Scale transitions in solid mechanics based on computational ... - Cism
Scale transitions in solid mechanics based on computational ... - Cism
Scale transitions in solid mechanics based on computational ... - Cism
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
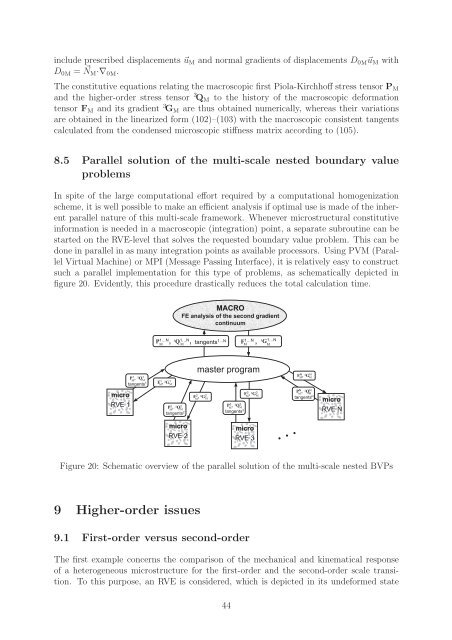
<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>clude prescribed displacements ⃗u M and normal gradients of displacements D 0M ⃗u M withD 0M = N ⃗ M·∇ 0M .The c<strong>on</strong>stitutive equati<strong>on</strong>s relat<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>g the macroscopic first Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor P Mand the higher-order stress tensor 3 Q M to the history of the macroscopic deformati<strong>on</strong>tensor F M and its gradient 3 G M are thus obta<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>ed numerically, whereas their variati<strong>on</strong>sare obta<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>ed <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g> the l<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>earized form (102)–(103) with the macroscopic c<strong>on</strong>sistent tangentscalculated from the c<strong>on</strong>densed microscopic stiffness matrix accord<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>g to (105).8.5 Parallel soluti<strong>on</strong> of the multi-scale nested boundary valueproblemsIn spite of the large computati<strong>on</strong>al effort required by a computati<strong>on</strong>al homogenizati<strong>on</strong>scheme, it is well possible to make an efficient analysis if optimal use is made of the <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>herentparallel nature of this multi-scale framework. Whenever microstructural c<strong>on</strong>stitutive<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>formati<strong>on</strong> is needed <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g> a macroscopic (<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>tegrati<strong>on</strong>) po<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>t, a separate subrout<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>e can bestarted <strong>on</strong> the RVE-level that solves the requested boundary value problem. This can bed<strong>on</strong>e <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g> parallel <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g> as many <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>tegrati<strong>on</strong> po<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>ts as available processors. Us<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>g PVM (ParallelVirtual Mach<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>e) or MPI (Message Pass<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>g Interface), it is relatively easy to c<strong>on</strong>structsuch a parallel implementati<strong>on</strong> for this type of problems, as schematically depicted <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>figure 20. Evidently, this procedure drastically reduces the total calculati<strong>on</strong> time.Figure 20: Schematic overview of the parallel soluti<strong>on</strong> of the multi-scale nested BVPs9 Higher-order issues9.1 First-order versus sec<strong>on</strong>d-orderThe first example c<strong>on</strong>cerns the comparis<strong>on</strong> of the mechanical and k<str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g>ematical resp<strong>on</strong>seof a heterogeneous microstructure for the first-order and the sec<strong>on</strong>d-order scale transiti<strong>on</strong>.To this purpose, an RVE is c<strong>on</strong>sidered, which is depicted <str<strong>on</strong>g>in</str<strong>on</strong>g> its undeformed state44