Water management in irrigated rice - Rice Knowledge Bank ...
Water management in irrigated rice - Rice Knowledge Bank ...
Water management in irrigated rice - Rice Knowledge Bank ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
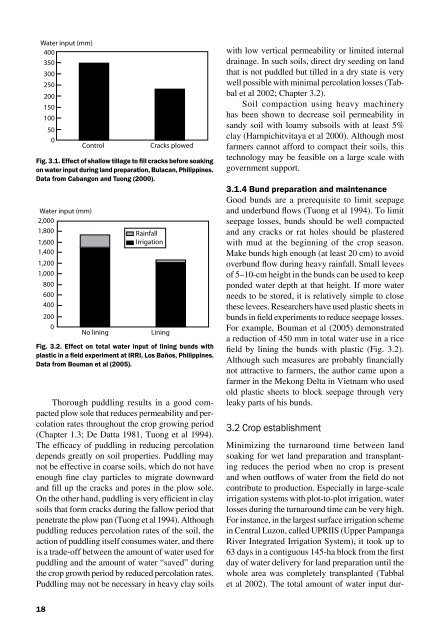
<strong>Water</strong> <strong>in</strong>put (mm)400350300250200150100500ControlCracks plowedFig. 3.1. Effect of shallow tillage to fill cracks before soak<strong>in</strong>gon water <strong>in</strong>put dur<strong>in</strong>g land preparation, Bulacan, Philipp<strong>in</strong>es.Data from Cabangon and Tuong (2000).<strong>Water</strong> <strong>in</strong>put (mm)2,0001,8001,6001,4001,2001,0008006004002000No l<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gRa<strong>in</strong>fallIrrigationL<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>gFig. 3.2. Effect on total water <strong>in</strong>put of l<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g bunds withplastic <strong>in</strong> a field experiment at IRRI, Los Baños, Philipp<strong>in</strong>es.Data from Bouman et al (2005).Thorough puddl<strong>in</strong>g results <strong>in</strong> a good compactedplow sole that reduces permeability and percolationrates throughout the crop grow<strong>in</strong>g period(Chapter 1.3; De Datta 1981, Tuong et al 1994).The efficacy of puddl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> reduc<strong>in</strong>g percolationdepends greatly on soil properties. Puddl<strong>in</strong>g maynot be effective <strong>in</strong> coarse soils, which do not haveenough f<strong>in</strong>e clay particles to migrate downwardand fill up the cracks and pores <strong>in</strong> the plow sole.On the other hand, puddl<strong>in</strong>g is very efficient <strong>in</strong> claysoils that form cracks dur<strong>in</strong>g the fallow period thatpenetrate the plow pan (Tuong et al 1994). Althoughpuddl<strong>in</strong>g reduces percolation rates of the soil, theaction of puddl<strong>in</strong>g itself consumes water, and thereis a trade-off between the amount of water used forpuddl<strong>in</strong>g and the amount of water “saved” dur<strong>in</strong>gthe crop growth period by reduced percolation rates.Puddl<strong>in</strong>g may not be necessary <strong>in</strong> heavy clay soilswith low vertical permeability or limited <strong>in</strong>ternaldra<strong>in</strong>age. In such soils, direct dry seed<strong>in</strong>g on landthat is not puddled but tilled <strong>in</strong> a dry state is verywell possible with m<strong>in</strong>imal percolation losses (Tabbalet al 2002; Chapter 3.2).Soil compaction us<strong>in</strong>g heavy mach<strong>in</strong>eryhas been shown to decrease soil permeability <strong>in</strong>sandy soil with loamy subsoils with at least 5%clay (Harnpichitvitaya et al 2000). Although mostfarmers cannot afford to compact their soils, thistechnology may be feasible on a large scale withgovernment support.3.1.4 Bund preparation and ma<strong>in</strong>tenanceGood bunds are a prerequisite to limit seepageand underbund flows (Tuong et al 1994). To limitseepage losses, bunds should be well compactedand any cracks or rat holes should be plasteredwith mud at the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g of the crop season.Make bunds high enough (at least 20 cm) to avoidoverbund flow dur<strong>in</strong>g heavy ra<strong>in</strong>fall. Small leveesof 5–10-cm height <strong>in</strong> the bunds can be used to keepponded water depth at that height. If more waterneeds to be stored, it is relatively simple to closethese levees. Researchers have used plastic sheets <strong>in</strong>bunds <strong>in</strong> field experiments to reduce seepage losses.For example, Bouman et al (2005) demonstrateda reduction of 450 mm <strong>in</strong> total water use <strong>in</strong> a <strong>rice</strong>field by l<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the bunds with plastic (Fig. 3.2).Although such measures are probably f<strong>in</strong>anciallynot attractive to farmers, the author came upon afarmer <strong>in</strong> the Mekong Delta <strong>in</strong> Vietnam who usedold plastic sheets to block seepage through veryleaky parts of his bunds.3.2 Crop establishmentM<strong>in</strong>imiz<strong>in</strong>g the turnaround time between landsoak<strong>in</strong>g for wet land preparation and transplant<strong>in</strong>greduces the period when no crop is presentand when outflows of water from the field do notcontribute to production. Especially <strong>in</strong> large-scaleirrigation systems with plot-to-plot irrigation, waterlosses dur<strong>in</strong>g the turnaround time can be very high.For <strong>in</strong>stance, <strong>in</strong> the largest surface irrigation scheme<strong>in</strong> Central Luzon, called UPRIIS (Upper PampangaRiver Integrated Irrigation System), it took up to63 days <strong>in</strong> a contiguous 145-ha block from the firstday of water delivery for land preparation until thewhole area was completely transplanted (Tabbalet al 2002). The total amount of water <strong>in</strong>put dur-18










![International Standards' Organization â Rice Specification [ISO 7301]](https://img.yumpu.com/36696862/1/190x245/international-standards-organization-a-rice-specification-iso-7301.jpg?quality=85)




