Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
Discrete & Continuous Random Variables - Statistics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
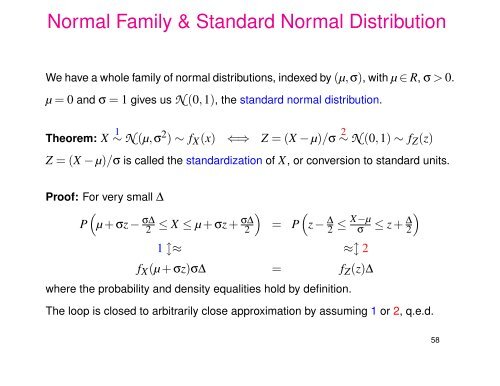
Normal Family & Standard Normal DistributionWe have a whole family of normal distributions, indexed by (µ,σ), with µ ∈ R, σ > 0.µ = 0 and σ = 1 gives us N (0,1), the standard normal distribution.Theorem: X 1 ∼ N (µ,σ 2 ) ∼ f X (x) ⇐⇒ Z = (X − µ)/σ 2 ∼ N (0,1) ∼ f Z (z)Z = (X − µ)/σ is called the standardization of X, or conversion to standard units.Proof: For very small ∆()P µ + σz − σ∆ 2 ≤ X ≤ µ + σz + σ∆ 2(= P z − ∆ 2 ≤ X−µ )σ ≤ z + ∆ 21 ↕≈ ≈↕ 2f X (µ + σz)σ∆ = f Z (z)∆where the probability and density equalities hold by definition.The loop is closed to arbitrarily close approximation by assuming 1 or 2, q.e.d.58