k dk lkaL—frd oSHko 165<strong>BCA</strong> - 207: ‘C’ PROGRAMMING LABORATORYMax. Marks: 50List of Practicals• To sum n different nos. using array.• To generate fibonacci series.• To find nth fibonacci no.• To generate prime nos. series.• To find nth prime no.• To find G.C.D of two nos.24
• Binary Search & Linear Search.• Bubble sort• Selection sort.• Matrix addition.• Matrix Multiplication.• Exchanging the values of third nos. without using third variable.• Exchanging the values of two nos. using third variable.• To find square root of a nos. without using built in function.• To find factorial of a no.• To find factorial of a no. using recursion.• To reverse the digit of a no.• To reverse the given string.• To find whether year is leap year or not.• To create a record having five fields.• To search a name in a record of students.• To exchange the value of two variable using function.• To add two no. using pointer.• To create a file of character.• To read a file.• To create a file of integer.• To create a file of record.• To copy a file.• To merge two files.• Find the sum of series i) 1+2+….n ii) 2+4+….niii) 1+3+…niv)1+2/2! + 3/3! +…. v) 1+ x /1! + x 2 /2! +x 3 /3! +….vi)l- x/1! + x 2 /2! - x 3 /3! +….• To find the space and required by different types of element.• To find transpose of a matrix.• To find inverse of a matrix.• To convert lowercase string to uppercase.• To read character from one text file convert into uppercase and lengthinto other file.• Write a program which ask date of birth in dd/mm/yy format and spell itin word.• To find out twins prime no..25
• To enter a four digit no. & print it all combination.• Write a Mark sheet program using file.• Write a payroll program using file.• Partitioning of an array.• Removal of duplicity in an arrayNOTE: .1. Every student will be given 6 periods/week laboratory(1 period = 45 minutes)2. Every student will work on independent Computer(Student: Computer = 1: 1)<strong>BCA</strong> - 208 : INTERNET PRACTICALSMax. Marks: 50List of suggested Practical work• Understanding of a dial up connection through modem.• Configuring a computer for an e-mail and using Outlook Express orNetscape Messenger.• Registering an e-mail address.• Understanding of address book maintenance for e-mail.• Understanding of e-mail drafting.• Understanding of different Mail program tools.• Send and receive functions of e-mail.• Using the Internet for search using search engines.• Understanding of sites like BSNL, Rediff, Indiainfoline, Zeenext, AOL,yahoo, Hotmail, mail city etc.• News services on Internet.• Downloading of Tutorials from the Internet from educational sites.• Using Internet Explorer.• Using Netscape Navigator.• Using Netscape Communication suite.• Using Front page or Notepad etc. for web Design.NOTE: Minimum laboratory teaching of six hours in a week.26
BOOKS:1. Internet: Complete Reference by Sybex Pub.2. Any other suitable and Latest Reference.NOTE:• Every student will be given 6 periods/week laboratory (1 period = 45minutes)• Every student will work on independent Computer (Student:Computer = 1: 1)27
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> II <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: <strong>2008</strong>-2009 and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – III SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-301Mathematics-III<strong>BCA</strong>-302Object OrientedProgramming through C++<strong>BCA</strong>-303Digital ComputerElectronics<strong>BCA</strong>-304Accounting & FinancialManagement<strong>BCA</strong>-305Data Structure<strong>BCA</strong>-306Communication Skills<strong>BCA</strong>-307Practical (C++)<strong>BCA</strong>-308Practical (Data Structure)<strong>BCA</strong>-309Practical (DigitalComputer Electronics)THEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMINMARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1725 --- 25 09--- 50 50 17--- 25 25 09--- 25 25 09GRAND TOTAL 275 100 375 ---28
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> II <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: <strong>2008</strong>-2009 and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – IV SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-401Coordinate Geometry ofThree Dimension<strong>BCA</strong>-402Data base ManagementSystem<strong>BCA</strong>-403Data and NetworkCommunication<strong>BCA</strong>-404Digital ComputerOrganization<strong>BCA</strong>-405Unix Operating System<strong>BCA</strong>-406EnvironmentalAwareness<strong>BCA</strong>-407Practical (Data BaseManagement System)<strong>BCA</strong>-408Practical (DigitalComputer organization)<strong>BCA</strong>-409Practical (Unix OperatingSystem)THEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMINMARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1725 --- 25 09--- 50 50 17--- 25 25 09--- 25 25 09GRAND TOTAL 275 100 375 ---29
SEMESTER - III<strong>BCA</strong> - 301 : MATHEMATICS-III (Differential Equations)OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Mathematics.Max Marks:50EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT-IDifferential equations of first order & first degree:Homogeneous Differential Equations, Reducible to HomogeneousDifferential Equations, Linear Differential Equations, Reducible to LinearDifferential Equations (Bernoulli's Equation, Exact Differential Equations,Change of Variables).Differential equations of first order and higher degree:Differential Equations - Solvable for P, Solvable for Y, Solvable for X,Clairaut’s Equation.UNIT-IIFamily of Curves: Trajectories, Orthogonal Trajectories, Self-OrthogonalFamilies, Linear Differential Equations of Higher order with constantcoefficients, Differential Equations reducible to Linear DifferentialEquations with Constant Coefficients.UNIT-IIILinear Differential Equations of second order, Method of variable ofparameters. Simultaneous differential equation of first order.UNIT-IVInitial & Boundary Value Problem, Picard's Method of Successiveapproximation, Series Solution - method of Ferobenius.30
