2.2. The SIESTA method 47that the fundamental band gap (E g ) of a semiconductor or insulator is only approximatelypredicted using the LDA or GGA exchange-correlation functionals. One of the reasons for thatin the KS approach the gap, E KS , is defined as the difference between the lowest unoccupied(ϵ lumoKS ) and highest occupied (ϵ homoKS ) eigenvalues which differs from the definition of the gapE g . The latter is defined as E g = I − A, where I is the ionisation potential and A the electronaffinity. The relation between E g and E KS is given by E g = E KS + δ xc , where δ xc is thederivative discontinuity, i.e., a finite kink that the exchange-correlation potential exhibits as theparticle number crosses the integer number of particles N in the system [93]. In some casesδ xc can be small but numerical investigations show that it is usually not negligible [94–96].Therefore, this can limit the prediction of the fundamental gap E g from the eigenvalues ϵ KSeven if the exact energy functional would be known.2.2 The SIESTA methodHere we briefly mention some important aspects of the SIESTA method that were used in thisthesis. This code was chosen due to its widespread use and efficiency. A detailed descriptionof the SIESTA code can be found in Ref. [97]. SIESTA is an ab initio pseudopotential methodwhich employs a linear combination of atomic orbitals as a basis set. Due to the use of atomicorbitals as a basis set, it seems to be similar to a tight binding technique [98] but in fact itstrongly differs: the single-particle Hamiltonian is obtained by projecting the KS-DFT Hamiltonian(Eq. 2.10) onto this basis set of atomic orbitals; thus, it is not a set of fitting parameterslike in empirical tight-binding methods. Many approximations necessary to solve the oneparticleHamiltonian in SIESTA as for instance the pseudopotential approach, the treatment ofexchange and correlation explicitly by means of approximate functionals (e.g. LDA, GGA)and the already cited Born-Oppenheimer approximation are also commom to other ab initiomethods. Apart from that, the method is also characterised by a set of parameter that controlsthe accuracy of the self-consistent KS solution. Just to cite some of them: the size (number ofatomic basis orbitals) and range (radius of the basis orbitals) of the basis set, the fineness ofreal-space integration grid, the non-linear core correction to treat exchange-correlation interactionbetween core and valence states, etc.2.2.1 Periodic boundary conditionIn order to solve the KS differential equations one needs to specify the boundary conditions(BCs) for the problem. In the SIESTA method one uses periodic BCs within the supercellapproach [89]. This is the natural choice for bulk crystals, which in reality are periodic. Thesupercell approach can also be applied to non-periodic structures if a sufficient amount of vacuumis included in the supercell, to effectively separate the objects. In this way molecules,wires, and surfaces can be studied by including vacuum in three, two, or one directions, respectively.Since the supercell is periodic, Bloch’s theorem applies and the wavefunctions can bewritten asψ nk (r) = u nk (r)e ik·r (2.14)
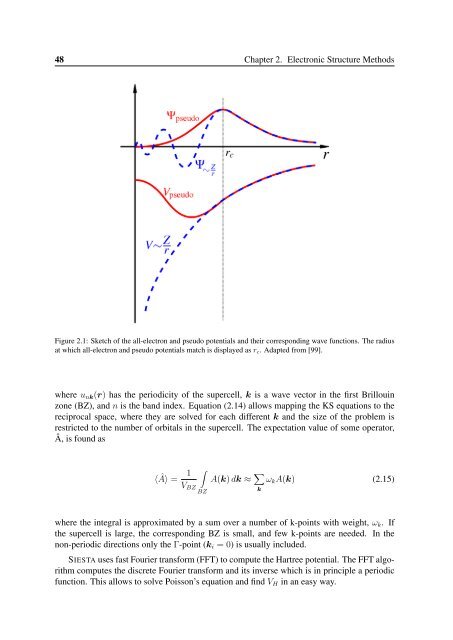
48 Chapter 2. Electronic Structure MethodsFigure 2.1: Sketch of the all-electron and pseudo potentials and their corresponding wave functions. The radiusat which all-electron and pseudo potentials match is displayed as r c . Adapted from [99].where u nk (r) has the periodicity of the supercell, k is a wave vector in the first Brillouinzone (BZ), and n is the band index. Equation (2.14) allows mapping the KS equations to thereciprocal space, where they are solved for each different k and the size of the problem isrestricted to the number of orbitals in the supercell. The expectation value of some operator,Â, is found as⟨Â⟩ = 1V BZ∫BZA(k) dk ≈ ∑ kω k A(k) (2.15)where the integral is approximated by a sum over a number of k-points with weight, ω k . Ifthe supercell is large, the corresponding BZ is small, and few k-points are needed. In thenon-periodic directions only the Γ-point (k i = 0) is usually included.SIESTA uses fast Fourier transform (FFT) to compute the Hartree potential. The FFT algorithmcomputes the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse which is in principle a periodicfunction. This allows to solve Poisson’s equation and find V H in an easy way.