Science Focus 2 - Chapter Tests - Pearson Australia Media Resources
Science Focus 2 - Chapter Tests - Pearson Australia Media Resources
Science Focus 2 - Chapter Tests - Pearson Australia Media Resources
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
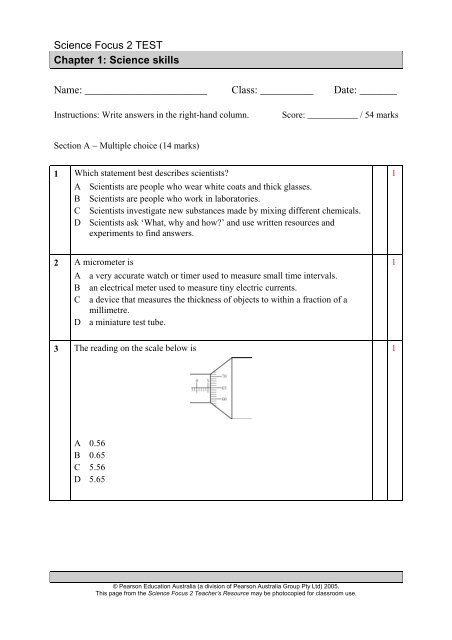
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 54 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (14 marks)<br />
1 Which statement best describes scientists?<br />
A Scientists are people who wear white coats and thick glasses.<br />
B Scientists are people who work in laboratories.<br />
C Scientists investigate new substances made by mixing different chemicals.<br />
D Scientists ask ‘What, why and how?’ and use written resources and<br />
experiments to find answers.<br />
2 A micrometer is<br />
A a very accurate watch or timer used to measure small time intervals.<br />
B an electrical meter used to measure tiny electric currents.<br />
C a device that measures the thickness of objects to within a fraction of a<br />
millimetre.<br />
D a miniature test tube.<br />
3 The reading on the scale below is<br />
A 0.56<br />
B 0.65<br />
C 5.56<br />
D 5.65<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
4 A series of experiments investigating one topic is called<br />
A observation.<br />
B research.<br />
C explanation.<br />
D hypothesis.<br />
5 A Year 8 student is designing an experiment to test the effect of variables when<br />
cooking a pizza.<br />
Which of the following is the least logical variable for this experiment?<br />
A The size of each pizza base.<br />
B The length of time the pizza is in the oven.<br />
C The day of the week on which the experiment is performed.<br />
D The temperature of the oven.<br />
6 Which statement about observations is correct?<br />
A Observations are always quantitative.<br />
B Observations are things you see.<br />
C Observations involve some guesswork.<br />
D Observations may be made with any of the five senses.<br />
7 The match below is approximately<br />
A 4.0 cm long.<br />
B 4.2 cm long.<br />
C 4.4 cm long.<br />
D 4.5 cm long.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
8 Which is the odd one out?<br />
A Mistake.<br />
B Parallax error.<br />
C Human reaction time.<br />
D Instrument error.<br />
9 A measurement thought to be between 20 and 30 mm may be written as<br />
A 15 ± 5 mm.<br />
B 25 ± 5 mm.<br />
C 20 ± 10 mm.<br />
D 30 ± 10 mm.<br />
10 A bibliography is<br />
A a list of resources used to gather information.<br />
B the study of information in the Bible.<br />
C a diagram in a scientific report.<br />
D a scientific reference book.<br />
11 When plotting a graph of results, the independent variable<br />
A should be plotted on the horizontal axis.<br />
B should be plotted on the vertical axis.<br />
C may be plotted on either the horizontal or vertical axis.<br />
D is the heading for the graph.<br />
12 In the graph below, as t increases, then B<br />
A doubles.<br />
B more than doubles.<br />
C increases then levels out.<br />
D decreases.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
13 Which of the following is not a prefix?<br />
A Kilo.<br />
B Centi.<br />
C Joules.<br />
D Nano.<br />
14 A megagram is equal to<br />
A a kilogram.<br />
B 1 tonne.<br />
C one-thousandth of a gram.<br />
D one-millionth of a gram.<br />
Section B − Written answers (40 marks)<br />
1 Identify four well-known inventions.<br />
2 Define the two terms:<br />
a qualitative observation.<br />
b quantitative observation.<br />
3 Identify four possible variables in an<br />
experiment that tests the effect of a<br />
Bunsen burner flame on a beaker<br />
containing water.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
4<br />
2<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
4 Brad uses a bread-making machine<br />
every morning, to bake a loaf of bread<br />
for his family’s breakfast. There are<br />
only three ingredients specified on the<br />
bread mix packet:<br />
yeast (1.5 teaspoons), bread mix (3<br />
cups) and water (1 cup). He uses the<br />
built-in timer to control how long the<br />
bread is cooked.<br />
a List the variables in Brad’s bread<br />
making.<br />
b Explain how Brad could test the<br />
effect of slightly changing the<br />
amount of yeast and water, on the<br />
final product.<br />
5 Identify two examples of estimates.<br />
6 a Illustrate the position of an eye so<br />
the correct measurement may be<br />
read below.<br />
b What is the correct reading?<br />
7 Identify examples of<br />
a an instrument error.<br />
b a human reaction time error.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
6<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
8 Calculate the average number of goals<br />
per game scored by a player if she<br />
scored 3, 6, 2, 4 and 15 goals in five<br />
games.<br />
9 Identify the main features of a scientific<br />
report.<br />
10 Recall<br />
a how many litres are in a gigalitre.<br />
b what a micrometre is.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
7<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
11 The graph below shows the temperature<br />
of a room after a heater has been<br />
operating for a given time.<br />
a Calculate the temperature of the<br />
room when you turned on the<br />
heater.<br />
b Calculate the temperature in the<br />
room after the heater had been on<br />
for 15 minutes.<br />
c Calculate how long the heater<br />
had been on when the<br />
temperature was 20°C.<br />
d Use the graph to predict the<br />
room temperature after 1 hour.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 1: <strong>Science</strong> skills<br />
12 a Plot the following grass growth<br />
data on the grid provided.<br />
Day<br />
Height (mm)<br />
0<br />
0<br />
5<br />
3<br />
10<br />
7<br />
15<br />
15<br />
20<br />
32<br />
25<br />
51<br />
30<br />
30<br />
b Draw a line of best fit through<br />
your points to show any pattern<br />
that exists.<br />
c Predict when the grass was<br />
mown.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
5
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 67 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (15 marks)<br />
1 Which of the following is an element?<br />
A Carbon.<br />
B Paper.<br />
C Plastic.<br />
D Sugar.<br />
2 The chemical symbol for sodium is<br />
A S<br />
B So<br />
C Na<br />
D No<br />
3 An element is a<br />
A chemical obtained from mineral ore.<br />
B pure substance made up of only one type of atom.<br />
C group of different atoms bonded together.<br />
D synthetic substance created in the laboratory.<br />
4 The symbol K denotes<br />
A copper.<br />
B cobalt.<br />
C polonium.<br />
D potassium.<br />
5 Pure water is made up of numerous<br />
A atoms.<br />
B spheres.<br />
C molecules.<br />
D compounds.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
6 Quartz has the chemical formula SiO2 . This means that in quartz<br />
A for every atom of silicon, there are 2 atoms of oxygen.<br />