UNIT-VPartial differential equations: definition and formation. Partial differentialequation of first order, Lagranges method standard forms. Charpit’sMethod, Linear Partial Differential Equation of Higher order with ConstantCoefficients.BOOKS:1. A textbook of Differential Equation by H.K.Pathak and D.C.Agrawal.(TEXT), Shiksha sahitya Prakashan, Meerut.2. A textbook of differential equations by M.M. Kapoor, Pithampur Pub.CO.888. East Part Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi.3. A textbook of Differential Equations by S.N. Agrawal, YougbodhPrakashan, Raipur.4. Ordinary differential equation by Gunandhar Paria, Scholar Pub.Indore<strong>BCA</strong>-302:OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING THROUGH C++Max Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Object Oriented Programmingthrough C++.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT-IIntroduction, OOP’s Languages, characteristics of OOP’s languages,application of OOP, OOP’s paradigm, concepts: Objects, class, dataabstraction, data encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, static anddynamic binding, message passing, benefit of OOP’s, Disadvantages ofOOP’s.UNIT-IIC++ programming basics, basic program structure, preprocessor directive,data types, operators, manipulator, type conversions, C++ stream class.31
Control structures: for, do, while, do-while, if, if-else, switchJump statement: break, continue, goto, exit.UNIT-IIIFunctions and arrays. Classes and instances. Building and destroyinginstances, (Constructors and Destructors). Defining classes in ObjectOriented Language, modifiers, friend and in-line functions, string handlingfunctions.UNIT-IVData Encapsulation, implementation of Encapsulation. Polymorphism,operator overloading, function overloading, virtual functions.UNIT-VInheritance, Reusability of code through inheritance, type inheritance, dataabstraction, abstract classes, specification of code.Templates and exception handling.BOOKS:1. The Art of Programming And Computer Science with C++ By Steven C.Lawlor2. Object Oriented Programming with C++ by Balaguruswamy.3. Object Oriented Programming in C++ by Robert Lafore.<strong>BCA</strong> – 303: DIGITAL COMPUTER ELECTRONICSOBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Digital Electronics.Max.Marks:50EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT – INumber systems and codes, Decimal, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal and theirinterconversion. ASCII, Grey code, Excess-3 code, BCD numbers, Binary32
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division(1’s and 2’s Complement methods).UNIT- IILogic Gates: NOT, OR, AND, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR gates. BooleanAlgebra, De Morgan’s Theorem. Application of gates, Half adder and fulladder.UNIT-IIIBoolean functions & truth table, SOP, POS, minterms, Simplification oflogical circuits using Boolean Algebra & Karnaugh maps.UNIT-IVTTL Circuits, Digital ICs, 74 series, TTL, characteristics, Totempole andopen collector gates, comparison between different types of TTL,Multiplexer, Demultiplexer, Encoders, Decoders.UNIT-VFlip-flop, Registers and Counters, RS flip-flop, Level clocked DF/F edgetriggered D Flip-flop, edge triggered JK flip-flop, Racing in F/F, JK masterslaveFlip flop, Buffer registers, shift registers, ripple counters,synchronous counters, ring counters, presettable counters, Mod counters.BOOKS:1. Digital Computer Electronics by Malvino.2. Digital Fundamentals by Basavraj B.3. Digital Computer Fundamentals by Bartee<strong>BCA</strong> - 304: ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTMax Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Accounting and FinancialManagement.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt any33
one of these two within each unit.UNIT-IBasic accounting concepts. Accounting structures: Process of accounting,journal, ledger and trial balance based on double entry book keeping.UNIT- IIPractical System of accounting: cash book, sales and purchase of goods,bills of exchange, book reconciliation statement.UNIT- IIIPreparation of financial statement: Income statement (profit and lossaccount), statement of financial position (balance sheet) and adjustment.Valuation of assets and depreciation methods.UNIT- IVCash and fund flow statements. Analysis of financial statement - financialratio.UNIT- VIntroduction to cost accounting: Elements of cost, cost determinations,direct and indirect cost, cost centers and cost units, the behavior of cost.BOOKS:1. Introduction to Accountancy by T.S. Grewal2. Accounting Principles by Robert Anthony3. Advanced Accountancy by R.I. Gupta4. An Introduction to Accounting by S.N. Maheshwari.<strong>BCA</strong>-305: DATA STRUCTUREMax Marks:50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Data Structures.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt any34
one of these two within each unit.UNIT- IDefinition of data structure, types, static and dynamic variables,representation and address calculation of single and multidimensional arrayin memory, pointers, Sparse matrix representation, time and spacecomplexity and algorithm.UNIT- IIStacks: Representation of stacks, operations on stacks, infix and post fixnotations, multiple stacks, exchanging the value of two stacks, recursiontechniques, expression evaluations, applications of stacks.UNIT- IIIQueues: representation of queues, operations on queues, multiple queues,circular queues, D-queues, Application of queues.UNIT- IVLink List: Singly link list, Doubly link list, Circular link list, Generalizedlists, problem solving with dynamic storage management, list traversal,insertion and deletion algorithms.UNIT- VTrees: Basic concepts and definitions, basic operations on Binary trees, treesearch and insertion, tree deletion, balanced tree, balanced tree insertion anddeletion, B-tree, Hash table and Hash techniques.BOOKS:1. Algorithm+ data structure= program by Niklaus Wirth2. Data structures using C by Robert Kruse.3. Data Structure with C++ By Drozdek35
<strong>BCA</strong> – 306 : COMMUNICATION SKILLSOBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Communication Skills.Max Marks:25EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IThe Language Component, Structure of simple sentences, the basicframeworks, the complex sentences, Usage of ‘but’, ‘or’, ‘other<strong>wise</strong>’, elseetc. Clauses & sub-ordinate clauses.UNIT- IIThe Tense – Past, Present & Future, the models, the Verb structures goingto, used to, to+infinitives, the –ing forms.UNIT- IIIAsking simple questions and providing short and simple answers, the usageof ‘why’ questions along with their answers, Question answer with theauxiliaries, Vocabulary, knowledge of at least 25 words, their meaningpronunciation & their usages.UNIT- IVWriting skill, writing simple paragraphs, developing a given ideas, writingsimple letters and applications.UNIT- VThe spoken part of the language through a given material, pronunciation,discussions on a given topic.BOOKS:1. English for Indian students, by Tandon & Dixit(M.P. Uchha Shiksha Anudan Ayog)2. Living English Literature, by W.S. Allen36
