Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
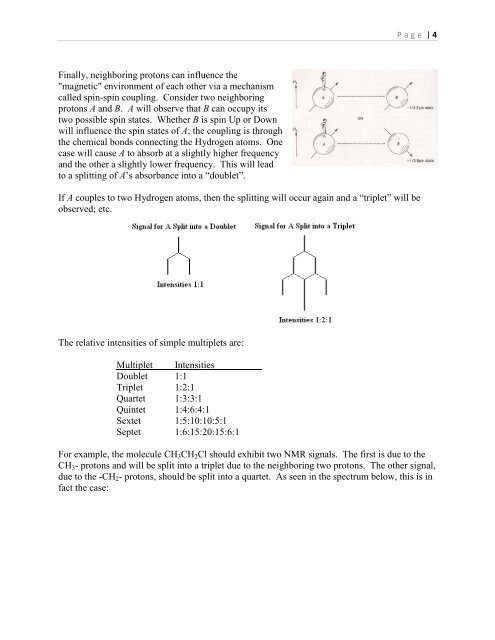
P a g e | 4Finally, neighboring protons can influence the"magnetic" environment of each other via a mechanismcalled spin-spin coupling. Consider two neighboringprotons A and B. A will observe that B can occupy itstwo possible spin states. Whether B is spin Up or Downwill influence the spin states of A; the coupling is throughthe chemical bonds connecting the Hydrogen atoms. Onecase will cause A to absorb at a slightly higher frequencyand the other a slightly lower frequency. This will leadto a splitting of A’s absorbance into a “doublet”.If A couples to two Hydrogen atoms, then the splitting will occur again and a “triplet” will beobserved; etc.The relative intensities of simple multiplets are:Multiplet IntensitiesDoublet 1:1Triplet 1:2:1Quartet 1:3:3:1Quintet 1:4:6:4:1Sextet 1:5:10:10:5:1Septet 1:6:15:20:15:6:1For example, the molecule CH 3 CH 2 Cl should exhibit two NMR signals. The first is due to theCH 3 - protons and will be split into a triplet due to the neighboring two protons. The other signal,due to the -CH 2 - protons, should be split into a quartet. As seen in the spectrum below, this is infact the case: