Glancing Angle X-ray Diffraction (GAXRD) Technique
Glancing Angle X-ray Diffraction (GAXRD) Technique
Glancing Angle X-ray Diffraction (GAXRD) Technique
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
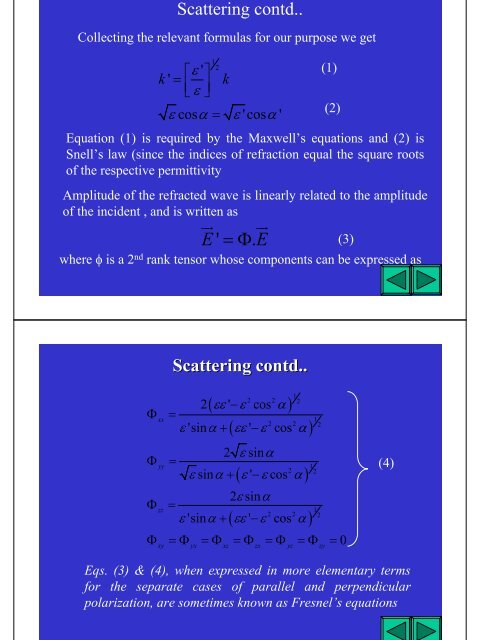
Scattering contd..<br />
Collecting the relevant formulas for our purpose we get<br />
1 2<br />
ε '<br />
k'= ⎡ ⎤<br />
⎢⎣ε⎥⎦ k<br />
ε cosα = ε'cosα' Equation (1) is required by the Maxwell’s equations and (2) is<br />
Snell’s law (since the indices of refraction equal the square roots<br />
of the respective permittivity<br />
Amplitude of the refracted wave is linearly related to the amplitude<br />
of the incident , and is written as<br />
ur ur<br />
E ' =Φ.<br />
E<br />
where φ is a 2 nd rank tensor whose components can be expressed as<br />
Scattering contd..<br />
2 ( εε −ε<br />
1<br />
2 2 α )<br />
+ ( − )<br />
2 ' cos<br />
Φ = xx<br />
ε'sinα εε'ε cos α<br />
1<br />
2 2 2<br />
Eqs. (3) & (4), when expressed in more elementary terms<br />
for the separate cases of parallel and perpendicular<br />
polarization, are sometimes known as Fresnel’s equations<br />
(1)<br />
(2)<br />
(3)<br />
Φ yy =<br />
2 εsinα 1<br />
2 2<br />
εsinα + ( ε'−εcosα) 2εsinα Φ = zz<br />
1<br />
2 2 2<br />
ε'sinα + ( εε'−ε cos α)<br />
Φ =Φ =Φ =Φ =Φ =Φ = 0<br />
xy yx xz zx yz zy<br />
(4)<br />
7<br />
8