3. A practical English Grammar, by Thomson & martinet.<strong>BCA</strong>- 307: PRACTICAL EXERCISE (C++)Max marks:501. Write a program to illustrate the use of various stream classes of C++.2. Write a program to find the maximum of three using conditionaloperator.3. Write a program to find the largest, second largest and third largest ina given array.4. Write a program to generate Armstrong series.5. Write a program to find the factorial of a given no.6. Write a program to generate the fibonacci series.7. Write a program to check whether the given no. is palindrome or not.8. Write a program to find the GCD and LCM of two nos.9. Write a program to read a n x m matrix and find.a. The average of each row.b. The average of each column.c. The average of mn entries.10.Write a program to print the boundary elements of matrix.11.Write a program to print the diagonal elements of matrix.12.Write a program to illustrate the use of structure and union.13.Write a function which accepts objects as a parameter and returnsobject.14.Write a program to overload ++ operator to increment age of personby one month.37
15.Write a program to overload + operator to concentrate two strings.16.Write a program to illustrate the use of scope resolution operator.17.Write a program to find the square root using inline function.18.Write a program to illustrate the use of friend function.19.If a class D is derived from two base class B1 and B2, then writethese classes each containing zero argument constructor. Ensurewhile building an object of type D firstly the constructor of B2 shouldget called followed by that of B1. Also provide destructor in eachclass. In what order would these destructor get called.20.Write a program to overload two operators > and – as follows:Let t1, t2 and t3 be three objects of time classIf (t1 > t2)t3 = t1 – t2;elset3 = t2 – t1;<strong>BCA</strong> – 308 : PRACTICAL EXERCISE (DATA STRUCTURE)Max. Marks: 251. Store records of 100 students using array.2. Representation of upper triangular and lower triangular sparse matrixin linear array.3. Push and Pop operation on stack using array.4. Insertion and deletion operation on queue using array.5. Insertion and deletion operation on circular queue using array.6. Program for Bubble sort.7. Program for Quick sort.8. Program for Selection sort.9. Program for Linear Search.38
10.Program for Binary Search.11.Program for Exchanging the value of two variables using pointers.12.Linked List creation, insertion and deletion.13.Count no of elements in linked list.14.Sort a Linked List.15.Doubly linked list creation, insertion and deletion.16.Creation of Binary search tree.17.Insertion and deletion of Binary Search tree.18.Traversal of Binary search tree (inorder, preorder, postorder).19.Complete program for Binary search tree.20.Representation of Polynomial in Linked List.<strong>BCA</strong> – 309 : PRACTICAL EXERCISE (Digital Computer Electronics)1. Study of Logic Gates (AND, OR, NOR, XOR, NAND).2. Study of Flip-flop (JK, D, T etc.).3. Study of Counter & Shift Register.4. Study of Timer IC 555.5. Study of Multiplexer & Demultiplexer.6. Study of Encoder & decoder.7. Study of Analog to Digital Converter.8. Study of Digital to Analog Converter.9. Study of Scmitt trigger.10.Study of Half & Full Adder.Max. Marks: 2539
SEMESTER-IV<strong>BCA</strong>-401: COORDINATE GEOMETRY OF THREE DIMENSIONSMax Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of coordinate geometry of threedimensionEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IRectangular Cartesian of a point in space, Distance between two points,Cylindrical coordinates, Spherical Coordinates, direction cosines, point ofdivision, orthogonal projections, angle between straight lines. Examples andexercises.Shortest distance between the straight line. Line of greatest slope.Conditions for line intersection. Orthogonal projection of a plane area. Areaof triangle in space, volume of triangle in space. Examples and Exercises.UNIT- IISphere circle and related topics. Tangent lines and tangent planes to asphere, radial plane, radial line, coaxial spheres, limiting points. Examplesand Exercises.Surface and conicoid: transformation of axes. Invarient and DecrementingCube, centre, tangent planes, normal lines, principle directions, Diametricaland principle planes. Examples and Exercises.UNIT- IIIConicoid polar planes. Locus of chords. Pole with respect to conicoid.Examples and Exercises. Parabolic, definition and description, Elliptical andHyperbolic parabolic, Parabolic of revolution. Tangent planes and normal toa parabolic. Diametrical and Conjugate planes. Examples and Exercises.40
UNIT- IVThe Ellipsoid, normal plane to it, director sphere of an ellipsoid, normal lineto ellipsoid. diametrical plane to ellipsoid, conjugate diameters anddiametrical planes to ellipsoid, locus of chords. polar planes. Exampls andExercises.UNIT- VThe definition and description, Finding equation of cone, standard equation,condition of general Quadratic equation representing cone. Angle betweentwo generators, enveloping cone of coincoids, right circular cone. Examplesand Exercises.The Cylinder definition, equation, right circular cylinder, envelopingcylinder to a conicoid. Examples and Exercises.BOOKS:1. Coordinate Geometry of Three Dimension by G. Paria, ScholarPublishing House Indore<strong>BCA</strong>-402 : DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMMax Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Data Base ManagementSystem.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IIntroduction: Purpose of DBMS, view of data, data models: physical model,logical model, conceptual model, hierarchical model, network model, Objectoriented model. Database Languages, database administrator, databaseusers, overall system structure.41
