A NEW METHOD OF JOB EVALUATION - ResearchGate
A NEW METHOD OF JOB EVALUATION - ResearchGate
A NEW METHOD OF JOB EVALUATION - ResearchGate
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
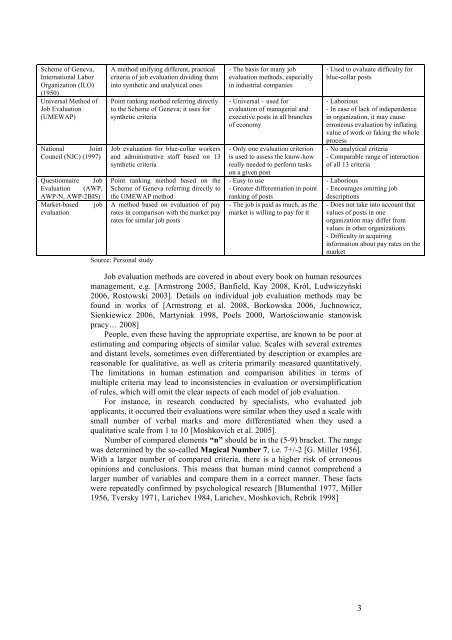
Scheme of Geneva,International LaborOrganization (ILO)(1950)Universal Method ofJob Evaluation(UMEWAP)National JointCouncil (NJC) (1997)Questionnaire JobEvaluation (AWP,AWP-N, AWP-2BIS)Market-based jobevaluationA method unifying different, practicalcriteria of job evaluation dividing theminto synthetic and analytical onesPoint ranking method referring directlyto the Scheme of Geneva; it uses forsynthetic criteriaJob evaluation for blue-collar workersand administrative staff based on 13synthetic criteriaPoint ranking method based on theScheme of Geneva referring directly tothe UMEWAP methodA method based on evaluation of payrates in comparison with the market payrates for similar job postsSource: Personal study- The basis for many jobevaluation methods, especiallyin industrial companies- Universal – used forevaluation of managerial andexecutive posts in all branchesof economy- Only one evaluation criterionis used to assess the know-howreally needed to perform taskson a given post- Easy to use- Greater differentiation in pointranking of posts- The job is paid as much, as themarket is willing to pay for it- Used to evaluate difficulty forblue-collar posts- Laborious- In case of lack of independencein organization, it may causeerroneous evaluation by inflatingvalue of work or faking the wholeprocess- No analytical criteria- Comparable range of interactionof all 13 criteria- Laborious- Encourages omitting jobdescriptions- Does not take into account thatvalues of posts in oneorganization may differ fromvalues in other organizations- Difficulty in acquiringinformation about pay rates on themarketJob evaluation methods are covered in about every book on human resourcesmanagement, e.g. [Armstrong 2005, Banfield, Kay 2008, Król, Ludwiczyński2006, Rostowski 2003]. Details on individual job evaluation methods may befound in works of [Armstrong et al. 2008, Borkowska 2006, Juchnowicz,Sienkiewicz 2006, Martyniak 1998, Poels 2000, Wartościowanie stanowiskpracy… 2008]People, even these having the appropriate expertise, are known to be poor atestimating and comparing objects of similar value. Scales with several extremesand distant levels, sometimes even differentiated by description or examples arereasonable for qualitative, as well as criteria primarily measured quantitatively.The limitations in human estimation and comparison abilities in terms ofmultiple criteria may lead to inconsistencies in evaluation or oversimplificationof rules, which will omit the clear aspects of each model of job evaluation.For instance, in research conducted by specialists, who evaluated jobapplicants, it occurred their evaluations were similar when they used a scale withsmall number of verbal marks and more differentiated when they used aqualitative scale from 1 to 10 [Moshkovich et al. 2005].Number of compared elements “n” should be in the (5-9) bracket. The rangewas determined by the so-called Magical Number 7, i.e. 7+/-2 [G. Miller 1956].With a larger number of compared criteria, there is a higher risk of erroneousopinions and conclusions. This means that human mind cannot comprehend alarger number of variables and compare them in a correct manner. These factswere repeatedly confirmed by psychological research [Blumenthal 1977, Miller1956, Tversky 1971, Larichev 1984, Larichev, Moshkovich, Rebrik 1998]3