B for every atom of oxygen, there are 2 atoms of silicon.<br />
C silicon and oxygen form groups, containing two of each type of atom.<br />
D one atom of silicon bonds with one atom of oxygen, to make a group<br />
containing two atoms.<br />
7 Which of the following is a chemical change?<br />
A Sawdust is produced from wood being cut by a power saw.<br />
B Water freezes to form ice.<br />
C Fireworks explode in a colourful display.<br />
D Juice is obtained from an orange.<br />
8 A combination reaction is best described as one in which<br />
A a substance is broken down to form two or more different substances.<br />
B a new substance is formed by the combination of two or more substances.<br />
C an insoluble, sometimes colourful, solid is formed from two liquids.<br />
D a substance reacts with oxygen.<br />
9 A chemical reaction may be sped up by<br />
A using more concentrated reactants.<br />
B heating the reactants.<br />
C using more finely ground reactants.<br />
D all of the above.<br />
10 A catalyst<br />
A speeds up a chemical reaction without actually combining with reactants.<br />
B dissolves chemicals that water is unable to.<br />
C is one of the ‘ingredients’ in a chemical reaction.<br />
D is a large molecule that is broken down by a smaller one.<br />
11 In the chemical reaction: iron + sulfur → iron sulfide<br />
A iron and sulfur are products.<br />
B iron sulfide is the product.<br />
C iron, sulfur and iron sulfide are products.<br />
D sulfide is the product.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
12 Which of the following famous scientists is not known for their theory of atomic<br />
structure?<br />
A Dalton.<br />
B Thomson.<br />
C Rutherford.<br />
D Newton.<br />
13 An atom consists of<br />
A a nucleus containing neutrons and protons, surrounded by fast-moving<br />
electrons.<br />
B central neutrons, surrounded by fast-moving electrons and protons.<br />
C central electrons, surrounded by fast-moving protons.<br />
D a mixture of protons and electrons spread evenly in a neutral ‘dough’.<br />
19<br />
14 An atom of 9F<br />
contains<br />
A 19 protons and 9 electrons.<br />
B 9 protons, 9 electrons and 10 neutrons.<br />
C 10 protons, 9 neutrons and 9 electrons.<br />
D 9 protons, 19 neutrons and 10 electrons.<br />
15 A phosphorus atom has an atomic number of 15. How many electrons does it<br />
have in its third (outermost) shell?<br />
A 0<br />
B 2<br />
C 5<br />
D 8<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
Section B − Written answers (40 marks)<br />
1 Define each of the following.<br />
a Element.<br />
b Atom.<br />
c Molecule.<br />
d Compound.<br />
e Mixture.<br />
2 a Sketch a molecule of NH 3 .<br />
b Identify the following formula.<br />
3 Identify and name the elements whose<br />
symbols are given below.<br />
a Al<br />
b Ca<br />
c Au<br />
d He<br />
e O<br />
f Mg<br />
g Kr<br />
h Pb<br />
i S<br />
j Zn<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
5<br />
2<br />
5
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
4 Identify the symbol for each of the<br />
following.<br />
a Hydrogen.<br />
b Chlorine.<br />
c Silver.<br />
d Neon.<br />
e Europium.<br />
f Boron.<br />
g Iodine.<br />
h Iron.<br />
i Tin.<br />
j Carbon.<br />
5 Identify four examples of a physical<br />
change.<br />
6 Identify four examples of a chemical<br />
change.<br />
7 Classify each reaction below as one of<br />
the following:<br />
combination, decomposition,<br />
precipitation, combustion<br />
a Methane burns in a Bunsen<br />
burner.<br />
b Light breaks down silver chloride<br />
to form silver and chlorine.<br />
c A solid forms when two liquids<br />
are mixed.<br />
d Copper reacts with oxygen to<br />
form copper oxide.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
5<br />
4<br />
4<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
8 Complete each of the following<br />
chemical reactions.<br />
a Lead nitrate + potassium iodide<br />
→<br />
lead iodide + ________<br />
________<br />
b Zinc + copper chloride →<br />
________ ________ + ________<br />
c Iron + chlorine → ________<br />
________<br />
9 Define each of the following in relation<br />
to a chemical reaction.<br />
a (s)<br />
b (l)<br />
c (g)<br />
d (aq)<br />
10 Define an enzyme. 2<br />
11 Identify three ways a chemical reaction<br />
may be sped up.<br />
12 Clarify by drawing a diagram the parts<br />
of an atom of lithium which has 3<br />
protons, 4 neutrons and 3 electrons.<br />
Show the charge (if any) on each type<br />
of particle.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
4<br />
3<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 2: Atoms<br />
64<br />
13 Copper may be denoted by 29 Cu<br />
Calculate how many of each of the<br />
following are in one atom of copper.<br />
a Neutrons.<br />
b Electrons.<br />
c Protons.<br />
89<br />
14 Yttrium may be denoted by 39 Y<br />
Calculate the<br />
a mass number of yttrium.<br />
b atomic number of yttrium.<br />
15 An atom of oxygen contains 8 electrons.<br />
Calculate the number of electrons in<br />
the<br />
a innermost shell of an atom of<br />
oxygen.<br />
b outer shell of an atom of oxygen.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
2<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 94 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (20 marks)<br />
1 The scientifically correct name for ‘germs’ is<br />
A bugs.<br />
B disease.<br />
C flu.<br />
D microbes.<br />
2 A scientist who studies microorganisms is known as a<br />
A microbiologist.<br />
B biologist.<br />
C microgeologist.<br />
D doctor.<br />
3 Which of the following microbes may be seen with the naked eye?<br />
A Viruses.<br />
B Bacteria.<br />
C Fungi.<br />
D Protozoa.<br />
4 What instrument magnifies objects up to 100 000 times?<br />
A Light microscope.<br />
B Electron microscope.<br />
C Magnifying glass.<br />
D Digital camera.<br />
5 Bacteria are used to make<br />
A yogurt.<br />
B wine.<br />
C bread.<br />
D butter.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
6 The common mushroom is an example of a<br />
A virus.<br />
B bacterium.<br />
C fungus.<br />
D plant.<br />
7 The tiny hairs used by some protists to move around are called<br />
A flagella.<br />
B cilia.<br />
C pseudopod.<br />
D hair.<br />
8 AIDS is caused by a<br />
A virus.<br />
B bacterium.<br />
C fungus.<br />
D protist.<br />
9 Which fungi do we use to make food and drink such as bread, cereals, wine and<br />
beer?<br />
A Mould.<br />
B Mushrooms.<br />
C Flour.<br />
D Yeast.<br />
10 Bacteria and protists reproduce by cell division or<br />
A binary fusion.<br />
B cellular changes.<br />
C primary fission.<br />
D binary fission.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
11 Some bacteria can undergo binary fission in as little as 20 minutes, and in seven<br />
hours will become a colony of over<br />
A 100<br />
B 10 000<br />
C 100 000<br />
D 1 000 000<br />
12 Bacteria grow and reproduce very rapidly only when the conditions are right.<br />