UNIT- IIEntity relationship model: basic concepts, mapping constraints, keys, E-Rdiagram, Weak entity features, design of an E-R database schema, reductionof E-R schema to table.UNIT- IIIStructured Query Language (SQL): Basic structure, set operations,aggregate functions, null values, nested subqueries, data definition language(DDL), data manipulation language (DML), Data control Language (DCL),Transaction Control language (TCL), QBE, QUEL.UNIT- IVRelational Database Design: Pittfalls in Relational Database Design,decomposition, Normalization using functional dependencies, normalizationusing multivalued dependencies, normalization using joint dependencies.Integrity constraints: Domain constraints, Entity Integrity constraints,referential integrity constraints, assertion, triggers.UNIT- VConcepts of RDBMS, characteristics of RDBMS, Codd’s 12 rules,Introduction to oracle tools, security.BOOKS:1. Database System Concept by A. Silberschatz, H.E Korth, S.Sudershan2. An Introduction To Database Management System by Vipin Desai.3. Modern Data Base System by Mcfadden<strong>BCA</strong>-403 : DATA AND NETWORK COMMUNICATIONMax Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Data and NetworkCommunicationEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt any42
one of these two within each unit.UNIT- IData Communication System, data communication links, character codes,digital data rates, serial data formats, encoded data format, telephonesystems, error detection and correction.UNIT- IIModel, data-topologies, data switching, type of networks, networkingmedium twisted pairs, coaxial cables, optical fibres, system networkarchitecture, SNA operating systems.UNIT- IIILimits of Communication, RS449 interface standards, RS422 & RS423,F5K and V0 modems, multiplexing methods, sampling theorem andQuatization, Delta modulation, Digital T carrier, CODEC.UNIT- IVData Link Protocol, character oriented protocols and bit oriented protocols,network architecture protocols, Ethernet and token ring.UNIT- VIntegrated services and Routing protocols, B-ISDN, DSL and ATM, Internetand TCP/IP.BOOKS:1. Data and Network Communication by Michael A. Miller2. Computer Network by Andrew S. Tannenbaum3. Understanding of Data Communications & Networks by William A.Shay<strong>BCA</strong>-404 : DIGITAL COMPUTER ORGANIZATIONMax.Marks:50OBJECTIVE: To introduce the concept of Digital Computer Organization.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questions43
choosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IBlock diagram of computer, stored program concepts, working of computer,word length and processing speed of computer, user interface. Hardware-Software concepts, microprocessor and single chip microcomputerconcepts. [problem in chapter 1 reference 1]UNIT- IIInput and Output units, floppy disk, hard disk, keyboard, mouse, joy sticks,scanners, serial printer, letter qualify printers, plotters, laser printer,graphics display device.UNIT- IIIComputer Memory, memory cell, memory organization, Read only memory,random access memory, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, serial access memory.Magnetic hard disk and floppy disk driver. Magnetic tape drive, cachememory, memory controller, optical disk, program and data memory.Memory management [problem in chapter 6 reference 1].UNIT- IVDistributed processing or multiprocessing, Batch processing,multiprogramming and multiuser system. Dumb and Smart terminals,computer network, local area network, parallel processing, centralprocessing unit [problem in chapter 1 and 5 of reference 1]UNIT- VMemory management U-bits for Virtual addressing <strong>scheme</strong>s.I/O architecture: properties of simple I/O devices and their controller(s),transfer of information between I/O device, CPU and Memory, programcontrol and interrupt control information transfer, I/O processor, Interruptcontrollers, hardware and software interrupts, traps and exceptions. DMAtransfer, DMA controllers, cycle stealing, block transfer and burst mode ofdata transfer.BOOKS:1. Computer Fundamentals Architecture and Organization by B. Ram2. Computer Organization by J.P. Hayes44
<strong>BCA</strong>-405: UNIX OPERATING SYSTEMMax.Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of UNIX operating system.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IUnix Operating System, background, philosophy, help facility.The tile system: structure of file system, pwd, cd. ls, mkdir, chmod, cp, mv,rm commands.UNIT- IIUtilities: More, file, we, cmp, comm, diff, lp, banner, cal, date, who, tty, sttycommands. The Bourne Shell: sh preceding a command by its owncombining commands, pattern matching, echo, pipes, tees, shell variables,shell scripts.UNIT- IIISimple tilters: pr, head, tell, cut, paste, sort, uniqa, nl commands.Advanced filters: grep, egrep, fgrep, sed, tr, join, awk, filtering. Theprocess: shell process. Parent and children, process status, system processes,multiple jobs in background, wait commands, premature termination ofprocess, job execution with low priority. Multiple jobs in foreground, shelllayers, timing process.UNIT- IVCommunication and Scheduling: bulletin board, message of the day, twoway communication, insulation from the other users, mail box, address allusers, delay, execute at later running jobs periodically.Programming with shell: System variables, profile, conditional execution,script termination, if, case, while, until, for, set and shift statements.45
UNIT- VSystem Administration: super user, security, user services, floppy disk,management operation. file system, administration backups.BOOKS:1. Unix Operating System by Smitabha Das2. An Introduction to Operating System by Deitel<strong>BCA</strong>-406 : ENVIRONMENTAL AWARENESSMax Marks: 25OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Environmental Awareness.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IEnvironment meaning, structure and type of environment, components ofenvironment and society environment and resources. Man Environmentalrelationship; Approach to study; man Interaction with environment(historical to present day).UNIT- IIEnvironmental Degradation: Meaning of degradation, types of degradation,process of degradation, cause of degradation, Religious and Philosophicalfactors deforestation agricultural development and degradation populationgrowth and Degradation, urbanization and degradation, Modern technologyand degradation.UNIT- IIIEcology: Definition of ecology and ecosystem. Types of Ecosystem,components of ecosystem, functions of ecosystem, Productivity and stabilityof ecosystems.Environmental Disasters: Meaning and concepts, types of hazards anddisaster, man induced and natural hazards, global warming, ozone depletion,46
