II. ScvO2 as a helpful parameter during the weaning phase
II. ScvO2 as a helpful parameter during the weaning phase
II. ScvO2 as a helpful parameter during the weaning phase
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
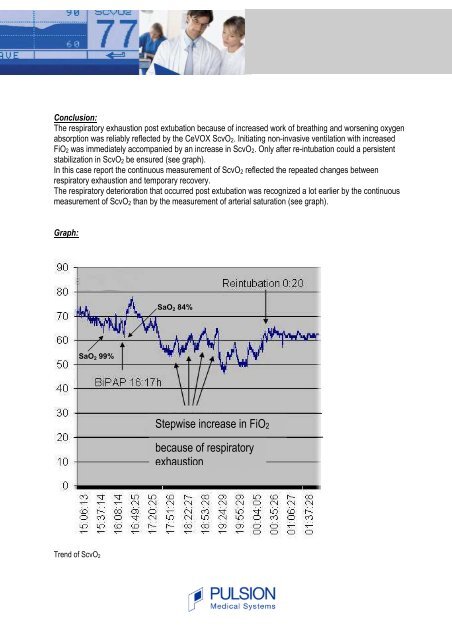
Conclusion:<br />
The respiratory exhaustion post extubation because of incre<strong>as</strong>ed work of breathing and worsening oxygen<br />
absorption w<strong>as</strong> reliably reflected by <strong>the</strong> CeVOX <strong>ScvO2</strong>. Initiating non-inv<strong>as</strong>ive ventilation with incre<strong>as</strong>ed<br />
FiO2 w<strong>as</strong> immediately accompanied by an incre<strong>as</strong>e in <strong>ScvO2</strong>. Only after re-intubation could a persistent<br />
stabilization in <strong>ScvO2</strong> be ensured (see graph).<br />
In this c<strong>as</strong>e report <strong>the</strong> continuous me<strong>as</strong>urement of <strong>ScvO2</strong> reflected <strong>the</strong> repeated changes between<br />
respiratory exhaustion and temporary recovery.<br />
The respiratory deterioration that occurred post extubation w<strong>as</strong> recognized a lot earlier by <strong>the</strong> continuous<br />
me<strong>as</strong>urement of <strong>ScvO2</strong> than by <strong>the</strong> me<strong>as</strong>urement of arterial saturation (see graph).<br />
Graph:<br />
SaO2 99%<br />
Trend of <strong>ScvO2</strong><br />
SaO2 84%<br />
Stepwise incre<strong>as</strong>e in FiO2<br />
because of respiratory<br />
exhaustion