These conditions are<br />
A warm and dry.<br />
B cold and dry.<br />
C warm and moist.<br />
D cold and moist.<br />
13 Identify the chemicals or drugs that kill bacteria.<br />
A Biotics.<br />
B Antibiotics.<br />
C Aspirin.<br />
D Antifungicides.<br />
14 The capsule called a sporangium holds<br />
A spores.<br />
B eggs.<br />
C pollen.<br />
D sporangs.<br />
15 Viruses are only able to reproduce inside a<br />
A human cell.<br />
B plant cell.<br />
C bacterium.<br />
D host cell.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
16 These two microbe groups are more foe than friend.<br />
A Fungi and protists.<br />
B Viruses and bacteria.<br />
C Bacteria and fungi.<br />
D Protists and viruses.<br />
17 Bacteria carried by fleas caused the death of one quarter of the population of<br />
Europe in the 1300s. This period is called<br />
A the Black Years.<br />
B the Black Death.<br />
C the Black Flea Deaths.<br />
D the Black European Plague.<br />
18 The fungal disease tinea is also known as<br />
A athlete’s foot.<br />
B toe jam.<br />
C ring worm.<br />
D thrush.<br />
19 In 1928, Alexander Fleming discovered the mould that produces<br />
A aspirin.<br />
B insulin.<br />
C penicillin.<br />
D bactrum.<br />
20 The process whereby yeast feeds on the sugar (glucose) in fruit, vegetables or<br />
cereal grains to produce carbon dioxide gas is called<br />
A glucosis.<br />
B fermentation.<br />
C aerobic respiration.<br />
D binary fission.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
Section B − Written answers (74 marks)<br />
1 Identify the microbes that can be seen<br />
with a<br />
a light microscope.<br />
b electron microscope.<br />
2 Identify the coarse focus, base, stage,<br />
eye piece, objective lens and mirror on<br />
the following diagram of a microscope.<br />
3 Classify each of the following<br />
statements as true or false<br />
a 1 centimetre = 0.01 metre<br />
b 1 nanometre can be written as 1<br />
mm.<br />
c Fungi can only be seen with a<br />
microscope.<br />
d An electron microscope is needed<br />
to see viruses.<br />
e Bacteria are about 1 micrometre<br />
in size.<br />
4 The human body is home to many<br />
bacteria. Identify three areas of the<br />
body where they may be found.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
6<br />
5<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
5 Describe how fungi feed and what<br />
function they play in the natural cycles<br />
of the environment.<br />
6 a Explain why the protist euglena<br />
is plant-like.<br />
b Describe how euglena can move<br />
in water.<br />
7 Identify each type of bacteria shown by<br />
their shape using the following labels.<br />
a Cocci.<br />
b Bacilli.<br />
c Spirilla.<br />
8 Label the following structure of a virus.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
4<br />
3<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
9 Explain why care must be taken when<br />
performing experiments with bacteria or<br />
fungi.<br />
10 Explain why you can become sick very<br />
quickly when even a single bacterium<br />
invades your body.<br />
11 Identify the three conditions needed by<br />
bacteria to reproduce.<br />
12 Draw a diagram to show how bacteria<br />
reproduce.<br />
13 Define an antibiotic. 2<br />
14 Label the diagram of a fungus to show<br />
the following structures:<br />
spores, sporangium, hyphae<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
4<br />
3<br />
3<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
15 Summarise how a virus reproduces. 6<br />
16 Explain how vaccinations work. 6<br />
17 Explain why decomposition by bacteria<br />
is not always a good thing when it<br />
comes to your food.<br />
18 Identify one place where<br />
decomposition by bacteria is a good<br />
thing.<br />
19 Some bacteria can destroy food while<br />
others are used to make it. Identify<br />
three foods that are made using bacteria.<br />
20 Identify three foods that use the fungus<br />
yeast in their production.<br />
21 Contrast aerobic and anaerobic<br />
respiration.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
1<br />
3<br />
3<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 3: Microbes<br />
22 a Write a word equation for<br />
fermentation.<br />
b Both wine and champagne are<br />
produced by fermentation.<br />
Explain why wine is flat while<br />
champagne is bubbly.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 109 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (30 marks)<br />
1 Which of the following is not a type of tooth?<br />
A Molar.<br />
B Pre-molar.<br />
C Canine.<br />
D Scissor.<br />
2 The crown of a tooth is the<br />
A tip.<br />
B space in the jaw in which the tooth sits.<br />
C part of the tooth above the gum.<br />
D inner cavity of the tooth.<br />
3 Which of the following is the odd one out?<br />
A Digestive tract.<br />
B Gut.<br />
C Alimentary canal.<br />
D Kidney.<br />
4 How much fluid does the digestive system produce each day?<br />
A 1 L<br />
B 2 L<br />
C 8 L<br />
D 16 L<br />
5 Peristalsis is<br />
A the chewing of food in the mouth.<br />
B the contraction and relaxation of muscles that moves food through the<br />
alimentary canal.<br />
C the absorption of broken-down food into the bloodstream.<br />
D the clumping together of faeces in the large intestine.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
6 Which of the following is/are not found in the digestive system?<br />
A Perpoofer valve.<br />
B Sphincters.<br />
C Villi.<br />
D Chyme.<br />
7 The liver may be described as<br />
A a J-shaped organ.<br />
B a chemical factory.<br />
C the smallest digestive organ.<br />
D the longest organ.<br />
8 The scientific name for released digestive gases is<br />
A sulfur dioxide.<br />
B flatus.<br />
C fartus.<br />
D odourus unpleasantus.<br />
9 When matter is moved more slowly than usual through the digestive system,<br />
which of the following is more likely to occur?<br />
A Diarrhoea.<br />
B Heartburn.<br />
C Constipation.<br />
D Vomiting.<br />
10 The tiny filtration units in your kidneys are called<br />
A nephrons.<br />
B filtrons.<br />
C urinators.<br />
D ureters.<br />
11 Dialysis is the medical term for<br />
A a kidney transplant.<br />
B kidney failure.<br />
C filtering of blood by a machine.<br />
D a build-up of poisonous wastes in the blood.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
12 Kidney stones can cause extreme pain. A recently developed method to<br />
eliminate kidney stones uses<br />
A ultrasound.<br />
B lasers.<br />
C chemicals.<br />
D surgery.<br />
13 The function of plasma is to<br />
A fight infection.<br />
B carry carbon dioxide.<br />
C carry the red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets around the body.<br />
D determine blood type.<br />
14 The pulmonary vein carries<br />
A deoxygenated blood to the lungs.<br />
B newly oxygenated blood to the lungs.<br />
C deoxygenated blood to the rest of the body (not the lungs).<br />
D newly oxygenated blood to the heart.<br />