green house effect and other major Environmental problems.UNIT- IVEnvironmental Pollution: Air, water, solid, noise pollution, Meaning,definition, sources, types, adheres effects and methods of control.UNIT- VEnvironmental Planning and Management: Concepts, aspects andApproaches, resources management, ecological Mgt. Biosphere Reserves,Management of wild life. Environmental Regulation and Rules: Vision ofenvironment by Govt. of India, Environmental Policies, waste disposal rulesand laws and legislation enacted by Parliament for environmentalprotection.BOOKS:1. Environmental Geography by Savinder Singh.2. Environmental Concept/Issues by Rupa And Co.3. Environment Rules and Regulation.4. Environment Mgt., by G.N.Pandey, Vikas Publication.<strong>BCA</strong> – 407: PRACTICAL EXERCISE(Data Base Management System)Max. Marks:501. E-R diagram based on queries.2. Queries based on SQL including set operation and aggregatefunction.3. Queries based on SQL including other operators like in operator,between operators, like operators, check operators.4. Retrieve data from the table using SQL statement.5. Queries based on QUEL and QBE (Query by Example).<strong>BCA</strong> – 408: PRACTICAL EXERCISE(Digital Computer Organization)Max. Marks:251. Conversion from decimal to Binary.47
2. Conversion from decimal to Octal.3. Conversion from decimal to Hexadecimal.4. Convert Decoder to Encoder.5. Convert Encoder to Decoder.6. Addition of two 8 bit numbers.7. Subtraction of two 8 bit numbers.8. Multiplication of two 8 bit numbers.9. Division of two 8 bit numbers.10.Exchange of two 8 bit numbers.<strong>BCA</strong> – 409: PRACTICAL EXERCISE(Unix Operating System)Max. Marks:251. Shell programming of Bourne shell.2. Shell programming of Bourne shell including if, for, while, case andshift statement.3. Shell programming of C shell.48
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> III <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: 2009-2010 and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – V SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-501Introduction to Java<strong>BCA</strong>-502Computer Organizationand Architecture<strong>BCA</strong>-503Software Engineering<strong>BCA</strong>-504Discrete Mathematics &Linear Algebra<strong>BCA</strong>-505Web Designing & WebTechnology<strong>BCA</strong>-506Entrepreneurship<strong>BCA</strong>-507Practical (Java)<strong>BCA</strong>-508ProjectTHEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMINMARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1725 --- 25 09--- 50 50 17--- 50 50 17GRAND TOTAL 275 100 375 ---49
<strong>BCA</strong> <strong>PART</strong> III <strong>semester</strong>-<strong>wise</strong> <strong>scheme</strong>: 2009-2010 and OnwardsCourse of studies for the <strong>BCA</strong> – VI SemesterCOURSE<strong>BCA</strong>-601Computer Graphics &Multimedia<strong>BCA</strong>-602Operating System<strong>BCA</strong>-603Computer OrientedNumerical Methods<strong>BCA</strong>-604Microprocessor &Assembly LanguageProgramming<strong>BCA</strong>-605Principles & Practices ofManagement<strong>BCA</strong>-606Practical on Visual basic<strong>BCA</strong>-607Practical (Graphics &Multimedia)<strong>BCA</strong>-608Practical (CONM using C)<strong>BCA</strong>-609Practical (Microprocessor& Assembly LanguageProgramming)THEORYMAX.MARKSPRACTICALMAX.MARKSMAX.MARKSMINMARKS50 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 1750 --- 50 17--- 50 50 17--- 25 25 09--- 25 25 09--- 25 25 09GRAND TOTAL 250 125 375 ---50
SEMESTER-V<strong>BCA</strong> - 501 : INTRODUCTION TO JAVAOBJECTIVE : Introduce the basics of Java.Max. Marks: 50EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IPrimitive data types- integer, short, long, byte, float, double, UnicodeCharacter set, Boolean, their ranges, defaults initial values, wrapping ofinteger arithmetic, casting comments, identifiers and reserved words, localvariables, operators and operator precedence. Examples and Exercises.UNIT- IIStatements simple and compound, Uses of control do, for, while, switch,break, case of continue, label. Class type Data: String, Arrays, Examplesand Exercises.UNIT- IIIDefinitions and Naming Conventions for the members of the Java Classes,Instance fields and methods, Initialization by Constructor, Initialization byDefault Constructor, Multiple Definition of Constructors, Creation ofobjects, access methods. Examples and Exercises.UNIT- IVInheritance, Super class, Subclass, Method overloading, Interface, Thread,Multithreading example, Synchronized, Exception (try-catch-final blocksexamples). Examples and Exercises.UNIT- VJava Virtual Machine concept, Java Platform overview. ProgrammingExamples to clarify use of objects, threads, exceptions and packages for I/O,file and string handling. Examples and Exercises.51
BOOKS:1. Herbert Schildts, The Complete Reference Java 2, Tata McGraw Hill,New Delhi, 4 th edition,2001.2. Joseph O’Neil, Teach yourself Java, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi,2001.3. E. Balagurusamy, Programming with Java, Tata McGraw Hill, NewDelhi. 2 nd edition, 2002.4. JavaScript: Don Gosselin, Thomson Learning, (Vikas publication).<strong>BCA</strong> - 502: COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTUREMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To familiarize with the concepts of Computer architectureand organization.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IIntroduction to Organization and Architecture, structure and function. Abrief history of Computers, their designing for performance, Pentium andpower PC evolution, Computer components, computer functions,Interconnection structure, Bus Interconnections, PCI, Futurebust.UNIT - IIComputer Memory System, Semiconductor main memory, cache memory,advance DRAM organization, Magnetic Disk, RAID. Optical memory,Magnetic tap.UNIT - IIIMachine Instruction characteristics, Types of Operands, type of Operations,Assembly Language, Addressing; Instruction formats.CPU Structure & function: Process Organization, register organization, The52
Instruction Cycle, Instruction Pipelining, The Pentium Processor, ThePower PC Processor.UNIT- IVMicro Operations, control of the CPU, Hardwired Implementations, BasicConcepts of Microprogrammed control, microinstruction sequencing,microinstruction execution, applications of micro programming.UNIT - VExternal Devices, I/O modules, Programmed I/O, Interrupt-Driven I/O,Direct Memory Access, I/O channels and Processors, External Interface,The MESI protocol vector computation, parallel processors.BOOKS:1. Computer Organization & Architecture by William Stallings (FifthEdition) 1999, PHI (Text).2. Computer Organization & Architecture by Hayes ( Tata McGraw Hill)<strong>BCA</strong> - 503: SOFTWARE ENGEENERINGMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : Introduce with the concept of Software Engineering andsystem analysisEXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IGeneral business environment, Business system concept, system analysis,system development life cycle.UNIT -IIProject selection:- Source of project request, managing project review &selection, preliminary investigation, system requirement specification &analysis: Fact Finding technique, Feasibility Study, Cost & Benefit analysis.53
