Astro 160: The Physics of Stars
Astro 160: The Physics of Stars
Astro 160: The Physics of Stars
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
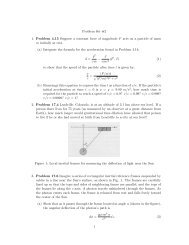
for the proton-He interaction we findr c = e2 Z 1 Z 2E 0≈ 1.44 × 10 −10 cmthus the probability is given byE G ≈ 3.15 MeVP ≈ 5.8 × 10 −18(b) What energy E would be required for i) the two 4 He nuclei, ii) the proton and the 4 He nucleus, andiii) two 12 C nuclei to have the same probability <strong>of</strong> penetrating the Coulomb barrier as the two protons?For particles with energies equal to the mean thermal energy <strong>of</strong> the plasma, what temperatures do thesecorrespond to?Since we know thatfor the He-He interaction we findfor the proton-He interaction we findE =E G(lnP) 2E He−He ≈ 0.125 MeVE p−He ≈ .013 MeVfor the carbon-carbon interaction the Gamow energy is given byE G ≈ 2592π 2 α 2 6m p c 2 ≈ 7.7 GeVand thuswe know thatE c−c ≈ 31 MeVT ≈ E k bsoT He−He ≈ 1.45 × 10 9 KT p−He ≈ 1.5 × 10 8 KT c−c ≈ 3.6 × 10 11 KProblem # 5Calculations <strong>of</strong> nuclear reaction rates are done in the center <strong>of</strong> mass (COM) frame, so it is useful toremember a few results about the COM. Consider two particles <strong>of</strong> mass m 1 and m 2 with positions x 1 andx 2 and velocities v 1 and v 2 .(a) .What is the velocity <strong>of</strong> the COM?We kbnow that the center <strong>of</strong> mass is given bycom = m 1r 1 + m 2 r 2m 1 + m 224











![Problem #1 [Structure Formation I: Radiation Era]](https://img.yumpu.com/37147371/1/190x245/problem-1-structure-formation-i-radiation-era.jpg?quality=85)