Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
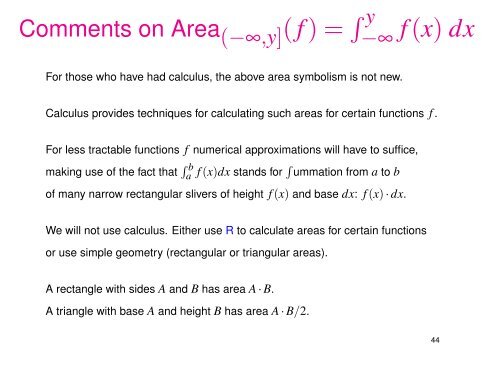
Comments on Area (−∞,y] ( f ) = R y−∞ f (x) dxFor those who have had calculus, the above area symbolism is not new.Calculus provides techniques for calculating such areas for certain functions f .For less tractable functions f numerical approximations will have to suffice,making use of the fact that R ba f (x)dx stands for R ummation from a to bof many narrow rectangular slivers of height f (x) and base dx: f (x) · dx.We will not use calculus. Either use R to calculate areas for certain functionsor use simple geometry (rectangular or triangular areas).A rectangle with sides A and B has area A · B.A triangle with base A and height B has area A · B/2.44