15 Which of the following refers to a lower heart chamber?<br />
A Atrium.<br />
B Septum.<br />
C Ventricle.<br />
D Valve.<br />
16 Which of the following is closest to a normal ECG?<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
17 An artery may become narrowed due to a build-up of<br />
A dead blood cells.<br />
B cholesterol.<br />
C angina.<br />
D polyunsaturates.<br />
18 What two recent scientific developments have helped heart sufferers?<br />
A Ultrasonic treatment.<br />
B Chemicals to lower cholesterol.<br />
C Heart valves and pacemakers.<br />
D Polyunsaturates.<br />
19 What fraction of the human body is made up of water?<br />
1<br />
A<br />
10<br />
B<br />
C<br />
D<br />
1<br />
3<br />
1<br />
2<br />
2<br />
3<br />
20 Which of the following shows the approximate percentages of three major gases<br />
in inhaled air?<br />
A 50% nitrogen, 49% oxygen, 1% carbon dioxide.<br />
B 79% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide.<br />
C 79% nitrogen, 14% oxygen, 6% carbon dioxide.<br />
D 59% nitrogen, 41% oxygen, 0.04% carbon dioxide.<br />
21 Which of the following is not a property of alveoli?<br />
A Their cell walls are only one cell thick.<br />
B They lie close to the walls of capillaries.<br />
C They have a dry surface to allow efficient diffusion.<br />
D They are shaped to give maximum surface area.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
22 Most oxygen is transported in the bloodstream<br />
A bound to haemoglobin.<br />
B as gaseous oxygen molecules.<br />
C bound to platelets.<br />
D as dissolved carbon dioxide molecules and hydrogen carbonate ions.<br />
23 We need fibre because<br />
A it contains large amounts of vitamins and minerals.<br />
B it provides bulk which helps move substances through the digestive system.<br />
C it is the major source of energy in foods.<br />
D it is used for growth and repair.<br />
24 Pasta, bread and rice are foods that are all rich in<br />
A carbohydrates.<br />
B proteins.<br />
C fats.<br />
D vitamin C.<br />
25 Which of the following diseases is caused by a lack of vitamins?<br />
A Hepatitis C.<br />
B AIDS.<br />
C Scurvy.<br />
D Polio.<br />
26 Which two of the following are minerals?<br />
A Calcium.<br />
B Potassium.<br />
C Folic acid.<br />
D Riboflavin.<br />
27 From which one of the following categories should you have most serves each<br />
day for a healthy diet?<br />
A Vegetables.<br />
B Meat and meat alternatives.<br />
C Breads and cereals.<br />
D Milk and milk products.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
28 Which food item is high in kilojoules and high in calcium?<br />
A Ice-cream.<br />
B Can of soft drink.<br />
C Hamburger.<br />
D Margarine.<br />
29 Obesity<br />
A is an eating disorder in which sufferers unrealistically perceive they need to<br />
lose weight.<br />
B involves binge eating followed by purging.<br />
C is a condition in which a person is more than 24 per cent overweight.<br />
D is a town where a large number of OBE recipients reside.<br />
30 Respiration is a chemical reaction which<br />
A occurs only in the body cells of animals.<br />
B always has oxygen as a reactant.<br />
C involves a sequence of reactions.<br />
D is endothermic (absorbs energy).<br />
Section B − Written answers (79 marks)<br />
1 Identify the tooth type for the function<br />
of<br />
a biting.<br />
b grinding.<br />
c cutting.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
2 Label the tooth diagram below with the<br />
tooth type and function where indicated.<br />
3 Explain how acid is created in the<br />
mouth, and what can it cause.<br />
4 Identify the parts of the digestive<br />
system on the following diagram.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
2<br />
5
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
5 Identify the location in the digestive<br />
system where<br />
a stools form.<br />
b insulin is produced.<br />
c nutrients pass through villi.<br />
d considerable heat energy is<br />
produced.<br />
e saliva produced.<br />
f peristalsis occurs.<br />
g you find hydrochloric acid.<br />
h digestion begins.<br />
6 a Identify the end-product of<br />
digestion that provides energy to<br />
cells.<br />
b How is this substance transported<br />
around the body?<br />
c Give two ways this end-product<br />
is stored in the body.<br />
7 Explain<br />
a a stomach ulcer.<br />
b a possible cause of cirrhosis.<br />
8 Identify two waste products produced<br />
by cells in your body.<br />
9 Classify the following in the order in<br />
which fluid flows, starting with the first<br />
stage.<br />
bladder, kidney, urethra, ureter.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2<br />
1<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
10 Explain the main function of<br />
a red blood cells.<br />
b white blood cells.<br />
c platelets.<br />
d antigens.<br />
11 Assess whether a person with type B+<br />
blood could safely<br />
a donate blood to a person with<br />
type B− blood.<br />
b donate to a person with type O+<br />
blood.<br />
c receive blood from a donor with<br />
type O+ blood.<br />
12 Label the heart diagram below.<br />
13 Identify the type of blood tubes that<br />
a are one cell thick.<br />
b carry blood at low pressure.<br />
c have the thickest outer layer.<br />
14 Describe the role of the lungs in the<br />
circulatory system.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
3<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
15 Identify four structures which air<br />
passes through on its journey from the<br />
atmosphere to the alveoli in your lungs.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
16 The questions that follow refer to the<br />
diagram below of the human respiratory<br />
system.<br />
Identify the structure shown (use the<br />
numbers 1 to 8 to answer) that<br />
a prevents food from entering the<br />
trachea.<br />
b contracts and flattens when you<br />
breathe in.<br />
c filters, warms and humidifies air.<br />
d contracts to raise the rib cage<br />
when you breathe in.<br />
e is the site of gaseous exchange<br />
between the lungs and the<br />
bloodstream.<br />
f is a bronchus.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
6
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
17 Describe what happens to each of the<br />
following structures during expiration<br />
(breathing out).<br />
a Ribs (raised or lowered?).<br />
b Diaphragm (flattens or is domeshaped?)<br />
c Pressure in the chest cavity<br />
(increases or decreases?).<br />
d Intercostal muscles (contract or<br />
relax?).<br />
18 Identify five types of nutrients, and<br />
give an example of a food rich in each<br />
one.<br />
19 Identify the part of food or nutrient that<br />
a assists chemical reactions in the<br />
body.<br />
b repairs body tissue.<br />
c is required in small amounts for<br />
good health.<br />
d provides a rich source of energy.<br />
20 Classify the following in order from<br />
least required each day to most required<br />
