A Tour of the Cell
A Tour of the Cell
A Tour of the Cell
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
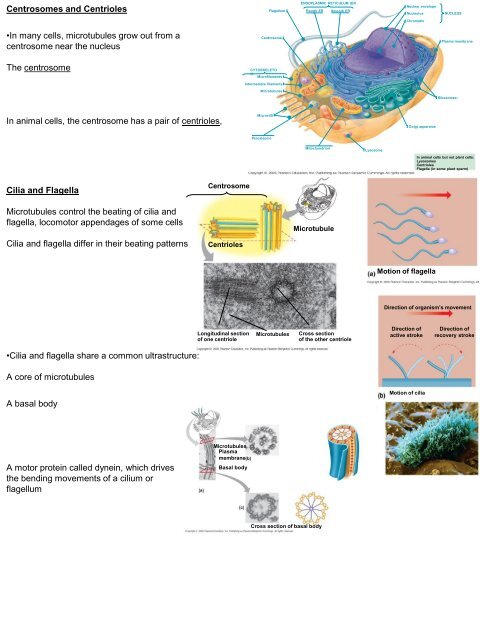
Centrosomes and CentriolesFlagellumENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ERRough ERSmooth ERNuclear envelopeNucleolusNUCLEUSChromatin•In many cells, microtubules grow out from acentrosome near <strong>the</strong> nucleusCentrosomePlasma membraneThe centrosomeCYTOSKELETONMicr<strong>of</strong>ilamentsIntermediate filamentsMicrotubulesRibosomes:In animal cells, <strong>the</strong> centrosome has a pair <strong>of</strong> centrioles,MicrovilliGolgi apparatusPeroxisomeMitochondrionLysosomeIn animal cells but not plant cells:LysosomesCentriolesFlagella (in some plant sperm)Cilia and FlagellaCentrosomeMicrotubules control <strong>the</strong> beating <strong>of</strong> cilia andflagella, locomotor appendages <strong>of</strong> some cellsCilia and flagella differ in <strong>the</strong>ir beating patternsCentriolesMicrotubuleMotion <strong>of</strong> flagellaDirection <strong>of</strong> organism’s movementLongitudinal section<strong>of</strong> one centrioleMicrotubulesCross section<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r centrioleDirection <strong>of</strong>active strokeDirection <strong>of</strong>recovery stroke•Cilia and flagella share a common ultrastructure:A core <strong>of</strong> microtubulesA basal bodyMotion <strong>of</strong> ciliaA motor protein called dynein, which drives<strong>the</strong> bending movements <strong>of</strong> a cilium orflagellumMicrotubulesPlasmamembraneBasal bodyCross section <strong>of</strong> basal body