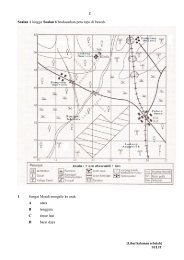
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
papercollection1SULITPERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUASEKOLAH MENENGAHNEGERI KEDAH DARUL AMANPEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM 2009 4531/1<strong>PHYSICS</strong>Kertas 111 jam Satu jam lima belas minit4JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU1. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalam dwibahasa.2. Soalan dalam bahasa Inggeris mendahului soalan yang sepadan dalam bahasa Melayu.3. Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat di halaman belakang kertas soalan ini.Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 35 halaman bercetakSULIT
2papercollection
3papercollection
papercollection1 Hot FM is transmitted with a frequency of 88.2 MHz. This frequency is equal toHot FM dipancar dengan frekuensi 88.2 MHz. Frekuensi ini adalah sama dengan4ABCD8.82 x 10 5 Hz8.82 x 10 6 Hz8.82 x 10 7 Hz8.82 x 10 8 Hz2 Diagram 1 shows a student holding a glass rod.Rajah 1 menunjukkan seorang pelajar memegang sebatang rod kaca.Diagram 1 / Rajah 1The best choice of measuring instruments to measure the length and diameter of theglass rod isPilihan alat pengukur yang terbaik untuk mengukur panjang dan diameter rod kaca ituialahABCDLength / PanjangMetre rulePembaris meterVernier calipersAngkup vernierVernier calipersAngkup vernierMetre rulePembaris meterDiameter / DiameterVernier calipersAngkup vernierMicrometer screw gaugeTolok skru mikrometerVernier calipersAngkup vernierMicrometer screw gaugeTolok skru mikrometer
papercollection3 A student carries out an experiment where the variables are as follows:Manipulated variable : PResponding variable : QConstant variable : RWhich is the graph that should be drawn?5Seorang pelajar menjalankan suatu eksperimen dengan pembolehubah seperti berikut:Pembolehubah dimanipulasikan : PPembolehubah bergerak balas : QPembolehubah dimalarkan : RGraf manakah yang patut dilukis?APBR0Q0PCQDQ0R0P4 Diagram 2 shows two strips of ticker tapes which were attached to two moving trolleysX and Y.Rajah 2 menunjukkan dua pita detik yang dilekat pada dua buah troli X dan Y yangsedang bergerak.Trolley X / Troli XTrolley Y / Troli YWhich statement is correct?Pernyataan yang manakah betul?Diagram 2 / Rajah 2ABCThe time taken by both trolleys are the sameMasa yang diambil oleh kedua-dua troli adalah samaThe distance travelled by both trolleys are the sameJarak dilalui oleh kedua-dua troli adalah samaThe velocity of both trolleys are the sameHalaju kedua-dua troli adalah sama
papercollection5 Diagram 3 shows a velocity-time graph of a moving bicycle.Rajah 3 menunjukkan graf halaju-masa bagi sebuah basikal yang sedang bergerak.6VelocityHalajuXYWDiagram 3 / Rajah 3TimeMasaWhich statement describes the motion of the bicycle in the region WX and XY?Pernyataan yang manakah menerangkan pergerakan basikal tersebut dalam bahagianWX dan XY?ABCDWXIncreasing accelerationPecutan bertambahIncreasing accelerationPecutan bertambahZero accelerationPecutan sifarUniform accelerationPecutan seragamXYDecreasing accelerationPecutan berkurangUniform accelerationPecutan seragamUniform accelerationPecutan seragamZero accelerationPecutan sifar6 Which object moves with the largest acceleration?Objek yang manakah bergerak dengan pecutan paling besar?A2 kg3 N4 NB9 N 4 N3 kgC6 N 11 N2 kgD2 N1 N1 kg
papercollection7 Which vehicle has the largest momentum?Kenderaan manakah mempunyai momentum yang paling besar?[m = mass, v = velocity / m = jisim, v = halaju]7ABCm = 12 000 kg, v = 2 m s –1 m = 1800 kg, v = 30 m s –1Dm = 250 kg, v = 40 m s –1 m = 1200 kg, v = 35 m s –18 Diagram 4 shows a force acting on an object.Rajah 4 menunjukkan satu daya bertindak pada suatu objek.ForceDayaDiagram 4 / Rajah 4The impulse given to the object is affected byImpuls yang diberikan kepada objek itu dipengaruhi olehX : force / dayaY : time of impact / masa hentamanZ : mass of the object / jisim objekABCDX and Y only / X dan Y sahajaX and Y only / X dan Y sahajaX and Y only / X dan Y sahajaX, Y and Z / X, Y dan Z