each day for a healthy diet.<br />
fruits, indulgence items, milk and milk<br />
products, breads and cereals,<br />
vegetables, meat and alternatives.<br />
21 a Describe the process of aerobic<br />
respiration by writing a chemical<br />
equation.<br />
b State whether the reaction is<br />
exothermic or endothermic.<br />
c Define the process of aerobic<br />
respiration.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4: Body systems<br />
22 Describe the function of an enzyme. 2<br />
23 Identify<br />
a the two products of anaerobic<br />
respiration in yeast cells.<br />
b two industrial uses of the<br />
anaerobic respiration reaction in<br />
yeast cells.<br />
c the product of anaerobic<br />
respiration in human muscle<br />
cells.<br />
24 Recall two reasons why a person at rest<br />
would need energy.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 63 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (16 marks)<br />
1 A neutral object is one that contains<br />
A no charges.<br />
B an equal number of positive and negative charges.<br />
C only neutrons.<br />
D an excess of one type of charge.<br />
2 Which of the following will attract each other?<br />
A Two positive charges.<br />
B Two negative charges.<br />
C A neutral charge and a positive charge.<br />
D None of the above.<br />
3 A large device used to demonstrate the effects of static electricity is the<br />
A Electrostatic precipitator.<br />
B Vandenburg ioniser.<br />
C Van de Graaff generator.<br />
D Steffi Graf imitator.<br />
4 A dangerous static charge may build up on an aircraft due to<br />
A charges in the atmosphere being attracted to the aircraft’s metallic body.<br />
B chemical reactions involving aircraft exhaust gases.<br />
C movement of air against the outside of the aircraft.<br />
D electrical discharges from the instrument panel.<br />
5 Lightning occurs when<br />
A charge flows between clouds.<br />
B charge flows between a cloud and the ground.<br />
C charge flows from one part of a cloud to another part of the same cloud.<br />
D all of the above.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
6 Lines representing electric fields are<br />
A always evenly spaced.<br />
B always curved.<br />
C closer together near charges.<br />
D drawn with arrows showing the direction a negative charge would move if<br />
free to do so.<br />
7 Voltage is the<br />
A number of charges passing a point in a circuit every second.<br />
B measure of the energy given to or lost by moving charges.<br />
C number of charges in a cell.<br />
D time taken for a charge to move around a circuit once.<br />
8 Which circuit below shows how to measure voltage and current for a single<br />
globe in a circuit?<br />
9 A battery is<br />
A a group of cells.<br />
B another name for a single cell.<br />
C a collection of objects in a circuit.<br />
D one of the ends of a cell or the terminals of a power supply.<br />
10 Which of the following is a good conductor?<br />
A Plastic.<br />
B Copper.<br />
C Water.<br />
D Air.<br />
11 In an electric circuit, resistance is<br />
A a connection terminal that is difficult to unscrew or tighten.<br />
B something which does not allow any charge to flow.<br />
C a component connected the wrong way around.<br />
D something that restricts the flow of charge, transferring energy in the<br />
process.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
12 A photovoltaic cell is a<br />
A solar cell.<br />
B technical term for a light bulb.<br />
C high voltage source.<br />
D circuit symbol used to denote a voltage source such as a battery or cell.<br />
13 The circuit below contains<br />
A 3 globes in parallel.<br />
B 3 globes in series.<br />
C globe in series with 2 globes in parallel.<br />
D 2 globes in parallel with one globe in series.<br />
14 When a globe is removed from the circuit below<br />
A the other two will continue to glow just as brightly as before.<br />
B the other two will glow more brightly than before.<br />
C the other two will glow less brightly than before.<br />
D all globes will go out.<br />
15 What will happen to the current leaving the cell in the circuit below if point X is<br />
joined to point Y with a copper connecting wire?<br />
A It will stay the same.<br />
B It will be one third of its previous value.<br />
C It will initially triple and possibly ‘blow’ the globe.<br />
D No current will flow, but no globe will be damaged.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
16 What would happen if all the power points in part of your home were wired in<br />
series?<br />
A The voltage would be too great and damage anything plugged into one of<br />
them.<br />
B If more than one power point was being used, the voltage would be too<br />
small for devices to operate normally.<br />
C They would work normally as long as used sensibly (ie not overloaded) −<br />
power points are frequently wired in parallel with each other.<br />
D All power points would have to be ‘on’ in order for any to work.<br />
Section B − Written answers (47 marks)<br />
1 Describe the force between each of the<br />
following as A (attract), R (repel) or N<br />
(no force).<br />
a<br />
b<br />
c<br />
d<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
2 Explain the science behind a situation<br />
in which a person experiences a static<br />
electricity effect.<br />
3 Predict where you think the word<br />
‘photostat’ comes from.<br />
4 An electric charge produces an electric<br />
field. Explain what happens to the size<br />
of an electric field when<br />
a you move closer to the charge.<br />
b the size of the charge is<br />
increased.<br />
5 Identify several electric field lines by<br />
drawing them on the diagram below.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
2<br />
2<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
6 Explain why the metal foil strips at the<br />
lower end of the electroscope below<br />
repel each other, despite the rod not<br />
touching the device.<br />
7 Describe the direction of conventional<br />
current in the conductor below.<br />
8 Complete these sentences.<br />
a ________ is a measure of the rate<br />
at which charge flows, and is<br />
measured in ________.<br />
b ________ is a measure of the<br />
energy given to or lost by<br />
charges, and is measured in<br />
________.<br />
9 Identify the basic ‘ingredients’ in a cell<br />
or battery.<br />
10 a Define a conductor.<br />
b Define an insulator.<br />
c Identify two examples of a<br />
conductor.<br />
d Identify two examples of an<br />
insulator.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
2<br />
4<br />
2<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
11 Identify two examples of a resistance in<br />
a circuit.<br />
12 State the reading on each meter below.<br />
Each meter is either a voltmeter or<br />
ammeter and is connected correctly.<br />
Assume globes in the same circuit are<br />
identical.<br />
a<br />
b<br />
c<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
10
