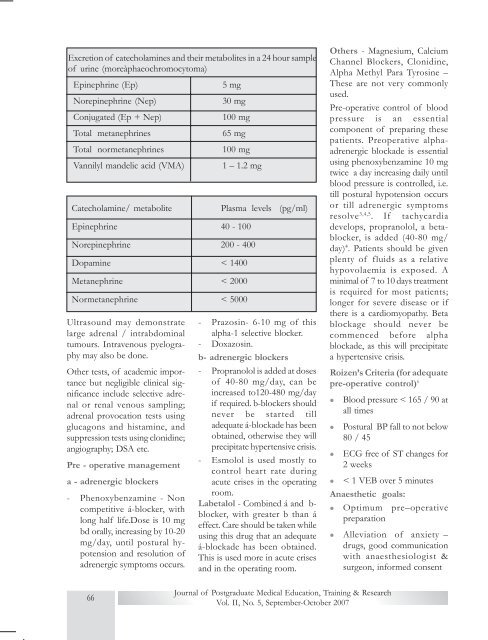
<strong>Ex</strong>cretion of catecholamines and their metabolites in a 24 hour sampleof urine (moreàphaeochromocytoma)Epinephrine (Ep)5 mgNorepinephrine (Nep)30 mgConjugated (Ep + Nep)100 mgTotal metanephrines65 mgTotal normetanephrines100 mgVannilyl mandelic acid (VMA)1 – 1.2 mgCatecholamine/ metaboliteEpinephrine 40 - 100Norepinephrine 200 - 400Dopamine < 1400Metanephrine < 2000Normetanephrine < 5000Ultrasound may demonstratelarge adrenal / intrabdominaltumours. Intravenous pyelographymay also be done.Other tests, of academic importancebut negligible clinical significanceinclude selective adrenalor renal venous sampling;adrenal provocation tests usingglucagons and histamine, andsuppression tests using clonidine;angiography; DSA etc.Pre - operative managementa - adrenergic blockers- Phenoxybenzamine - Noncompetitive á-blocker, withlong half life.Dose is 10 mgbd orally, increasing by 10-20mg/day, until postural hypotensionand resolution ofadrenergic symptoms occurs.Plasma levels (pg/ml)- Prazosin- 6-10 mg of thisalpha-1 selective blocker.- Doxazosin.b- adrenergic blockers- Propranolol is added at dosesof 40-80 mg/day, can beincreased to120-480 mg/dayif required. b-blockers shouldnever be started tilladequate á-blockade has beenobtained, otherwise they willprecipitate hypertensive crisis.- Esmolol is used mostly tocontrol heart rate duringacute crises in the operatingroom.Labetalol - Combined á and b-blocker, with greater b than áeffect. Care should be taken whileusing this drug that an adequateá-blockade has been obtained.This is used more in acute crisesand in the operating room.Others - Magnesium, CalciumChannel Blockers, Clonidine,Alpha Methyl Para Tyrosine –These are not very commonlyused.Pre-operative control of bloodpressure is an essentialcomponent of preparing thesepatients. Preoperative alphaadrenergicblockade is essentialusing phenoxybenzamine 10 mgtwice a day increasing daily untilblood pressure is controlled, i.e.till postural hypotension occursor till adrenergic symptomsresolve 3,4,5 . If tachycardiadevelops, propranolol, a betablocker,is added (40-80 mg/day) 4 . Patients should be givenplenty of fluids as a relativehypovolaemia is exposed. Aminimal of 7 to 10 days treatmentis required for most patients;longer for severe disease or ifthere is a cardiomyopathy. Betablockage should never becommenced before alphablockade, as this will precipitatea hypertensive crisis.Roizen’s Criteria (for adequatepre-operative control) 6lllBlood pressure < 165 / 90 atall timesPostural BP fall to not below80 / 45ECG free of ST changes for2 weeksl < 1 VEB over 5 minutesAnaesthetic goals:l Optimum pre–operativepreparationl Alleviation of anxiety –drugs, good communicationwith anaesthesiologist &surgeon, informed consent66Journal of Postgraduate Medical Education, Training & ResearchVol. II, No. 5, September-October 2007
l Gentle induction ofanaesthesial Reduction of sympatheticstimulationl Avoidance of hypoxia,hypercarbial Coping with acute changes– HT, arrhythmias etcThe surgical procedure can beeither open or laparoscopic. Aftershifting the patient into theoperating room, at least two largebore venous cannulae sould be inplace. ECG, SpO2, EtCO2, temperatureand urine output shouldbe monitored. Invasive arterialblood pressure and centralvenous pressure should be monitored.Optional monitors includepulmonary capillary wedge pressureand neuromuscular blockademonitoring. A number of drugsshould be kept ready for use inacute hypertensive and hypotensivecrises, such as sodium nitroprusside,phentolamine, magnesiumsulphate, propranolol,esmolol, phenylephrine, dopamine,adrenaline and noradrenaline.Drugs that cause arrhythmias andtachycardia should be avoided,such as atropine, ketamine,succinyncholine, halothane,desflurane, pancuronium,atracurium etc. The anaesthetictechnique can be either controlledgeneral anaesthesia withmuscle relaxation or general anaesthesiacombined with epiduralanaesthesia 7 . Though it has alsobeen done with a regional anaesthetictechnique alone, it is notrecommended as control ofacute fluctuations of blood pressureis better with general anaesthesia.Any combination of drugscan be used for induction andmaintenance, avoiding the onesspecified before. Episodes of tachycardiashould be treated withesmolol or propranolol. Hypertensioncan occur, especially duringlaryngoscopy and tumor handling,and should be controlledwith sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerineand labetolol. It hasbeen found that the peak totalcatecholamine level found duringsurgery correlated quite well withmore operative instability suggestingthat patients withphaeochromocytomas with highproduction of catecholaminesare more likely to show cardiovascularinstability 8 . Adequatevolume loading is necessary. Followingligation of the venousdrainage of the tumor, there isusually a sudden fall in bloodpressure