Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
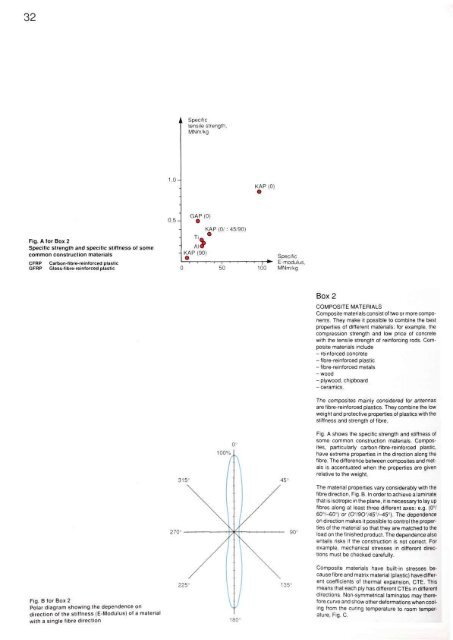
32Fig. A <strong>for</strong> Box 2Specific strength and specific stiffness of somecommon construction materialsCFRP Carbon-fibre-reintorced plasticGFRP Glass-fibre-reintorced plasticBox 2COMPOSITE MATERIALSComposite materials consist of two or more components.They make it possible to combine the bestproperties of different materials; <strong>for</strong> example, thecompression strength and low price of concretewith the tensile strength of rein<strong>for</strong>cing rods. Compositematerials include- rein<strong>for</strong>ced concrete- fibre-rein<strong>for</strong>ced plastic-fibre-rein<strong>for</strong>ced metals-wood- plywood, chipboard- ceramics.The composites mainly considered <strong>for</strong> antennasare fibre-rein<strong>for</strong>ced plastics. They combine the lowweight and protective properties of plastics with thestiffness and strength of fibre.Fig. A shows the specific strength and stiffness ofsome common construction materials. Composites,particularly carbon-fibre-rein<strong>for</strong>ced plastic,have extreme properties in the direction along thefibre. The difference between composites and metalsis accentuated when the properties are givenrelative to the weight.The material properties vary considerably with thefibre direction, Fig.B. In order to achieve a laminatethat is isotropic in the plane, it is necessary to lay upfibres along at least three different axes: e.g. (0°/60°/-60°) or (0 0 /90°/45 0 /-45°). The dependenceon direction makes it possible to control the propertiesof the material so that they are matched to theload on the finished product. The dependence alsoentails risks if the construction is not correct. Forexample, mechanical stresses in different directionsmust be checked carefully.Fig. B <strong>for</strong> Box 2Polar diagram showing the dependence ondirection of the stiffness (E-Modulus) of a materialwith a single fibre directionComposite materials have built-in stresses becausefibre and matrix material (plastic) have differentcoefficients of thermal expansion, CTE. Thismeans that each ply has different CTEs in differentdirections. Non-symmetrical laminates may there<strong>for</strong>ecurve and show other de<strong>for</strong>mations when coolingfrom the curing temperature to room temperature,Fig. C.