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 5: Electricity<br />
13 Consider the circuit below.<br />
Identify which other globes would go<br />
out if<br />
a globe B blows.<br />
b globe D blows.<br />
c globe A blows.<br />
d a copper wire is used to create a<br />
short circuit from X to Y (assume<br />
no globes blow).<br />
14 Consider the party light circuit below.<br />
a What would be the effect on the<br />
other globes in the circuit if one<br />
globe blew?<br />
b How could the circuit be<br />
redesigned so that if a globe<br />
blows, none of the others do?<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 77 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (18 marks)<br />
1 All living plants and animals in a particular region may be described as<br />
A a community.<br />
B an organism.<br />
C the environment.<br />
D an ecosystem.<br />
2 A biome refers to<br />
A a chemical pollutant.<br />
B an artificial environment such as a greenhouse.<br />
C areas having similar climatic conditions.<br />
D a biogeographical region.<br />
3 A habitat is<br />
A the most specific level possible for an organism’s ‘address’.<br />
B the broadest category for an organism’s address.<br />
C an organism’s typical behaviour.<br />
D a specific area such as a sand dune or tree.<br />
4 Physical characteristics or behaviours that help an organism live in a particular<br />
environment are called<br />
A attributes.<br />
B adaptations.<br />
C camouflage.<br />
D instincts.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
5 Which of the following is an abiotic factor that influences where an organism<br />
can live?<br />
A Humidity.<br />
B Predation.<br />
C Human intervention.<br />
D Competition from other organisms.<br />
6 Salinity is a measure of<br />
A the number of organisms in a particular region.<br />
B the acidity of soil.<br />
C the amount of water vapour in the air.<br />
D the salt content of water.<br />
7 The original source of all energy used by organisms is<br />
A plants.<br />
B water.<br />
C glucose.<br />
D the Sun.<br />
8 A secondary consumer is<br />
A a plant.<br />
B an animal that eats plants.<br />
C an animal that eats an animal that eats plants.<br />
D an omnivore.<br />
9 Each ‘link’ in a food chain is<br />
A a plant.<br />
B an animal.<br />
C an organism.<br />
D a carnivore.<br />
10 Communities with high biodiversity are more likely to survive environmental<br />
changes because they<br />
A contain more than one type of food source for the organisms within them.<br />
B have denser plant growth, which insulates the community from such<br />
changes.<br />
C are generally popular tourist attractions and are protected by law.<br />
D consist of large numbers of only a few species.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
11 The number of producers in a food chain is<br />
A less than the number of producers.<br />
B the same as the number of consumers.<br />
C greater than the number of consumers.<br />
D possibly any of the above, depending on the organisms involved.<br />
12 A decomposer is<br />
A an animal that eats another animal.<br />
B a plant that loses its leaves in winter.<br />
C an organism which breaks down organic matter so it is recycled.<br />
D an animal that uses sound as its main method of communication.<br />
13 The interaction between a remora (a type of sucker fish) and a shark to which it<br />
attaches is an example of commensalism because<br />
A the remora benefits, but the shark is harmed.<br />
B the remora benefits, but the shark is unaffected.<br />
C the remora is unaffected, but the shark is harmed.<br />
D both fish benefit from their relationship.<br />
14 The impact of humans on the ecosystem increased suddenly after the<br />
A environmental convolution.<br />
B mechanical inspiration.<br />
C climatic illusion.<br />
D industrial revolution.<br />
15 A pollutant is<br />
A a substance created by human activity that harms the environment.<br />
B a natural or artificial substance that makes the environment unhealthy for<br />
some organisms.<br />
C a gas such as sulfur dioxide that is able to reach the atmosphere.<br />
D something produced when a fossil fuel is burnt.<br />
16 The greenhouse effect occurs because gases released into the atmosphere cause<br />
A plants to grow too quickly and rob the atmosphere of vital gases.<br />
B heat to be trapped on the Earth.<br />
C the hole in the ozone layer to increase in size.<br />
D the atmosphere to become too thin and allow more energy to escape from<br />
the Earth.<br />
17 Which of the following are introduced species as far as <strong>Australia</strong> is concerned?<br />
A Rabbit.<br />
B Carp.<br />
C Pig.<br />
D All of the above.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
18 Frogs in <strong>Australia</strong> are considered to be environmental indicators because<br />
A they are the most common <strong>Australia</strong>n animal and so may be easily caught<br />
and studied.<br />
B they are at the bottom of the food chain.<br />
C they breathe through their skin and depend on water, so pollutants tend to<br />
affect them strongly.<br />
D they change colour in response to pollutants.<br />
Section B − Written answers (59 marks)<br />
1 Classify the following in order from<br />
smallest to largest:<br />
biome, microhabitat, biosphere, habitat,<br />
biogeographical region<br />
2 Match each of the following with one of<br />
the regions given in the previous<br />
question.<br />
a Just under the surface of some<br />
desert sand.<br />
b The part of our planet where life<br />
exists.<br />
c Grassland.<br />
d A tussock of grass.<br />
e <strong>Australia</strong>.<br />
3 Identify two examples of<br />
a organisms.<br />
b the non-living environment.<br />
4 Describe the characteristics of an<br />
organism which lives most of its life<br />
under the desert sand.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
3<br />
5<br />
4<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
5 Animal species suffer reductions in<br />
populations during or immediately after<br />
a fire. Identify how some escape the<br />
fire.<br />
6 Identify<br />
a an animal and describe two<br />
physical adaptations.<br />
b an animal (it may be the same<br />
one as above) and describe two<br />
behavioural adaptations.<br />
7 Describe how each of the following<br />
affects organisms. Give a specific<br />
examples.<br />
a Temperature.<br />
b Humidity.<br />
c Light availability.<br />
d Acidity.<br />
8 Clarify each of the following factors<br />
that affect where an organism can live.<br />
a Competition.<br />
b Dispersal.<br />
c Predation.<br />
d Human intervention.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
4<br />
4<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
9 Identify a biotic factor and an abiotic<br />
factor (in that order) that may affect a<br />
kookaburra.<br />
10 Classify each of the following as a<br />
herbivore, carnivore or omnivore.<br />
a Crocodile.<br />
b Deer.<br />