papercollection9 Diagram 5 shows an object at rest on a rough inclined plane.Rajah 5 menunjukkan satu objek dalam keadaan pegun di atas permukaan condongyang kasar.RF8θWWhich relationship is correct?Hubungan yang manakah betul?Diagram 5 / Rajah 5ABCDR = F cosqR = W sin qF = W cosqF = W sin q10 Diagram 6 shows a toy car moving up a slope with constant velocity.Rajah 6 menunjukkan sebuah kereta mainan sedang mendaki permukaan condongdengan halaju malar.Diagram 6 / Rajah 6What happens to the kinetic energy and potential energy of the car?Apakah yang sedang berlaku kepada tenaga kinetik dan tenaga keupayaan kereta itu?ABCDKinetic energy / Tenaga kinetikIncreasingBertambahDecreasingBerkurangConstantMalarIncreasingBertambahPotential energy / Tenaga keupayaanIncreasingBertambahDecreasingBerkurangIncreasingBertambahConstantMalar
papercollection11 Diagram 7 shows a graph of force against extension for an elastic string.Rajah 7 menunjukkan graf daya melawan pemanjangan bagi seutas tali kenyal.9ForceDayaXY0ZDiagram 7 / Rajah 7ExtensionPemanjanganThe elastic potential energy of the string is represented by theTenaga keupayaan kenyal tali tersebut diwakili olehABCDarea OXY / luas OXYarea OYZ / luas OYZarea OXYZ / luas OXYZgradient of OY / kecerunan bagi OY12 Gas pressure in a closed container is due to the gas moleculesTekanan gas di dalam sebuah bekas bertutup adalah disebabkan oleh molekul gasABCDmoving randomlybergerak secara rawakmoving with equal speedbergerak dengan halaju yang samacolliding with one anotherberlanggar sesama sendiricolliding with the walls of the containerberlanggar dengan dinding bekas
papercollection1013 Diagram 8 shows liquid X and liquid Y in glass tubes.Rajah 8 menunjukkan cecair X dan cecair Y di dalam tiub kaca.Density of X = 800 kg m –3Density of Y = 1 000 kg m –3Ketumpatan X = 800 kg m –3 Ketumpatan Y = 1 000 kg m –3STP S = pressure at SP S = tekanan di SP T = pressure at TP T = tekanan di TDiagram 8 / Rajah 8Which statement is correct?Pernyataan manakah betul?ABCDP S = P T because S and T are at the same depthP S = P T sebab S dan T berada pada kedalaman yang samaP S = P T because S and T are at the same levelP S = P T sebab S dan T berada pada aras yang samaP S < P T because the density of X is less than the density of YP S < P T sebab ketumpatan X lebih kecil daripada ketumpatan YP S > P T because S is nearer to the bottom of the tubeP S > P T sebab S lebih dekat kepada dasar tiub14 Diagram 9 shows a manometer used to measure the pressure of the gas in the container.Rajah 9 menunjukkan sebuah manometer digunakan untuk mengukur tekanan gasdalam sebuah bekas.GasGas24 cmDiagram 9 / Rajah 9
papercollection11Which statement is true about the pressure of the gas in the container if the atmosphericpressure is 76.0 cm Hg?Pernyataan yang manakah adalah benar mengenai tekanan gas di dalam bekas itu jikatekanan atmosfera adalah 76.0 cm Hg?ABCDThe gas pressure is zeroTekanan gas adalah sifarThe gas pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressureTekanan gas adalah sama dengan tekanan atmosferaThe gas pressure is 24.0 cm Hg more than atmospheric pressureTekanan gas adalah 24.0 cm Hg lebih daripada tekanan atmosferaThe gas pressure is 24.0 cm Hg less than atmospheric pressureTekanan gas adalah 24.0 cm Hg kurang daripada tekanan atmosfera.15 Diagram 10 shows a crane lifting a concrete beam.Rajah 10 menunjukkan sebuah kren mengangkat alang konkrit.PistonOmbohDiagram 10 / Rajah 10What principle is used to move the piston at the arm of the crane?Apakah prinsip yang digunakan untuk menggerakkan omboh pada lengan kren itu?ABCPascal's principle / Prinsip PascalArchimedes' principle / Prinsip ArchimedesBernoulli's principle / Prinsip Bernoulli
papercollection1216 Which situation occurs due to atmospheric pressure?Situasi yang manakah berlaku disebabkan tekanan atmosfera?ADented ping pong ball becomes round again whenimmersed in hot waterBola ping pong yang kemek menjadi bulat semulaapabila direndam dalam air panasBPouring water out of a bottleMenuang air keluar daripada botolCPressing icing onto a cakeMenekan aising pada kekDSucking water into a syringeMenyedut air ke dalam picagari
papercollection1317 Diagram 11 shows the cross-section of an iceberg floating on the surface of the sea.Rajah 11 menunjukkan keratan rentas sebuah bongkah ais terapung di permukaan laut.IcebergBongkah aisSea levelAras lautWhich statement is correct?Pernyataan yang manakah betul?Diagram 11 / Rajah 11ABCWeight of iceberg = Weight of sea water displacedBerat bongkah ais = Berat air laut tersesarVolume of iceberg = Volume of sea water displacedIsipadu bongkah ais = Isipadu air laut tersesarDensity of iceberg = Density of sea water displacedKetumpatan bongkah ais = Ketumpatan air laut tersesar
papercollection18 Which diagram shows the correct water levels when water flows steadily through theglass tube?14Rajah manakah menunjukkan aras air yang betul apabila air mengalir secara mantapmelalui tiub kaca itu?Afrom tapdari pili airGlass tube / Tiub kacato sinkke sinkiBfrom tapdari pili airGlass tube / Tiub kacato sinkke sinkiCDfrom tapdari pili airGlass tube / Tiub kacato sinkke sinkifrom tapdari pili airGlass tube / Tiub kacato sinkke sinki
papercollection1519 Diagram 12 shows cold milk being added to hot tea.Rajah 12 menunjukkan susu sejuk ditambahkan kepada teh panas.Diagram 12 / Rajah 12Which statement is correct if there are no heat losses to the surroundings?Pernyataan yang manakah betul jika tiada haba hilang ke persekitaran?ABCHeat gained by cold milk is less than heat lost by hot teaPenerimaan haba oleh susu sejuk adalah kurang daripada kehilangan haba olehteh panasHeat gained by cold milk is greater than heat lost by hot teaPenerimaan haba oleh susu sejuk adalah lebih banyak daripada kehilangan habaoleh teh panasHeat gained by cold milk is equal to heat lost by hot teaPenerimaan haba oleh susu sejuk adalah sama dengan kehilangan haba oleh tehpanas
papercollection20 Diagram 13 shows a metal cylinder of mass 5.0 kg and specific heat capacity400 J kg –1 o C –1 .16Rajah 13 menunjukkan satu silinder logam berjisim 5.0 kg dan muatan haba tentu400 J kg –1 o C –1 .1 000 W heaterPemanas 1000 WThermometerTermometerMetal cylinderSilinder logamDiagram 13 / Rajah 13What is the temperature rise of the cylinder 10 seconds after the heater is switched on?Berapakah kenaikan suhu silinder itu 10 saat selepas pemanas itu dihidupkan?A 0.20 o CB 0.80 o CC 1.25 o CD 5.00 o C21 Diagram14 shows the arm of a person being splashed by boiling water and the arm ofanother person being exposed to steam. Both the hot water and steam have the samemass.Rajah 14 menunjukkan tangan seorang disimbah air panas and tangan seorang lainyang terdedah kepada stim. Kedua-dua air panas dan stim mempunyai jisim yang sama.Boiling waterAir mendidihSteamStimDiagram 14 / Rajah 14The scalding on the skin caused by steam is more serious than the scalding caused byboiling water becauseKelecuran kulit yang disebabkan oleh stim lebih serius daripada kelecuran kulit yangdisebabkan oleh air mendidih sebab
papercollection17P : steam has a higher temperature / stim mempunyai suhu yang lebih tinggiQ : steam has a higher heat content / stim mengandungi lebih banyak habaR : steam has a higher specific heat capacity / stim mempunyai muatan haba tentuyang lebih tinggiA P only / P sahajaB Q only / Q sahajaC P and Q only / P dan Q sahajaD P, Q and R / P, Q dan R.22 Which graph shows the relationship between the volume and absolute temperature of afixed mass of gas at constant pressure?Graf yang manakah menunjukkan hubungan antara isipadu dan suhu mutlak bagi satujisim tetap gas pada tekanan malar?AV / m 3BV / m 30 T / K 0T / KCV / m 3DV / m 30 T / K 0T / K
papercollection23 Diagram 15(a) shows an air bubble released by a diver at the bottom of the sea.Diagram 15(b) shows the air bubble when it arrives at the surface of the sea.18Rajah 15(a) menunjukkan satu gelembung udara dilepaskan oleh seorang penyelam didasar laut.Rajah 15(b) menunjukkan gelembung udara itu apabila tiba di permukaan lautSurface of the seaPermukaan lautAir bubbleGelembung udara(a)Air bubbleGelembung udara(b)Diagram 15 / Rajah 15The difference in the size of the air bubble can be explained byPerbezaan dalam saiz gelembung udara itu boleh diterangkan olehABCBoyle's law / hukum BoyleCharles' law / hukum CharlesPressure law / hukum tekanan24 Diagram 16 shows an object in front of a convex lens and its image.Rajah 16 menunjukkan suatu objek di hadapan sebuah kanta cembung dan imejnya.ObjectObjek10 cm30 cmImageImejWhat is the focal length of the lens?Berapakah panjang fokus kanta itu?Diagram 16 / Rajah 16ABCD20.00 cm7.50 cm6.67 cm0.15 cm
papercollection25 Diagram 17 shows parallel light rays directed at the surface of a concave mirror.19Rajah 17 menunjukkan sinar cahaya selari ditujukan ke permukaan cermin cekung.Diagram 17 / Rajah 17Which diagram shows the path of the rays after striking the mirror?Rajah yang manakah menunjukkan lintasan cahaya selepas terkena cermin itu?ABCD
papercollection2026 Diagram 18 shows light travelling from glass to air.Rajah 18 menunjukkan cahaya merambat dari kaca ke udara.AirUdarapqtsGlassKacaThe refractive index of glass isIndeks biasan kaca ialahDiagram 18 / Rajah 18ABCDsin ssin psin psin ssin tsin qsin qsin t
papercollection2127 Diagram 19 shows a light ray travelling in medium P towards medium Q. The refractiveindex of P is higher than the refractive index of Q.Rajah 19 menunjukkan satu sinar cahaya yang bergerak dalam medium P menuju kemedium Q. Indeks biasan P lebih tinggi daripada indeks biasan Q.QPDiagram 19 / Rajah 19Which diagram shows a possible path of the light ray?Rajah manakah menunjukkan lintasan sinar cahaya yang mungkin betul?AQPBQPCQPDQP
papercollection2228 An astronomical telescope has an eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. The distance betweenthe objective lens and the eyepiece is 85 cm.What is the magnifying power of the telescope?Sebuah teleskop astronomi mempunyai kanta mata dengan panjang fokus 5 cm. Jarakantara kanta objek dan kanta mata ialah 85 cm.Berapakah kuasa pembesaran teleskop itu?A 16B 17C 80D 9029 Diagram 20 shows a transverse wave propagating from P to Q.Rajah 20 menunjukkan suatu gelombang melintang yang merambat dari P ke Q.PDiagram 20 / Rajah 20QWhich is the correct direction of vibration and the direction of energy transfer betweenP and Q?Manakah arah getaran dan arah pemindahan tenaga yang betul antara P dan Q?Direction of vibrationArah getaranDirection of energy transferArah pemindahan tenagaABCD
papercollection30 Diagram 21 shows the propagation of water waves from region X to Y.Rajah 21 menunjukkan perambatan gelombang air dari kawasan X ke Y.23XYv Xv Yv X = speed of wave in X / laju gelombang di Xv Y = speed of wave in Y / laju gelombang di YDiagram 21 / Rajah 21Which is the correct comparison of the wave speed and depth of water in X and Y?Perbandingan yang manakah betul bagi laju gelombang dan kedalaman air di X danY?Wave speed / Laju gelombangDepth of water / Kedalaman airA v X > v Y X > YB v X > v Y X < YC v X < v Y X > YD v X < v Y X
papercollection31 Diagram 22 shows a toy boat behind a barrier in a ripple tank.24Rajah 22 menunjukkan sebuah bot mainan di belakang suatu halangan di dalam sebuahtangki riak.BoatBotConcrete barrierHalangan konkritDiagram 22 / Rajah 22The boat moves up and down after the waves pass the barrier. This is due to ..…………of the water waves.Bot itu bergerak ke atas dan ke bawah selepas gelombang itu melalui halangan. Inidisebabkan oleh …………… gelombang air.ABCDreflection / pantulanrefraction / pembiasandiffraction / pembelauaninterference / interferens32 Which is not a property of an electromagnetic wave?Yang manakah bukan ciri gelombang elektromagnet?ABCDIt is a transverse wave / Ia adalah gelombang melintangIt is a longitudinal wave / Ia adalah gelombang membujurIt can travel through vacuum / Ia boleh bergerak melalui vakumIt can travel through air / Ia boleh bergerak melalui udara
papercollection33 Diagram 23 shows the superposition of two water waves.25Rajah 23 menunjukkan superposisi dua gelombang air.Crest / PuncakTrough / PalungRPSQDiagram 23 / Rajah 23At which points do constructive interference occur?Di titik manakah interferens membina berlaku?ABCDP and Q / P dan QQ and R / Q dan RR and S / R dan SP and S / P dan S34 Someone can be heard coming round a corner of a building before he can be seen.Which statement best explains the above situation?Seseorang yang datang dari sebalik penjuru bangunan boleh didengar sebelum diaboleh dilihat.Pernyataan manakah paling sesuai untuk menerangkan situasi di atas?ABCDLight travels faster than soundCahaya bergerak lebih laju dari bunyiSound travels faster than lightBunyi bergerak lebih laju dari cahayaLight is refracted less by air compared to soundCahaya kurang dibiaskan oleh udara berbanding bunyiSound has a longer wavelength than lightBunyi mempunyai panjang gelombang yang lebih besar dari cahaya
papercollection2635 Which voltage-current graph shows that resistance increases when current increases?Graf voltan-arus yang manakah menunjukkan rintangan bertambah apabila arusbertambah?ABVoltageVoltageVoltanVoltanCurrentCurrent00ArusArusCDVoltageVoltageVoltanVoltanCurrentCurrent0Arus0Arus36 Diagram 24 shows current flowing through two resistors in series. A 1 and A 2 areammeters while V 1 and V 2 are voltmeters.Rajah 24 menunjukkan arus mengalir melalui dua perintang yang disambung sesiri. A 1dan A 2 adalah ammeter manakala V 1 dan V 2 adalah voltmeter.V 1 V 2A 1 5 Ω 10 Ω A 2Diagram 24 / Rajah 24Which is the correct comparison of the ammeter and voltmeter readings?Perbandingan yang manakah benar tentang bacaan ammeter dan voltmeter?
papercollection27Ammeter reading / Bacaan ammeter Voltmeter reading / Bacaan voltmeterA A 1 < A 2 V 1 < V 2B A 1 > A 2 V 1 > V 2C A 1 = A 2 V 1 = V 2D A 1 = A 2 V 1 < V 237 Diagram 25 shows a circuit in which the cell has internal resistance.Rajah 25 menunjukkan suatu litar di mana sel itu mempunyai rintangan dalam.VE , rADiagram 25 / Rajah 25What are the changes in the reading of the ammeter and voltmeter when the resistanceof the rheostat is decreased?Apakah perubahan bacaan ammeter dan voltmeter apabila rintangan rheostatdikurangkan?Ammeter reading / Bacaan ammeter Voltmeter reading / Bacaan voltmeterA Increases / Bertambah Increases / BertambahB Increases / Bertambah Decreases / BerkurangC Decreases / Berkurang Increases / BertambahD Decreases / Berkurang Decreases / Berkurang
papercollection38 Diagram 26 shows the readings of an ammeter and voltmeter connected to a resistor.28Rajah 26 menunjukkan bacaan ammeter dan voltmeter yang disambung kepada suatuperintang.AVDiagram 26 / Rajah 26Calculate the power released by the resistor.Hitung kuasa yang dibebaskan pada perintang itu.ABCD0.72 W7.20 W8.00 W19.20 W39 Diagram 27 shows a compass near a straight wire XY.Rajah 27 menunjukkan sebuah kompas berhampiran dengan dawai lurus XY.KXNWSECompassKompasDiagram 27 / Rajah 27Where should the compass be placed such that it will point to the East when K isswitched on?Di manakah kompas itu harus diletakkan supaya ia menunjuk ke Timur apabila Kdihidupkan?YABCDAbove wire XY / Di atas dawai XYBelow wire XY / Di bawah dawai XYTo the left of wire XY / Di sebelah kiri dawai XYTo the right of wire XY / Di sebelah kanan dawai XY
papercollection40 Diagram 28 shows a current-carrying wire between the poles of a pair of permanentmagnets.What is the direction of the magnetic force on the wire?29Rajah 28 menunjukkan seutas dawai yang membawa arus di antara kutub-kutubsepasang magnet kekal.Apakah arah daya magnet pada dawai itu?AWire / DawaiNDBSCCurrent / ArusDiagram 28 / Rajah 2841 Diagram 29 shows a bar magnet being pushed towards a solenoid.Rajah 29 menunjukkan sebatang magnet bar ditolak ke arah sebuah solenoid.Bar magnet / Magnet barNSP : Induced e.m.f. / D.g.e. teraruhQ : Induced current / Arus teraruhR : Magnetic field / Medan magnetWhat is produced by the solenoid?Apakah yang dihasilkan oleh solenoid?Diagram 29 / Rajah 29ABCDP only / P sahajaQ only / Q sahajaP and Q / P dan QP, Q and R / P, Q dan R
papercollection3042 Which circuit shows voltage being stepped up?Litar manakah menunjukkan voltan diinjak naik?ABCD43 In a model of transmission of electricity, 24 W of power is transmitted at 48 V usingcables with a resistance of 2 Ω.What is the current in the cables and the power loss?Dalam suatu model penghantaran elektrik, kuasa 24 W dihantar pada 48 Vmenggunakan kabel dengan rintangan 2 Ω.Berapakah arus dalam kabel dan kehilangan kuasa?Current in the cables / Arus dalam kabel Power loss / Kehilangan kuasaA 0.5 A 0.5 WB 0.5 A 1.0 WC 2.0 A 4.0 WD 2.0 A 8.0 W
papercollection3144 Diagram 30 shows a waveform on cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) screen.Rajah 30 menunjukkan suatu bentuk gelombang pada suatu skrin osiloskop sinar katod(OSK)1 cm1 cmDiagram 30 / Rajah 30If the Y-input of CRO is set at 5.0 V cm –1 , what is the peak voltage?Jika input-Y pada OSK dilaraskan pada 5.0 V cm –1 , berapakah voltan puncaknya?ABCD20.0 V10.0 V5.0 V2.0 V45 Diagram 31 shows a circuit where the bulb does not light up.Rajah 31 menunjukkan litar di mana mentol tidak menyala.6 VWhich step will make the bulb light up?Diagram 31 / Rajah 31Langkah manakah akan menyalakan mentol?ABCDInserting a fuse in the circuitMemasang fiusReversing the battery connectionMenyongsangkan sambungan bateriChanging the power supply to a 3 V batteryMenukar bekalan kuasa kepada bateri 3 VReversing the bulb connectionMenyongsangkan sambungan mentol
papercollection46 In which circuit will the bulb light up when switch S is closed?Dalam litar manakah mentol akan menyala apabila suis S ditutup?32ASBS2 kΩ1 kΩ6 V1 kΩ6 V2 kΩ10 kΩCSDS2 kΩ2 kΩ1 kΩ6 V1 kΩ6 V10 kΩ10 kΩ47 Diagram 32 shows a logic gate circuit.Rajah 32 menunjukkan litar get logik.XYZWhich truth table is correct?Jadual kebenaran yang manakah betul?Diagram 32 / Rajah 32A B C DX Y Z0 0 00 1 01 0 11 1 1X Y Z0 0 10 1 01 0 01 1 1X Y Z0 0 10 1 01 0 11 1 0X Y Z0 0 10 1 11 0 01 1 0
papercollection48 X is a nuclide with nuclide notation 13 7X . Another nuclide Y has 2 protons and 3neutrons more than X. What is the nuclide notation for Y?33X ialah nuklida dengan notasi nuklida13 7X . Suatu nuklida yang lain Y mempunyai2 proton dan 3 neutron lebih daripada X. Apakah notasi nuklida bagi Y?ABCD13 9Y169Y189Y1810Y49 Diagram 33 shows a graph of activity against time for a radioactive sample.Rajah 33 menunjukkan graf aktiviti melawan masa untuk satu sampel radioaktif.Activity / counts per minuteAktiviti / pembilangan per minit120010008006004002000 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Time / minutesMasa / minitDiagram 33 / Rajah 33Which statement is correct?Pernyataan yang manakah benar?ABCDThe half life is 20 minutesSeparuh hayat bahan itu ialah 20 minitAfter 30 minutes, 25% of the sample have not decayedSelepas 30 minit, 25% daripada sampel itu belum mereputAfter 45 minutes, the activity will be 100 counts per minuteSelepas 45 minit, aktiviti akan menjadi 100 pembilangan per minitThe activity will become zero after a few daysAktiviti akan berkurang ke sifar selepas beberapa hari
papercollection50 A chain reaction can occur in a reactor because during nuclear fissionTindak balas berantai boleh berlaku di dalam sebuah reaktor sebab semasapembelahan nuklear34ABCDnew neutrons are produced / neutron baru dihasilkantwo fission fragments are produced / dua serpihan belahan dihasilkana large amount of energy is released / tenaga yang banyak dibebaskanthe temperature is very high / suhu adalah sangat tinggiEND OF QUESTION PAPERKERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
papercollection35INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATESMAKLUMAT UNTUK CALON1. This question paper consists of 50 questions.Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 50 soalan.2. Answer all questions.Jawab semua soalan.3. Each question is followed by either three or four options. Choose the best option foreach question and blacken the correct space on the answer sheet.Tiap-tiap soalan diikuti oleh sama ada tiga atau empat pilihan jawapan. Pilih satujawapan yang terbaik bagi setiap soalan dan hitamkan ruangan yang betul pada kertasjawapan anda.4. Blacken only one space for each question.Hitamkan satu ruangan sahaja bagi setiap soalan.5. If you wish to change your answer, erase the blackened mark that you have made. Thenblacken the space for the new answer.Sekiranya anda hendak menukar jawapan, padamkan tanda yang telah dibuat.Kemudian hitamkan jawapan yang baru.6. The diagrams in the questions provided are not drawn to scale unless stated.Rajah yang mengiringi soalan tidak dilukis mengikut skala kecuali dinyatakan.7. You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator.Anda dibenarkan menggunakan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh diprogram8. A list of formulae is provided on page 2.Satu senarai formula disediakan di halaman 2.
papercollection1SULITNO. KAD PENGENALANANGKA GILIRANNAMA: …….…………......…….............……..………. TINGKATAN: …….....………PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUASEKOLAH MENENGAHNEGERI KEDAH DARUL AMANPEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM 2009 4531/2<strong>PHYSICS</strong>Kertas 212 jam Dua jam tiga puluh minit2JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU1. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalamdwibahasa.2. Soalan dalam bahasa Inggeris mendahuluisoalan yang sepadan dalam bahasaMelayu.3. Calon dibenarkan menjawab keseluruhanatau sebahagian soalan sama ada dalambahasa Inggeris atau bahasa Melayu.4. Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat dihalaman belakang kertas soalan ini.Untuk Kegunaan PemeriksaBahagian SoalanMarkah MarkahPenuh Diperoleh1ABC23456789101112JumlahKertas soalan ini mengandungi 30 halaman bercetakSULIT
2papercollection
3papercollection
papercollection4Section ABahagian A[60 marks]Answer all questions in this section.Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini.1 Diagram 1.1 shows an electrical measuring instrument.Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan sebuah alat pengukur elektrik.Diagram 1.1 / Rajah 1.1(a) (i)What is the physical quantity measured by this instrument?Apakah kuantiti fizik yang diukur oleh alat ini?…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) Name the error found on this instrument.Namakan ralat yang terdapat pada alat ini.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection5(b)Diagram 1.2 shows two instruments, X and Y, that can be used to measure thethickness of a wire.Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan dua alat pengukur, X dan Y, yang boleh digunakan untukmenentukan ketebalan seutas dawai.XYDiagram 1.2 / Rajah 1.2(i)Which instrument is more suitable to measure the thickness of the wire?Alat pengukur yang manakah lebih sesuai untuk mengukur ketebalan dawaiitu?…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) State one reason for your answer in 1(b)(i).Nyatakan satu sebab bagi jawapan anda di 1(b)(i).…......................................................................................................................…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection2 Diagram 2 shows ice melting in a glass. The initial mass of the ice is 0.20 kg.Rajah 2 menunjukkan ais melebur di dalam sebuah gelas. Jisim awal ais itu ialah0.20 kg.6Thermometer / termometerIce / AisDiagram 2 / Rajah 2(a)Explain in terms of energy why the reading of the thermometer,Terangkan dalam sebutan tenaga mengapa bacaan termometer itu,(i)(ii)remains constant for the first 20 minutes.kekal malar untuk 20 minit yang pertama.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]increases after 20 minutes.meningkat selepas 20 minit.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](b) Calculate the heat absorbed by the ice during the first 20 minutes.[Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 x 10 5 J kg –1 ]Hitungkan haba yang diserap oleh ais itu semasa 20 minit yang pertama.[Haba pendam tentu pelakuran ais = 3.36 x 10 5 J kg –1 ][2 marks]
papercollection7(c)Which statement correctly describes the water in the glass after it is left for a fewhours. Mark ( ) in the correct box.Pernyataan manakah yang memerihalkan dengan betul tentang air dalam gelasitu selepas dibiarkan selama beberapa jam. Tanda ( ) pada kotak yang betul.There is no transfer of energy between the water and the surroundingsTiada pemindahan tenaga antara air dan persekitaranThere is no net transfer of energy between the water and thesurroundingsTiada pemindahan bersih tenaga antara air dan persekitaran[1 mark]3 Diagram 3 shows a block of concrete being lowered to the bottom of a lake. Thevolume of the block is 2.5 m 3 and its weight is 125 000 N. The density of the water inthe lake is 1 010 kg m –3 .Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu bongkah konkrit diturunkan ke dasar sebuah tasik. Isipadubongkah itu ialah 2.5 m 3 dan beratnya ialah 125 000 N. Ketumpatan air dalam tasik ituialah 1 010 kg m –3 .TWaterAirConcrete blockBongkah konkritDiagram 3 / Rajah 3(a)State the SI unit for pressure.Nyatakan unit SI bagi tekanan.………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark](b) State one factor that affects the pressure at a point below the surface of a liquid.Nyatakan satu faktor yang mempengaruhi tekanan pada satu titik di bawahpermukaan cecair.………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark]
papercollection(c) (i) Calculate the weight of the water displaced by the block.Hitungkan berat air yang disesarkan oleh bongkah itu.8(ii) Calculate the tension, T, in the cable.Hitungkan tegangan, T, dalam kabel itu.[2 marks][2 marks]4 Diagram 4.1 shows a transistor circuit for an alarm which is activated by heat.Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan satu litar transistor bagi penggera yang diaktifkan oleh haba.T1 kΩ IB6 VR(a) Name the component T.Namakan komponen T.Diagram 4.1 / Rajah 4.1………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark]
papercollection9(b) Complete the following sentences by underlining the correct word.Lengkapkan ayat-ayat berikut dengan menggariskan perkataan yang betul.When T is heated up, its resistance ( decreases / increases ).The base current, I B ( decreases / increases ) to switch on the transistor and lightup the bulb.Apabila T dipanaskan, rintangannya ( berkurang / bertambah ).Arus tapak, I B ( berkurang / bertambah ) untuk menghidupkan transistor danmenyalakan mentol.[2 marks](c)Diagram 4.2 shows the trace produced by an alternating current signal on thescreen of a cathode ray oscilloscope. The time base of the oscilloscope is set at0.02 s per division.Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan satu surih yang dihasilkan oleh satu isyarat arusulangalik pada skrin sebuah osiloskop sinar katod. Dasar masa osiloskop ituditetapkan pada 0.02 s per bahagian.Diagram 4.2 / Rajah 4.2 Diagram 4.3 / Rajah 4.3(i)What is the period of the alternating current signal?Berapakah tempoh bagi isyarat arus ulangalik itu?…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) Calculate the frequency of the alternating current signal.Hitung frekuensi bagi isyarat arus ulangalik itu.[2 marks](iii) On Diagram 4.3, draw the trace produced when the frequency of thealternating current signal is doubled.Pada Rajah 4.3, lukis surih yang dihasilkan apabila frekuensi isyarat arusulangalik itu menjadi dua kali ganda.[1 mark]
papercollection5 Diagram 5.1 shows a ray of light entering from air into water.Diagram 5.2 shows a ray of light entering from air into glass.Rajah 5.1 menunjukkan satu sinar cahaya bergerak dari udara ke dalam air.Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan satu sinar cahaya bergerak dari udara ke dalam kaca.10WaterAirGlassKacaDiagram 5.1 / Rajah 5.1 Diagram 5.2 / Rajah 5.2(a) (i) Compare the speed of light in water with the speed of light in air.Banding laju cahaya dalam air dengan laju cahaya dalam udara.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) Compare the speed of light in glass with the speed of light in air.Banding laju cahaya dalam kaca dengan laju cahaya dalam udara.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](iii) State the relationship between the speed of light in a medium and thedirection of bending of light in that medium.Nyatakan hubungan antara laju cahaya dalam suatu medium dan arahpembengkokannya dalam medium itu.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](iv) Name the phenomenon shown in Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2.Namakan fenomena yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection11(b)Diagram 5.3 shows a point P at the bottom of a swimming pool appears to be atthe point Q to the observer.Rajah 5.3 menunjukkan satu titik P pada dasar satu kolam renang kelihatan padatitik Q kepada pemerhati itu.ObserverPemerhatiQP1.2 m1.6 mDiagram 5.3 / Rajah 5.3(i)(ii)Complete Diagram 5.3 by drawing light rays to show how the image of thepoint P is seen at Q.Lengkapkan Rajah 5.3 dengan melukis sinar cahaya untuk menunjukkanbagaimana imej titik P kelihatan pada titik Q.[2 marks]Calculate the refractive index of the water in the swimming pool.Hitung indeks biasan air dalam kolam renang itu.[2 marks]
papercollection126 Diagram 6.1 shows the activity of a radioactive substance X and a radioactive substanceY being measured by a Geiger-Muller tube connected to a ratemeter.Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan aktiviti bahan radioaktif X dan bahan radioaktif Y diukuroleh tiub Geiger-Muller yang disambung kepada meter kadar.G-M tubeTiub G-MRatemeterMeter kadarRadioactive substance XBahan radioaktif XG-M tubeTiub G-MRatemeterMeter kadarRadioactive substance YBahan radioaktif YDiagram 6.1 / Rajah 6.1Diagram 6.2 shows the decay curves obtained for radioactive substance X andradioactive substance Y.Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan lengkungan pereputan yang diperoleh bagi bahan radioaktif Xdan bahan radioaktif Y.
