An interactive flower image recognition system
An interactive flower image recognition system
An interactive flower image recognition system
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
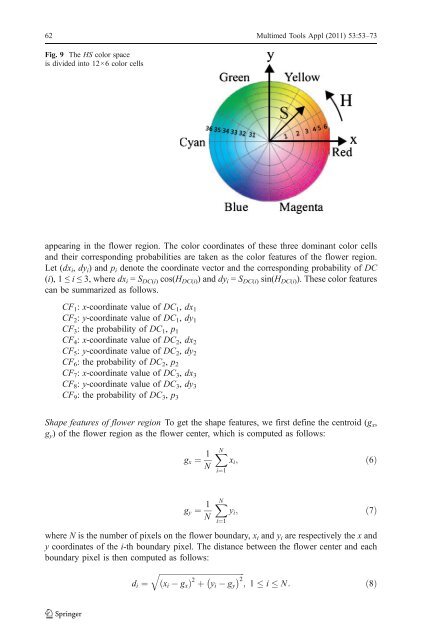
62 Multimed Tools Appl (2011) 53:53–73Fig. 9 The HS color spaceis divided into 12×6 color cellsappearing in the <strong>flower</strong> region. The color coordinates of these three dominant color cellsand their corresponding probabilities are taken as the color features of the <strong>flower</strong> region.Let (dx i , dy i ) and p i denote the coordinate vector and the corresponding probability of DC(i), 1 ≤ i ≤ 3, where dx i = S DC(i) cos(H DC(i) ) and dy i = S DC(i) sin(H DC(i) ). These color featurescan be summarized as follows.CF 1 : x-coordinate value of DC 1 , dx 1CF 2 : y-coordinate value of DC 1 , dy 1CF 3 : the probability of DC 1 , p 1CF 4 : x-coordinate value of DC 2 , dx 2CF 5 : y-coordinate value of DC 2 , dy 2CF 6 : the probability of DC 2 , p 2CF 7 : x-coordinate value of DC 3 , dx 3CF 8 : y-coordinate value of DC 3 , dy 3CF 9 : the probability of DC 3 , p 3Shape features of <strong>flower</strong> region To get the shape features, we first define the centroid (g x ,g y ) of the <strong>flower</strong> region as the <strong>flower</strong> center, which is computed as follows:g x ¼ 1 NX Ni¼1x i ;ð6Þg y ¼ 1 Nwhere N is the number of pixels on the <strong>flower</strong> boundary, x i and y i are respectively the x andy coordinates of the i-th boundary pixel. The distance between the <strong>flower</strong> center and eachboundary pixel is then computed as follows:qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffid i ¼ ð Þ 2 2þ y i g y ; 1 i N: ð8Þx ig xX Ni¼1y i ;ð7Þ