You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
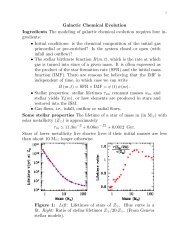
1<strong>Magnetism</strong>1.) Two 853.9 m long wires run parallel to each other separated by 30.45 mm and with a force between them of0.0286 N. If one of them carries a currents of 1.978 A, what is the current <strong>in</strong> the other?2.)A wire hav<strong>in</strong>g a mass per unit length of 0.500 g/cm carries a 2.00 A current horizontally to the south.What are the direction and magnitude of the m<strong>in</strong>imum magnetic field needed to lift this wire vertically upward?3.)A rectangular coil (0.2m x 0.8 m) has <strong>20</strong>0 turns of wire and is <strong>in</strong> a uniform magnetic field of 0.3 T. If theorientation of the coil is varied through all possible positions, the maximum torque on the coil by magnetic forces is0.08 Nm. What is the current <strong>in</strong> the coil?4.)A cosmic-ray proton <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>terstellar space has k<strong>in</strong>etic energy of 1.6x10 −12 J and executes a circular orbithav<strong>in</strong>g a radius equal to that of Mercury’s orbit around the sun (5.8x10 10 m). What is the magnetic field <strong>in</strong> thatregion?5.)Two long, parallel conductors carry currents I1 = 3.00 A and I2 = 3.00 A, both directed <strong>in</strong>to the page <strong>in</strong>the figure below. Determ<strong>in</strong>e the magnitude and direction of the resultant magnetic field at P.6.)A solenoid 2.50 cm <strong>in</strong> diameter and 30.0 cm long has 300 turns and carries 12.0 A. Determ<strong>in</strong>e the magneticfield <strong>in</strong>side the solenoid.7.) A long, tightly wound solenoidal coil of radius R = 0.30 m has its axis along the z direction and currentwhich flows counter-clockwise <strong>in</strong> the draw<strong>in</strong>g below, result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.55 T. a)Whatis the direction of the field B ? b.) An electron moves with velocity v = 5.010 6 m/s <strong>in</strong> the y direction <strong>in</strong> side thesolenoid. Determ<strong>in</strong>e the force (magnitude and direction) on the electron at this po<strong>in</strong>t.8.)A very long, straight wire carries a current I=7.5 A directed upward . a)Use Amperes Law to f<strong>in</strong>d the directionand magnitude of the magnetic field at a perpendicular distance 25 am from the wire. b)A second wire isplaced parallel to the first wire at P which carries a current I=3 A directed downward. Determ<strong>in</strong>e the direction ofthe force on the second wire and calculate the force per unit length.9.) A circular wire loop of diameter d = 10.0 cm and resistance 2.0 ohm is placed <strong>in</strong> a region with a uniformmagnetic field po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>side the plane of the paper. F<strong>in</strong>d the direction and magnitude of any current <strong>in</strong> theloop if B = 0.32 T and is constant.10.)An electron has a velocity of 6.0x10 6 m/s <strong>in</strong> the positive x direction. The magnetic field at the po<strong>in</strong>t of<strong>in</strong>terest has components, Bx= 3.0 T, By = 1.5 T. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron at thispo<strong>in</strong>t ? (mass of electron = 9.1x10 −31 kg)11.)Two long straight parallel wires separated by a distance of <strong>20</strong> cm carry currents of 30 A and 40 A <strong>in</strong> oppositedirections. What is the magnitude of the result<strong>in</strong>g magnetic field at a po<strong>in</strong>t that is 15 cm from the wire carry<strong>in</strong>g the30 A current and 25 cm from the other wire? (no typos here - the po<strong>in</strong>t of <strong>in</strong>terest is NOT <strong>in</strong> the plane of the two wires)
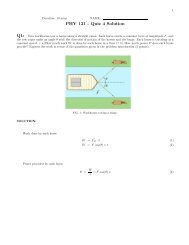
212.)What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a charged particle (Q = 5.0 microC) mov<strong>in</strong>g with aspeed of 80 km/s <strong>in</strong> the positive x direction at a po<strong>in</strong>t where Bx = 5.0 T, By = -4.0 T, and Bz = 3.0 T ?13.)A uniform magnetic field B, with magnitude B = 1.2x10 −3 T, po<strong>in</strong>ts vertically upward throughout thevolume of a laboratory chamber. A proton with a velocity v = 3.2x10 7 m/s enters the laboratory mov<strong>in</strong>g horizontallyfrom south to north. F<strong>in</strong>d (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of magnetic force on the proton.14.)A proton moves <strong>in</strong> a uniform magnetic field B with a speed of 10 7 m/s and experiences an accelerationof 2x10 13 m/s2 <strong>in</strong> the +X-direction when its velocity is <strong>in</strong> the +Z-direction. Determ<strong>in</strong>e the magnitude and directionof the magnetic field for which the magnitude of the field is a m<strong>in</strong>imum.15.)An electron moves with a speed v = 2x10 7 m/s through a magnetic field of B = 0.080 N-s/C-m. (a)What are the greatest and smallest forces the magnetic field may exert on the electron? (b) If the acceleration ofthe electron is 1.41x10 1 7 m/s2, what angle does the velocity make with the magnetic field? The electron has a massm = 9.1x10 −31 kg and its charge e = 1.6x10 −19 .16.)A particle of charge q = 10 −6 C moves to the right with velocity v = 10 3 m/s <strong>in</strong> a magnetic field B = 2N-s/C-m which makes an angle of 30 with v. F<strong>in</strong>d the magnitude of the force on the charged particle.