Simha Arom & Polo Vallejo - International Research Center For ...
Simha Arom & Polo Vallejo - International Research Center For ...
Simha Arom & Polo Vallejo - International Research Center For ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
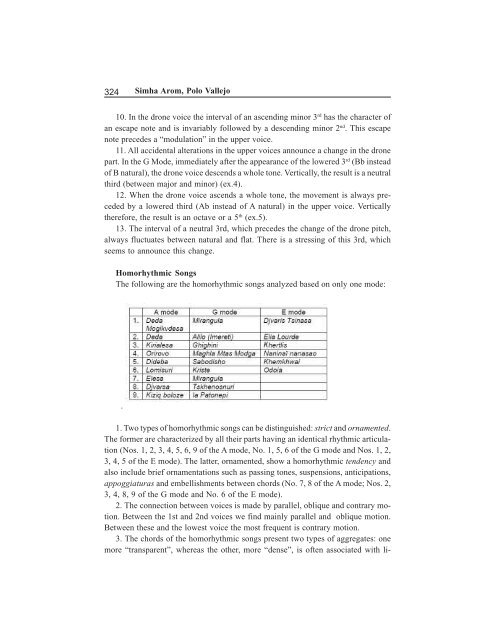
324 <strong>Simha</strong> <strong>Arom</strong>, <strong>Polo</strong> <strong>Vallejo</strong>10. In the drone voice the interval of an ascending minor 3 rd has the character ofan escape note and is invariably followed by a descending minor 2 nd . This escapenote precedes a “modulation” in the upper voice.11. All accidental alterations in the upper voices announce a change in the dronepart. In the G Mode, immediately after the appearance of the lowered 3 rd (Bb insteadof B natural), the drone voice descends a whole tone. Vertically, the result is a neutralthird (between major and minor) (ex.4).12. When the drone voice ascends a whole tone, the movement is always precededby a lowered third (Ab instead of A natural) in the upper voice. Verticallytherefore, the result is an octave or a 5 th (ex.5).13. The interval of a neutral 3rd, which precedes the change of the drone pitch,always fluctuates between natural and flat. There is a stressing of this 3rd, whichseems to announce this change.Homorhythmic SongsThe following are the homorhythmic songs analyzed based on only one mode:.1. Two types of homorhythmic songs can be distinguished: strict and ornamented.The former are characterized by all their parts having an identical rhythmic articulation(Nos. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9 of the A mode, No. 1, 5, 6 of the G mode and Nos. 1, 2,3, 4, 5 of the E mode). The latter, ornamented, show a homorhythmic tendency andalso include brief ornamentations such as passing tones, suspensions, anticipations,appoggiaturas and embellishments between chords (No. 7, 8 of the A mode; Nos. 2,3, 4, 8, 9 of the G mode and No. 6 of the E mode).2. The connection between voices is made by parallel, oblique and contrary motion.Between the 1st and 2nd voices we find mainly parallel and oblique motion.Between these and the lowest voice the most frequent is contrary motion.3. The chords of the homorhythmic songs present two types of aggregates: onemore “transparent”, whereas the other, more “dense”, is often associated with li-