Solutions to homework 2
Solutions to homework 2
Solutions to homework 2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
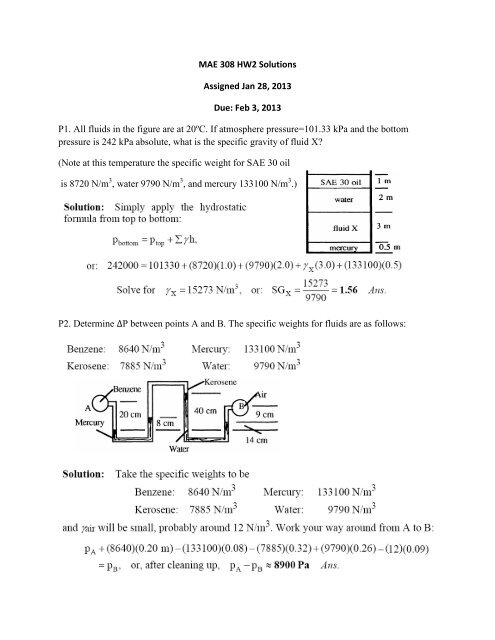
MAE 308 HW2 <strong>Solutions</strong>Assigned Jan 28, 2013Due: Feb 3, 2013P1. All fluids in the figure are at 20ºC. If atmosphere pressure=101.33 kPa and the bot<strong>to</strong>mpressure is 242 kPa absolute, what is the specific gravity of fluid X?(Note at this temperature the specific weight for SAE 30 oilis 8720 N/m 3 , water 9790 N/m 3 , and mercury 133100 N/m 3 .)P2. Determine ΔP between points A and B. The specific weights for fluids are as follows:
P3. In the attached figure, both the tank and the slanted tube are open <strong>to</strong> the atmosphere. IfL=2.13m, what is the angle of tilt ϕ of the tube.P4. Gate AB in the figure is 1.2 m long and 0.8 m in<strong>to</strong> the paper. Neglecting atmosphericpressure effects, compute the force F on the gate and its center of pressure position X.<strong>Solutions</strong>: The centroidal depth of the gate is
P5. Gate ABC in the figure has a fixed hinge at B and is 2 m wide in<strong>to</strong> the paper. If the waterlevel is high enough, the gate will open. Compute the depth h for which this happens.P6. A block of wood (SG=0.6) floats in fluid X in the figure such that 75% of its volume issubmerged in fluid X. Estimate the gage pressure of the air in the tank.
P7. The tank of liquid in the figure accelerates <strong>to</strong> the right with the fluid in rigid-body motion.(a) Compute a x in m/s2; (b) Why doesn’t the solution <strong>to</strong> part (a) depend on fluid density? (c)Compute gage pressure at point A if the fluid density is 1260 kg/m 3 .(c) For glycerol, the density is 1260 kg/m 3 . There are two ways <strong>to</strong> calculate P A :