Coastal Cutthroat Trout as Sentinels of Lower Mainland Watershed ...
Coastal Cutthroat Trout as Sentinels of Lower Mainland Watershed ...
Coastal Cutthroat Trout as Sentinels of Lower Mainland Watershed ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
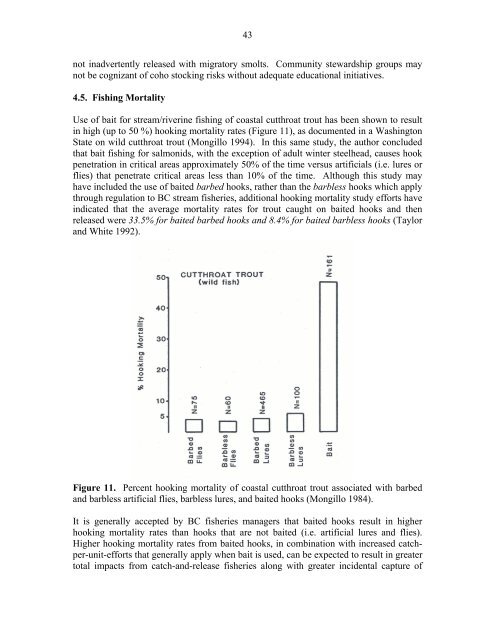
43not inadvertently rele<strong>as</strong>ed with migratory smolts. Community stewardship groups maynot be cognizant <strong>of</strong> coho stocking risks without adequate educational initiatives.4.5. Fishing MortalityUse <strong>of</strong> bait for stream/riverine fishing <strong>of</strong> co<strong>as</strong>tal cutthroat trout h<strong>as</strong> been shown to resultin high (up to 50 %) hooking mortality rates (Figure 11), <strong>as</strong> documented in a W<strong>as</strong>hingtonState on wild cutthroat trout (Mongillo 1994). In this same study, the author concludedthat bait fishing for salmonids, with the exception <strong>of</strong> adult winter steelhead, causes hookpenetration in critical are<strong>as</strong> approximately 50% <strong>of</strong> the time versus artificials (i.e. lures orflies) that penetrate critical are<strong>as</strong> less than 10% <strong>of</strong> the time. Although this study mayhave included the use <strong>of</strong> baited barbed hooks, rather than the barbless hooks which applythrough regulation to BC stream fisheries, additional hooking mortality study efforts haveindicated that the average mortality rates for trout caught on baited hooks and thenrele<strong>as</strong>ed were 33.5% for baited barbed hooks and 8.4% for baited barbless hooks (Taylorand White 1992).Figure 11. Percent hooking mortality <strong>of</strong> co<strong>as</strong>tal cutthroat trout <strong>as</strong>sociated with barbedand barbless artificial flies, barbless lures, and baited hooks (Mongillo 1984).It is generally accepted by BC fisheries managers that baited hooks result in higherhooking mortality rates than hooks that are not baited (i.e. artificial lures and flies).Higher hooking mortality rates from baited hooks, in combination with incre<strong>as</strong>ed catchper-unit-effortsthat generally apply when bait is used, can be expected to result in greatertotal impacts from catch-and-rele<strong>as</strong>e fisheries along with greater incidental capture <strong>of</strong>