Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
Dichroic Antenna Reflector for Space Applications CCITT ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
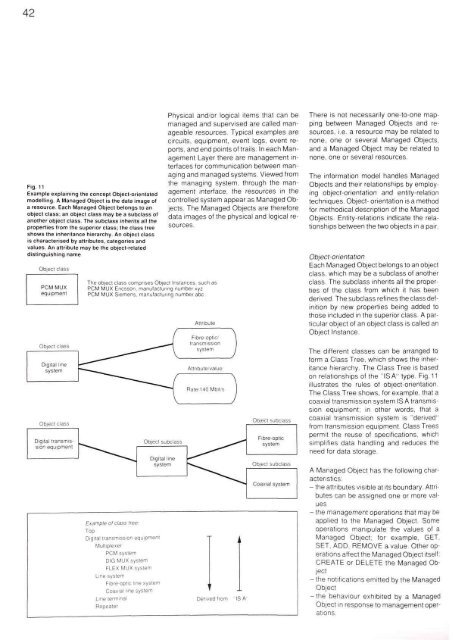
42Fig. 11Example explaining the concept Object-orientatedmodelling. A Managed Object is the data image ofa resource. Each Managed Object belongs to anobject class; an object class may be a subclass ofanother object class. The subclass inherits all theproperties from the superior class; the class treeshows the inheritance hierarchy. An object classis characterised by attributes, categories andvalues. An attribute may be the object-relateddistinguishing namePhysical and/or logical items that can bemanaged and supervised are called manageableresources. Typical examples arecircuits, equipment, event logs, event reports,and end points of trails. In each ManagementLayer there are management interfaces<strong>for</strong> communication between managingand managed systems. Viewed fromthe managing system, through the managementinterface, the resources in thecontrolled system appear as Managed Objects.The Managed Objects are there<strong>for</strong>edata images of the physical and logical resources.There is not necessarily one-to-one mappingbetween Managed Objects and resources,i.e. a resource may be related tonone, one or several Managed Objects,and a Managed Object may be related tonone, one or several resources.The in<strong>for</strong>mation model handles ManagedObjects and their relationships by employingobject-orientation and entity-relationtechniques. Object- orientation is a method<strong>for</strong> methodical description of the ManagedObjects. Entity-relations indicate the relationshipsbetween the two objects in a pair.Object-orientationEach Managed Object belongs to an objectclass, which may be a subclass of anotherclass. The subclass inherits all the propertiesof the class from which it has beenderived. The subclass refines the class definitionby new properties being added tothose included in the superior class. A particularobject of an object class is called anObject Instance.The different classes can be arranged to<strong>for</strong>m a Class Tree, which shows the inheritancehierarchy. The Class Tree is basedon relationships of the "ISA" type. Fig. 11illustrates the rules of object-orientation.The Class Tree shows, <strong>for</strong> example, that acoaxial transmission system ISA transmissionequipment; in other words, that acoaxial transmission system is "derived"from transmission equipment. Class Treespermit the reuse of specifications, whichsimplifies data handling and reduces theneed <strong>for</strong> data storage.A Managed Object has the following characteristics:- the attributes visible at its boundary. Attributescan be assigned one or more values- the management operations that may beapplied to the Managed Object. Someoperations manipulate the values of aManaged Object; <strong>for</strong> example, GET,SET, ADD, REMOVE a value. Other operationsaffect the Managed Object itself:CREATE or DELETE the Managed Object- the notifications emitted by the ManagedObject-the behaviour exhibited by a ManagedObject in response to management operations.