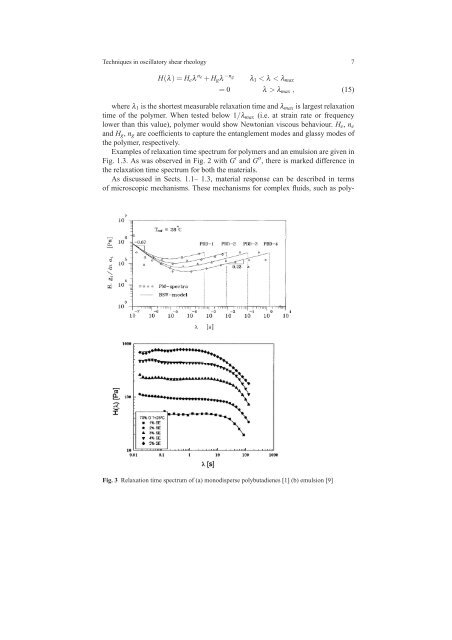
6 Abhijit P. Deshpandenation <strong>of</strong> Maxwell models (or generalized Maxwell model) with each mode correspond<strong>in</strong>gto a relaxation time. The strength <strong>of</strong> each mode may also be different. Therelaxation modulus for Maxwell model is given by,(G(t) = Gexp − t ), (8)λFor material response with several Maxwell modes, the relaxation modulus is,G(t) = G e + ∑G i exp(− t ), (9)iλ iwhere G e , equilibrium modulus is zero for fluidlike materials, and G i , elasticmodulus and λ i are elastic modulus and relaxation time for i th mode. Based on theabove equation, we can def<strong>in</strong>e a relaxation time spectrum, H(λ) as,H(λ) = ∑G i δ (λ − λ i ) . (10)iTherefore, relaxation modulus can be written <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> the relaxation time spectrumas,(G(t) = G e + ∑G i δ (λ − λ i )exp − t ). (11)iλSimilarly, we can def<strong>in</strong>e the relaxation modulus based on the cont<strong>in</strong>uous relaxationtime spectrum as,∫ H(λ)G(t) = G e +(−λ exp t )dλ . (12)λThe storage and loss moduli can be written <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> relaxation time spectrumas follows,G ′ = ∑iG i ω 2 λ 2i1+ω 2 λ 2i, G” = ∑iAlternately, <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>uous spectrum,∫ H(λ)ωG ′ 2 ∫λ=1+ω 2 λ 2 dλ , G” =G i ωλ i1+ω 2 λi2(13)H(λ)ω1+ω 2 dλ (14)λ 2Based on these equation, relaxation time spectrum can be estimated from datasuch as <strong>in</strong> Fig. 2 and the mechanisms <strong>of</strong> material behaviour can also be understood<strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong> the distribution <strong>of</strong> relaxation times.An example <strong>of</strong> discrete relaxation time spectrum (referred to as PM spectrum <strong>in</strong>the figure) evaluated from <strong>oscillatory</strong> <strong>shear</strong> data is shown <strong>in</strong> Fig. 3. These data arefor different molecular weights <strong>of</strong> monodisperse polybutadiene samples. Analyticalexpressions for relaxation time spectrum have also been proposed and one exampleis (BSW spectrum <strong>in</strong> the figure) [1],
<strong>Techniques</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>oscillatory</strong> <strong>shear</strong> <strong>rheology</strong> 7H(λ) = H e λ n e+ H g λ −n gλ 1 < λ < λ max= 0 λ > λ max , (15)where λ 1 is the shortest measurable relaxation time and λ max is largest relaxationtime <strong>of</strong> the polymer. When tested below 1/λ max (i.e. at stra<strong>in</strong> rate or frequencylower than this value), polymer would show Newtonian viscous behaviour. H e , n eand H g , n g are coefficients to capture the entanglement modes and glassy modes <strong>of</strong>the polymer, respectively.Examples <strong>of</strong> relaxation time spectrum for polymers and an emulsion are given <strong>in</strong>Fig. 1.3. As was observed <strong>in</strong> Fig. 2 with G ′ and G ′′ , there is marked difference <strong>in</strong>the relaxation time spectrum for both the materials.As discussed <strong>in</strong> Sects. 1.1– 1.3, material response can be described <strong>in</strong> terms<strong>of</strong> microscopic mechanisms. These mechanisms for complex fluids, such as poly-Fig. 3 Relaxation time spectrum <strong>of</strong> (a) monodisperse polybutadienes [1] (b) emulsion [9]