UNIT -IIIStructured System Analysis, Tools of Structured analysis, Software DesignFundamentals, Data Flow, Oriented Design, Object Oriented Design & DataOriented design method.UNIT - IVSoftware Quality Assurance, Software testing techniques, Software testingFundamentals, White Box Testing (Basis Path Testing, Control Structuredtesting), Black Box Testing, Software Testing Strategies:- A Strategicapproach to software testing, Strategic issue unit testing, integration testing,Validation testing, System Testing, The art of Debugging.UNIT - VSystem Implementation & Software Maintenance, Hardware & SoftwareSelection.BOOKS:1. System Analysis & Design by Elias M. Awad, Galgotia Pub.2. Software Engineering by Roger S. Pressman, McGraw Hill.3. An integrated Approach to software Engineering by Pankaj Jalote,Nakoda Publishing House.<strong>BCA</strong> - 504 : DISCRETE MATHEMATICS & LINEAR ALGEBRAMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : Introduce concepts of discrete mathematics and algebra.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IALGEBRA OF LOGIC:Recall of Statements & Logical Connectives, Tautologies & Contradictions,Logical Equivalence, Algebra of Propositions, Quantifiers, Universal &54
Existential Quantifiers.BOOLEAN ALGEBRA:Boolean Algebra and its Properties, Algebra of Propositions, De-Morgan’sLaws, Algebra of Electric Circuits & its Application, Design of SimpleAutomatic Control System.UNIT - IIBOOLEAN FUNCTION OF FUNDAMENTAL FORMS: Boolean Function- Disjunction and Conjunction Normal Forms, Bools Expansion Theorem -Fundamental Forms, Many Terminal Networks, Trees and BinomialNetworks.UNIT - IIIBASIC CONCEPTS:SETS: Union, Intersection, Difference, Complement, De- Morgan’s Laws &Cartesian Product.MAPPINGS: Type of Mappings, Identify & Inverse mappings, Product ofMappings.GROUPS: Definition, Order of an Element.SUBGROUPS: Definition, Necessary and Sufficient condition.COSET DECOMPOSITION: Right & Left Cosets, Lagrange’s Theorem.DEFINITIONS AND BASICS OF : Normal Subgroup, Quotient Group,Homomorphism & Isomorphism of groups, Kernel of Homomorphism, Ringand Field.UNIT - IVVECTOR SPACES: Vector Space, Subspaces and Quotient Spaces.Linearly Dependent and Independent Vectors.LINEAR MAPS: Definition & properties. Homomorphism & Isomorphismof Vector Spaces, Kernel of A Linear Map.UNIT - VMatrix Representation of A Linear Map, rank and Nullity of Linear Map.Fundamental Theorem of Vector Space Homomorphism.Eigen Values and Eigen Vector of Matrix, Cayley Hamilton Theorem: Proof& Applications.BOOKS:1. A text book of Discrete Mathematics by H.K.Pathak and D.CAgrawal, Shiksha Sahitya Prakashan, Meerut. (text)55
2. A text book of Algebra by H.K.Pathak and D.C Agrawal, ShikshaSahitya Prakashan,Meerut.3. A text book of Linear Algebra by H.K.Pathak and D.C Agrawal,Shiksha Sahitya Prakashan, Meerut. (text)4. Linear Algebra by S. N. Goel, Kedarnath Ramnath Publications,Meerut.5. Linear Algebra by Kenneth Hoffman and Ray Kunze, Prentice Hall oflndia Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.<strong>BCA</strong> - 505: WEB DESIGNING AND WEB TECHNOLOGYMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To familiarize with web designing and web technology.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IClient server Computing Concepts, Distributed computing on the Internet,Introduction to web pages and HTML, HTML elements and tags, formattingtext and pages, including pictures in a page, creating tables and lists,splitting pages into frames.UNIT - IISite design and Navigation: The Home page Navigational tools, Formattingthe body section - using block level, using text level, using font style, usingphrase elements.UNIT - IIIMultimedia with Web: Creating files, Streaming audio, streaminganimations, Java Script and Browser, Java Script and server, EmbeddingJava Script and HTML, Java Script fundamentals - Variables, value storehouse, statements, loops, condition and functions, objects properties andmethods, event handlers and non-script tag.56
UNIT- IVComparision of HTML, DHTML and XML web casting, Domain nameselection, web server selection, Web hosting, uploading and downloadingof web, incremental uploading of data, introduction to SQL-Server,Introduction to User management in SQL - Server.UNIT - VIntroduction to ASP, database handling with ASP, Connection object,record set object, request object, response object, Cookies, creating tablesand insert query through connection.BOOKS:1. Mastering ASP programming:- BPB Publication.2. Java Script, HTML, DHTML: - Ivan Bayrous.3. Java Script: Don Gosselin, Thomson Learning (Vikas Publication).4. Principles of Web Design, Joel Sklar, Thomson Learning(Vikas Publication).<strong>BCA</strong> - 506 : ENTREPRENEURSHIPMax. Marks: 25OBJECTIVE : To aware with the business entrepreneurship.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IEconomic Development and Entrepreneurship: Concept, social context,psychological factors in Entrepreneurship, Characteristics, qualities andPre-requisites of Entrepreneurship, Environmental factor affectingEntrepreneurship.UNIT -IIInstitutional Finance and Entrepreneurship; Mobility of Entrepreneurship,Different aspects of Entrepreneurship Organization and performance ofEntrepreneurship skills; Effectiveness of Entrepreneurship; new57