c Blue-tongue lizard.<br />
11 Draw arrows identifying the links<br />
between the following animals in a<br />
possible food web.<br />
snake, garden skink, kookaburra, fly<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
3<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
12 a Explain why a food web is more<br />
accurate than a food chain.<br />
b Use arrows to identify several<br />
connections in the food web<br />
below.<br />
13 Choose one of the terms listed to<br />
describe each of the following<br />
interactions.<br />
mutualism, competition, amensalism,<br />
herbivory, parasitism, predation<br />
a A small bird picks insects from a<br />
rhinoceros’s hide.<br />
b Wallabies using a particular route<br />
repeatedly eventually wear a trail<br />
in the bush.<br />
c A tick burrows into the skin of a<br />
stumpy tail lizard, causing minor<br />
skin irritation.<br />
d A koala eats the leaves on a<br />
branch of a gum tree.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
14 a Use the graph below to estimate<br />
what the human population was<br />
in the year 2000.<br />
b Predict the range of values that<br />
the population will lie between in<br />
the year 2020.<br />
15 Identify four types of waterway and<br />
ocean pollution.<br />
16 Describe the cause of two of the types<br />
of pollution in the previous question.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
4<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology<br />
17 Outline the problems caused by two<br />
different introduced species.<br />
18 Propose two ways of encouraging<br />
conservation of our native plants and<br />
animals.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
2<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 61 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (13 marks)<br />
1 The male part of a flower is made up of the<br />
A stigma, style and ovary.<br />
B petals and sepals.<br />
C anther and filament.<br />
D nectary and ovule.<br />
2 The openings in plant leaves that allow gases in and out and control water loss<br />
are called<br />
A the epidermis.<br />
B stomata.<br />
C mesophyll cells.<br />
D the cuticle.<br />
3 Which type of transport tube carries water and minerals from the roots in<br />
plants?<br />
A Chlorophyll.<br />
B Phloem.<br />
C Stoma.<br />
D Xylem.<br />
4 A vascular bundle is a<br />
A bunch of flowers or plant cuttings.<br />
B group of tubes within a plant.<br />
C group of guard cells on the underside of a leaf.<br />
D plant root system.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
5 In which of these plant leaf cells is the maximum rate of photosynthesis<br />
expected to occur?<br />
A Epidermal cells.<br />
B Palisade cells.<br />
C Xylem cells.<br />
D Mesophyll cells.<br />
6 If carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll are placed in a test tube in the sunlight<br />
A glucose and bubbles of oxygen will be produced immediately.<br />
B glucose and bubbles of oxygen will be produced, but only after a long<br />
period of time.<br />
C no reaction will occur because one reactant is missing.<br />
D no reaction will occur because necessary enzymes are missing.<br />
7 Photosynthesis may be considered a two-stage process. Which of the following<br />
occurs during stage 1?<br />
A Energy is released by chlorophyll molecules.<br />
B Energy is trapped by chlorophyll molecules.<br />
C Carbon dioxide is released.<br />
D Starch molecules are made.<br />
8 An experiment was conducted using the set-up shown below.<br />
The volume of gas collected in the test tube after 2 hours would not be affected<br />
by the<br />
A size of the test tube.<br />
B mass of plant used.<br />
C intensity of the light source.<br />
D temperature of the solution.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
9 At night the starch in leaves is reconverted to glucose. This is called<br />
A photosynthesis.<br />
B Benzyme release.<br />
C destarching.<br />
D respiration.<br />
10 The process of using oxygen to release energy from food is called<br />
A photosynthesis.<br />
B respiration.<br />
C breathing.<br />
D elimination.<br />
11 Respiration is a chemical reaction which<br />
A occurs only in the body cells of animals.<br />
B always has oxygen as a reactant.<br />
C involves a sequence of reactions.<br />
D is endothermic (absorbs energy).<br />
12 Which colour of light is not absorbed by chlorophyll?<br />
A Green.<br />
B Red.<br />
C Blue.<br />
D Orange.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
13 The graph below shows the amount of oxygen produced by a plant as light<br />
intensity was increased under two different sets of conditions.<br />
Which of the following would explain the difference between graphs X and Y?<br />
A Graph X was obtained with the plant in orange light, graph Y with the plant<br />
in red light.<br />
B Graph X was obtained with the plant at a higher temperature than for graph<br />
Y.<br />
C Graph X was obtained with the plant in a higher concentration of carbon<br />
dioxide than for graph Y.<br />
D Graph X was obtained using a larger mass of plant than for graph Y.<br />
Section B − Written answers (48 marks)<br />
1 Label the following parts of a plant<br />
stem cross-section using the terms<br />
below.<br />
xylem, phloem, cambium, vascular<br />
bundle<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
2 Identify two functions of<br />
a the roots.<br />
b the stem.<br />
3 Flowering plants may either be selfpollinated<br />
or cross-pollinated.<br />
a Define cross-pollination.<br />
b Propose two ways in which<br />
cross-pollination can be made to<br />
occur.<br />
4 A particular flower has its stigma placed<br />
higher than its anthers. Predict whether<br />
this flower could be self-pollinated.<br />
Explain your answer.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
4<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
5 The diagram below shows a section<br />
through a plant leaf.<br />
Identify which label (1 to 8) represents<br />
a an epidermal cell.<br />
b a palisade cell.<br />
c a xylem vessel.<br />
d a chloroplast.<br />
e a stoma cell.<br />
6 Propose explanations for<br />
a plants in the desert growing very<br />
slowly.<br />
b plants not being found in the<br />
ocean at depths greater than<br />
300 m.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
5<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
7 a Write a chemical equation for the<br />
process of photosynthesis.<br />
b Identify two other requirements<br />
(apart from the reactants) for<br />
photosynthesis to occur.<br />
c Define the reaction as either<br />
exothermic or endothermic.<br />
8 Identify the plant cell structures in<br />
which the following processes occur.<br />
a Stage 1 of respiration.<br />
b Stage 2 of respiration.<br />
c Photosynthesis.<br />
9 Identify three ways in which the<br />
glucose produced during photosynthesis<br />
may be used by a plant.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