due to sudden fall incatecholamine levels in the body,combination of residual alphaand beta blockade, receptordowngrading, and diminishedblood volume. This should betreated with i.v. fluids, and whichmay require noradrenaline oradrenaline infusions.Post-operatively, intensive carewith invasive monitoring is recommendedfor all patients. Inmost cases, cardiovascular stabilityreturns within a few hours ofcompletion of surgery and vasoactiveagents are withdrawn atthis stage. About 50% of patientsmight remain hypertensive for 1– 3 days. Adequate fluids shouldbe given post-operatively, titratedto CVP, and analgesia should bemaintained via epidural top-upsor intravenous narcotics. Thepatient should be extubated whenconsidered appropriate. Themortality as well as difficulty inmanagement of phaeochromocytomaincreases manifold whenit complicates other conditionssuch as pregnancy 9 , when magnesiumsulphate is one of thepreferred vasodilators 10 , or inpaediatric 11 patients. Other conditionsresembling phaeochromocytomainclude neuroblastomaand ganglione-uroma.It isessential to remember that not allcases of phaeochromocytomawill be well-controlled with medication,two other situations arepossible- when abdominal manipulationduring incidental surgeryleads to uncontrollable risesin blood pressure, leading to adiagnosis of phaeochromocytomain the operating room, andwhen a known case ofphaeochromocytoma, still notwell-controlled with drugs, presentsfor an emergency surgery.In both these cases, invasivemonitoring should be started,and the intra-operative fluctuationsof blood pressure controlledwith appropriateinotropes, dilators andfluids.Post-operative ICU carewith elective ventilation is a mustfor these patients till blood pressureis satisfactorily controlled.References1. St John Sutton MG,Sheps SG, Lie JT. Prevalenceof clinically unsuspectedphaeoch-romocytoma: Reviewof a 50-year autopsyseries.Mayo Clin Proc 56:354,1981.2. Geoghegan JG, Emberton M,Bloom SR, Lynn JA. Changingtrends in the managementof phaeochromocytoma. BrJ Surg. 1998 Jan;85(1):117-20.Journal of Postgraduate Medical Education, Training & Research67
- Page 1:
Global Phenomenon of e-healthP.S. S
- Page 4 and 5:
Basic Life SupportRavinder Kumar Ba
- Page 6 and 7:
age 5 . AHA recommends abdominalthr
- Page 8 and 9:
ficult when bleeding is brisk, andi
- Page 10 and 11:
orrhage, a non-bleeding visiblevess
- Page 12 and 13:
structures visualized with nakedeye
- Page 14 and 15:
LSCS is taken, patient shouldbe kep
- Page 16 and 17: in amniotic fluid), nor due to apre
- Page 18 and 19: l Reduction in induction-deliveryin
- Page 20 and 21: to the blood pressure changes.l Hyp
- Page 22 and 23: incidence of side-effects andPONV.
- Page 24 and 25: 2. Nasal injectionThe same needle i
- Page 26 and 27: injected. It blocks sensation fromt
- Page 28 and 29: Intraocular tumorsIn children, reti
- Page 30 and 31: A fast of six to eight hours forsol
- Page 32 and 33: lControl ventilation should beiniti
- Page 34 and 35: 6ReviewArticleAnaesthesia for Nonca
- Page 36 and 37: immunosuppression, andpreoperative
- Page 38 and 39: and the most frequent andimportant
- Page 40 and 41: ppressive drugs or chronic heartfai
- Page 42 and 43: 7ReviewArticleAnticoagulants and An
- Page 44 and 45: The dose of heparin varies withthe
- Page 46 and 47: and has a half -life of 24-48 hours
- Page 48 and 49: llPatients receiving heparin forgre
- Page 50 and 51: (5%). For patients with mitralprost
- Page 52 and 53: Cardiovascularl Hypertension- Over
- Page 54 and 55: elaxants, and provides goodpost-ope
- Page 56 and 57: l(CK-MB), and troponin. TotalCK lev
- Page 58 and 59: 9ReviewArticleObesity and Anesthesi
- Page 60 and 61: yet to be validated and should be u
- Page 62 and 63: prior to induction followed byPEEP
- Page 64 and 65: Anesthetic Implications-Thepreferre
- Page 68 and 69: 3. Tsioufis CP, Stefanadis CI,Touto
- Page 70 and 71: Diagnosisl Edrophonium (Tensilontes
- Page 72 and 73: erases may increase the needfor non
- Page 74 and 75: 2. Drachman DB. Myastheniagravis. N
- Page 76 and 77: ecommended to control psychoticsymp
- Page 78 and 79: espiratory complications due tothe
- Page 80 and 81: pain and a sensation of fullnessin
- Page 82 and 83: gastrointestinal stromaltumors: rec
- Page 84 and 85: 13Many new supraglotticairway devic
- Page 86 and 87: to the cuff size of the originalLMA
- Page 88 and 89: LMAs with valves that do notcontain
- Page 90 and 91: geal mask airway in paralyzed,anest
- Page 92 and 93: Foregger Midget) and diffusionof su
- Page 94 and 95: cause serious problems. Longersurge
- Page 96 and 97: positioning accuracy for CTguided s
- Page 98 and 99: decreases with increased optodesepa
- Page 100 and 101: observed that SJO 2of 50% ingeneral
- Page 102 and 103: ibility of cerebral circulatory arr
- Page 104 and 105: investigation and suggests thatesta
- Page 106: 14. Kiening ML, Unterberg AW,Bard T