Entrepreneurship; economic and sociological view - points.UNIT - IIISelf - employment: Need and Mode; methods and procedures to start andexpand one’s own business: relation between large and small Enterprisesdeveloping ancillary units for quality Production and cost-effectiveness.UNIT - IVPreparation of a new project-demand, Analysis and Market Potentials,Capital Saving and project costing, working capital requirement; calculationof Break-even point; Profit making in perspective.UNIT - VMain coverage of project Proposal- Technical, commercial and economic,Financial and Managerial Feasibility proforma on cost of production andprofitability. Entrepreneurship before independence and Entrepreneurshipgrowth after independence under planning system. Role of Marwaricommunity in Industrial Entrepreneurship.BOOKS:1. Project Planning and Entrepreneurship - Banga2. Entrepreneurship development - Jose Paul<strong>BCA</strong> – 507: PRACTICALS (JAVA)Max.Marks:501. Exercises related to use of primitive data types – integer, short, long,byte, float, double, Unicode Character set, Boolean, their ranges,defaults initial values, wrapping of integer arithmetic, casting.2. Exercises related to use of Comments, Identifiers and reservedwords, local variables, operators and operator-precedence.3. Exercises related to use of statements simple and compound, Uses ofcontrol do, for, while, switch, break, case of continue, label.4. Exercises related to use of class type Data: String, Arrays, ObjectArrays, Examples of use of class type data.58
5. Exercises related to use of instance fields and methods, Static fieldand methods, Exercises related to use of initialization byConstructor, Initialization by Default Constructor.6. Exercises related to use of creation of objects, access methods.7. Exercises related to use of inheritance, Super class, Subclass, Methodoverloading.8. Exercises related to use of interface.9. Exercises related to use of thread, Multithreading example,Synchronized.10.Exercises related to use of Exception (try-catch-final blocksexamples)11.Java Programming Exercises.59
SEMESTER – VI<strong>BCA</strong> - 601 : COMPUTER GRAPHICS & MULTIMEDIAMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of Computer Graphics andMultimedia.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IPixel, frame, buffer, application of computer graphics, Raster Graphicsfundamentals. Display Devices- Random Scan, Raster Scan Monitors, ColorCRT Monitor, DUST and Plasma Panel.UNIT-IIGraphics primitives:- Algorithms for Line Generation, circle generation,polygon generation and polygon filling algorithms, Anti aliasing.2-D Transformation:- Translation, Scaling, Rotation, Reflection,homogeneous Co-ordinates.UNIT-III3-D Transformation:- Translation, Scaling, Rotation, windowing &clipping- window, view port, line clipping, polygon clipping, window &viewport transformation.Display file, Segment table, Segment creation, deletion, rename.UNIT-IVMultimedia:Text - Fonts, Faces, animating Text, Hyper Text.Sound - MIDI, Digital audio basics, audio file formats, audio editing, MCIImage - Bitmaps, Vector drawing, color palate, concept of 3D Modelling,Image file formats (BMP, JPG).Animation- Principles of animation, cell animation, kinematics, morphing.60
UNIT - VVideo - Broadcast video standards (NTSC, PAL), Integrating Computer andtelevision, video capture board, video, colour, shooting and editing video,recording formats (S-VHS) video hardware resolution, video compression(JPEG, MPEG).Hard copy devices: printers & Plotters, Input devices: Mouse, Trackball,Lightpen, Scanner, Digital Camera.BOOKS:1. Computer Graphics: Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Prentice,Hall of India2. Multimedia Making it Works, 3 rd Edition, Tay Vaughan, TataMcGraw-Hill End., New Delhi.<strong>BCA</strong> - 602: OPERATING SYSTEMOBJECTIVE : To aware with the operating systemMax. Marks: 50EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IOperating System concept, History of operating system, Simple,Multiprogrammed, Batched systems, Time-sharing system; personalcomputer system, parallel systems, distributed systems, Real- time systems.Computer System Structure: System operation, I/O Structure, Storagestructure, Storage Hierarchy, General system architecture, systemcomponents, Operating System services, system calls, system programs,system structure, Virtual Machines, System generations.UNIT - IIProcesses: Process concepts, process scheduling, Operation on Processes,cooperating processes, Threads, Interprocess communication.Scheduling: Basic Concepts, scheduling criteria, scheduling algorithms,multiprocessor scheduling, Real - time scheduling.61
UNIT - IIIProcess Synchronization: The Critical-section problem, Synchronization,Hardware, semaphores, Problem in synchronization, Synchronization insolaris2.Deadlocks: Clocks, Deadlocks, methods for handling, Characterization,Deadlock detection and recovery, deadlock avoidance, deadlock prevention,two phase locking, non-resource deadlocks, starvation.UNIT - IVMemory Management: Memory Management with and without swapping,logical versus physical address space, contiguous allocation, paging,segmentation, segmentation with paging.Virtual Memory: Virtual memory, demand paging, Page-replacement, pagereplacementalgorithm, modeling paging algorithms, design issue of pagingsegmentation.UNIT - VFile System: File concepts, access methods, directory structure, protection.File system Implementation: file-system structure, allocation methods, freespacemanagement, directory Implementation, efficiency and performance,recovery, file system of UNIX & DOS. Secondary - storage structure: Goalsand domain of protection, security protection mechanism, security problem,authentication, threats, monitoring and encryption.BOOKS:1. Operating System Concepts by Silberschatz Galvin, Addison -Wesley Publication. (Text).2. Modern operating systems by Andrew S. Tannenbaum.<strong>BCA</strong> - 603 : COMPUTER ORIENTED NUMERICAL METHODS(Using “C” Language)Max. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To introduce the concept of computer oriented numericalmethods.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questions62
choosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - INUMERICAL COMPUTATIONS:Computer Arithmetic: Floating Point Number Operations, Normalizationand their consequences. Iterative Methods: Bisection Method, FalsePosition Method, Newton Raphson Method, Secant Method, Graffes RootSquaring Method, Convergence of Solution.UNIT - IISimultaneous Linear Equations: Solution of simultaneous Linear Equations- Gauss Elimination Method, Gauss - Seidal Method, Gauss - JordanElimination Method, Triangularization Method & Pivoting Condensation,III Conditioned Equation & Refinement of solutions.Curve Fitting: Curve Fitting Method, Least Curve fitting, Non Linear curvefitting.UNIT - IIIDifference Operators and Interpolation: Definition of Forward, Backward,Shifting, Divided Difference, Central and Averaging Operators and theirRelationships. Newton’s Forward Interpolation Formula, Newton’sbackward Interpolation Formula, Newton’s Divided Interpolation Formula,Lagrange’s Interpolation Formula.UNIT - IVNumerical Differentiation: Numerical Differentiation using Newton’sForward Interpolation Formula, Newton’s backward Interpolation Formula,Newton’s Divided Interpolation Formula. Numerical Integration: GeneralQuadrature Formula, Newton – Cote’s Formula, Trapezoidal Rule,Simpson’s One Third Rule, Simpson’s Three Eight Rule.UNIT - VNumerical Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations: Euler’s Method,Euler’s Modified Method, Taylor’s Series Method, Picard’s method, RungeKutta Second Order and Fourth order Method.BOOKS:1. Numerical Analysis by Gupta And Malik. (TEXT).63