3<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
10 The graph below shows the effect of<br />
light intensity on the rate of<br />
photosynthesis.<br />
Explain<br />
a why the rate increases in the first<br />
section (I) of the graph.<br />
b why the rate does not increase in<br />
the second section (II) of the<br />
graph.<br />
11 An experiment was conducted using the<br />
flasks shown below. All flasks<br />
contained water, were at the same<br />
temperature and were in sunlight.<br />
After two hours the carbon dioxide level<br />
in each flask was measured.<br />
a Identify the flask (A–D) in<br />
which the carbon dioxide level<br />
would be lowest after two hours.<br />
b Explain how you arrived at your<br />
choice in part (a).<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 7: Plant systems<br />
12 Which colour of light is strongly<br />
absorbed by<br />
a water?<br />
b green algae?<br />
c red algae?<br />
13 a Write a chemical word equation<br />
for the process of aerobic<br />
respiration.<br />
b Does this reaction absorb or<br />
release energy?<br />
c What does the word ‘aerobic’<br />
mean?<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
4
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
Name: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______<br />
Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column. Score: ___________ / 50 marks<br />
Section A − Multiple choice (15 marks)<br />
1 Astronomy is the study of the<br />
A Earth.<br />
B solar system.<br />
C Milky Way.<br />
D universe.<br />
2 A meteorite is<br />
A a small meteor.<br />
B a space rock that misses the Earth.<br />
C a small chunk of space rock that hits the Earth.<br />
D a piece of space junk originating from the Earth.<br />
3 Asteroids are also known as<br />
A megameteors.<br />
B minor planets.<br />
C planet killers.<br />
D dirty snowballs.<br />
4 Which type of non-planetary space rock orbits the Sun (ie is a member of the<br />
solar system)?<br />
A Asteroid.<br />
B Comet.<br />
C Meteor.<br />
D Shooting star.<br />
5 Which of the following contribute to the formation of a comet’s tails?<br />
A The Earth’s gravity.<br />
B The solar wind.<br />
C The size of the comet.<br />
D The Earth’s atmosphere.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
6 Most of the stars you see at night are<br />
A meteors.<br />
B galaxies.<br />
C planets.<br />
D suns.<br />
7 A light year is<br />
A the distance between the Earth and the Sun.<br />
B the distance light travels in a year.<br />
C the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy.<br />
D the time taken for a planet to revolve around its sun.<br />
8 Our nearest multiple star system is<br />
A Alpha Centauri.<br />
B Ceres.<br />
C the Southern Cross.<br />
D Orion.<br />
9 The dark circle shown on the celestial sphere below denotes a particular<br />
A altitude.<br />
B azimuth.<br />
C right ascension.<br />
D declination.<br />
10 An ecliptic is<br />
A the duration of an eclipse.<br />
B an object that blocks light from the Sun.<br />
C the path followed by the Sun on the celestial sphere.<br />
D a circular star chart used to locate stars during any time of year.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
11 Which of the following magnitudes indicates the faintest star?<br />
A 0<br />
B 0.5<br />
C 1.0<br />
D -0.6<br />
12 Which of the following is a major space-based telescope?<br />
A Bubble.<br />
B Hubble.<br />
C Keck.<br />
D Tech.<br />
13 The Milky Way is part of a larger group called<br />
A the big dipper.<br />
B the local group.<br />
C the Andromeda super galaxy.<br />
D the spiral arm.<br />
14 A geostationary orbit is one in which the satellite<br />
A moves in the same rotational direction and at the same speed as the Earth.<br />
B moves in a path at right angles to the rotation of the Earth.<br />
C moves in the same rotational direction as the Earth, but more quickly.<br />
D moves in the same rotational direction as the Earth, but more slowly.<br />
15 The transponder in a satellite like Intelsat 5<br />
A ‘cleans up’ and boosts a signal received by the satellite.<br />
B sends signals to a hand-held GPS receiver on the Earth.<br />
C measures temperature and pressure using special sensors.<br />
D analyses light reflected from the Earth’s surface.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
Section B − Written answers (35 marks)<br />
1 Examine the descriptions and match<br />
each one to the names in the list below.<br />
meteor, meteorite, asteroid, comet<br />
a Dirty snowball a few kilometres<br />
in diameter with long period<br />
orbits around the Sun.<br />
b Flaming meteoroid.<br />
c Large irregular-shaped object,<br />
potentially dangerous to the<br />
Earth.<br />
d Piece of space rock which<br />
occasionally hits the Earth<br />
usually without causing serious<br />
damage.<br />
2 a Identify the point from which the<br />
meteor shower shown below<br />
originates.<br />
b What is this point called?<br />
3 Identify<br />
a the location of the asteroid belt.<br />
b the approximate number of<br />
asteroids in the belt.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
4<br />
2<br />
2
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
4 Classify the space rocks as either<br />
comets, meteors or asteroids.<br />
a Ceres and Ida.<br />
b Hale−Bopp and<br />
Shoemaker−Levy 9.<br />
c The Orionids.<br />
5 List four things a giant space rock<br />
collision with the Earth might cause.<br />
6 Identify three constellations. 3<br />
7 The position of a star is marked on the<br />
celestial sphere below as a dot.<br />
Define<br />
a the right ascension of the star.<br />
b the declination of the star.<br />
Identify<br />
c on the sphere the position of a<br />
star whose coordinates may be<br />
described as RA 10 h, DEC 30°.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
3<br />
4<br />
3
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 TEST<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 8: Astronomy<br />
8 Define three different types of galaxy.<br />
Also sketch each type.<br />
9 Complete these sentences about parts of<br />
the Milky Way galaxy.<br />
a An ________ cluster contains a<br />
few hundred stars within the<br />
spiral arm of the galaxy.<br />
b A ________ cluster may be seen<br />
with the naked eye as a fuzzy<br />
star, but actually contains up to a<br />
million stars.<br />
10 Identify the types of waves detected by<br />
a an optical telescope.<br />
b a radio telescope.<br />
11 Recall<br />
a how high above the Earth’s<br />
surface a satellite in geostationary<br />
orbit is.<br />
b what it means when a satellite is<br />
in an asynchronous orbit.<br />
c which kind of orbit observation<br />
satellites are usually placed in.<br />
d which kind of orbit<br />
communication satellites are<br />
usually placed in.<br />
© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.<br />
This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.<br />
6<br />
2<br />
2<br />
4