2. Computer Oriented Numerical Methods by V. Rajaraman.3. Numerical Analysis by Shastri.4. Computer based Numerical Algorithm by Krishnamurthy.<strong>BCA</strong> - 604 : MICROPROCESSOR & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGEPROGRAMMINGMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To aware with the microprocessor & introduce the conceptof Assembly Language Programming.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT - IMICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE: Architecture & Programming of8085, Organization of CPU, Various Addressing Modes.UNIT - IIPROGRAMMING: Assembly Language Programming, Instruction and DataFlow, Instruction set of 8085.UNIT - IIIINTERFACING MEMORY AND I/O DEVICES: Memory interfacing,Various Schemes, Address space partitioning, Interfacing Techniques withvarious I/O Devices, Latches and Tristate Buffers.UNIT - IVINTERFACING DEVICES & PERIPHERAL SUBSYSTEMS:Programmable peripheral 8155 & 8255, their features, programming andapplications, Keyboard controller 8279.UNIT - VAPPLICATIONS: Microcontrollers, Architecture of 8051 microcontroller,Comparison of microprocessors of different series.64
BOOKS:1. Microprocessor Architecture Programming and Application with8085,Willy Eastern Limited, by R. S. Gaonkar.2. Microprocessor Family 8086/8088: Liu & Gibson.3. Introduction to Microprocessor Software, Hardware & Programming,PHI, by L. A. Laventhal.<strong>BCA</strong> - 605: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES OF MANAGEMENTMax. Marks: 50OBJECTIVE : To aware with the principles & practices of management.EXAMINATIONThe question paper will have the usual note saying “Attempt five questionschoosing one from each Unit”, Thus, the paper will clearly specify Units,and have a pattern of two questions per unit, with an option to attempt anyone of these two within each unit.UNIT- IThe Nature of Management: Definition and Role of Management, Functionsof Manager, Scientific Management, Human Relations School ofManagement, Contingency Theory of Management.UNIT- IIPlanning: Nature and Purpose of Planning, Components of Planning,Objectives of Business, Management by Objectives. Forecasting, DecisionMaking, Policy Formulation and Strategies.UNIT- IIIOrganizing: Nature and Purpose of Organizing, Departmentation, Span ofManagement, Delegation of Authority. Line and Staff Relationships.UNIT- IVDirecting Process: Principles of Direction, Problems in Human Relation,Strategies for Establishing. Healthy Human Relations.65
UNIT- VControl: Meaning and Process of Control, Control Techniques.BOOKS1. Management: Harold Koontz, O’Donnel and Heinz Welhrich, NewYork, McGraw Hill Book Co.2. Organization and Management: R. D. Agarwal, New Delhi, TataMcGraw Hill.,1995<strong>BCA</strong> - 606 : PRACTICALS ON VISUAL BASICMax. Marks : 501. Write a Program which asks login, password from user three times. if thepassword is right it wishes the user else it gives proper massage to theuser.2. Write a program which has three text boxes. and four buttons, buttons arelike.i. Addii. Subtractiii. Multiplyiv. DivideUser will enter two no. in first and second textbox and there result willbe displayed in third text box.3. Program which takes 10 records from the user, there are two buttons onthe form. Display, Modify. On clicking the button display informationabout the requested record, on clicking modify, information of particularstudent should be changed.4. Create a menuColorBoldLowerItalicFontCaseRedGreen66
UpperBold AndBlueItalicFont NameForm has one Textbox, on clicking any option properties of textboxshould change accordingly.5. Take Two LISTBOXS. First List box has 10 elements. There are threebuttons.i. >ii. >>iii. removeon clicking first button selected item from first list box should beinserted into second one. If second button is clicked than all items offirst should be inserted into second one (no duplicate element insecond list box). On clicking third button selected element from thesecond list box should be deleted.<strong>BCA</strong> - 607: PRACTICALS (GRAPHICS &MULTIMEDIA)Max. Marks: 251. Write a program for DDA Line Method.2. Write a program for Brasnham’s line drawing Algorithm.3. Write a program for Brasnham’s Circle drawing Algorithm.4. Write a program for Circle Drawing using Midpoint SubdivisionMethod.5. Write a program for Drawing a polygon.6. Write a program for Scan-Filling a Polygon7. Write a program for Sutherland hodgman Polygon clipping.8. Write a program for composite Transformation.9. Write a program to write your name in Hindi using any charactergeneration method.67
10.Write a program for cohen- Sutherland Line Clipping method and clipa line using this.<strong>BCA</strong> - 608 : PRACTICALS (CONM USING C)Problems related to Iterative Method• Zeros of a single transcendental equation.• Zeros of polynomials using bisection.• False Position.• Convergence of solution.Max. Marks: 25Problems related to• Simultaneous linear equation using Gauss Elimination Method.• Solution of simultaneous linear equations - Gauss EliminationMethod.• Solution related to pivoting.• III Conditioned equations and refinement of solution.• Gauss-Seidal iterative method.Problems related to• Numerical differentiation and Integration.• Solution of Differential equations; Runge-Kutta Method.Problems related to• Interpolation and Approximation: Polynomial interpolation.• Newton.• Lagrange.• Approximation of function by Taylor series<strong>BCA</strong> - 609: PRACTICALS(MICROPROCESSOR & ASSEMBLY LANGUAGEPROGRAMMING)68
Max. Marks: 251. Design of two pass or one assembler for a hypothetical assemblylanguage.2. Design of microprocessor.3. 10-15Assembly Language Programming Problems decided by theteacher to be done by the students.4. Interfacing of peripherals kits like 8255, 8251, 8253, etc. Withmicroprocessor 8085A Kit.69