papercollection13Activity / Counts per minuteAktiviti / Pembilangan per minit800700600500400300200100XY05 10 15 20 25 30Diagram 6.2 / Rajah 6.2Time / minutesMasa / minit(a) What is the meaning of half life?Apakah maksud separuh hayat?………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark](b) Based on the decay curves in Diagram 6.2,Berdasarkan lengkungan-lengkungan pereputan dalam Rajah 6.2,(i) State the half life of radioactive substance X and radioactive substance Y.Nyatakan separuh hayat bagi bahan radioaktif X dan bahan radioaktif Y.X : .................................Y : .................................[2 marks](ii) For radioactive substance X and radioactive substance Y, what percentageremains undecayed after 10 minutes?Bagi bahan radioaktif X dan bahan radioaktif Y, berapa peratuskah yangbelum mereput selepas 10 minit?X : .................................Y : .................................[2 marks]
papercollection14(c)Based on the answers to 6(b)(i) and 6(b)(ii), compare the decay rates ofradioactive substance X and radioactive substance Y.Hence state the relationship between decay rate and half life.Berdasarkan jawapan-jawapan kepada 6(b)(i) dan 6(b)(ii), banding kadarpereputan bagi bahan radioaktif X dan bahan radioaktif Y.Seterusnya, nyatakan hubungan antara kadar pereputan dan separuh hayat.………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2 marks](d) Give a reason why the readings of the ratemeters did not drop to zero afterradioactive substance X and radioactive substance Y were removed.Beri satu sebab mengapa bacaan-bacaan meter kadar itu tidak kembali ke sifarselepas bahan radioaktif X dan bahan radioaktif Y dikeluarkan.………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark]
papercollection157 Diagram 7 shows an electric motor lifting a 2.0 kg load. When the motor is switched on,the load moved through a height of 1.5 m in 2.5 s with constant speed. The currentflowing in the circuit is 1.7 A and the potential difference across the motor is 10.0 V.Rajah 7 menunjukkan sebuah motor elektrik sedang mengangkat satu beban 2.0 kg.Apabila motor itu dihidupkan, beban itu bergerak melalui ketinggian 1.5 m dalam 2.5 sdengan laju malar. Arus yang mengalir dalam litar ialah 1.7 A dan beza keupayaanmerentasi motor itu ialah 10.0 V.MotorMotorAxleGandarDiagram 7 / Rajah 7(a)(b)State the changes in energy that occur when the motor is switched on.Nyatakan perubahan tenaga yang berlaku apabila motor itu dihidupkan.………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark]Calculate,Hitung,(i) the electrical power supplied when the motor is lifting the load.kuasa elektrik yang dibekalkan semasa motor itu mengangkat beban.[2 marks](ii) the output power of the motor when the load moved through a height of1.5 m in 2.5 s.kuasa output motor apabila beban itu melalui ketinggian 1.5 m dalam 2.5 s.[2 marks]
papercollection16(iii) the efficiency of the electric motor.kecekapan motor itu.[2 marks](c)If some of the load is removed while the motor is still lifting the load, whatchange is observed on the ammeter? Explain your answer.Jika sebahagian daripada beban dikeluarkan semasa motor itu mengangkatbeban, apakah perubahan yang diperhatikan pada ammeter? Jelaskan jawapananda………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2 marks](d)Suggest one way to increase the efficiency of the motor.Cadangkan satu cara untuk menambah kecekapan motor itu.………………………………………………………………………………………[1 mark]
papercollection178 Diagram 8 shows the graph of force against extension for three springs P, Q and R.Rajah 8 menunjukkan graf daya melawan pemanjangan bagi tiga spring P, Q dan R.Force / NDaya / N120Q100P80R60402002 4 6 8 10 12Diagram 8 / Rajah 8Extension / cmPemanjangan / cm(a) (i)A law states that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to theforce applied if the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded.Name this law.Suatu hukum menyatakan bahawa pemanjangan seutas spring adalahberkadar terus dengan daya yang dikenakan jika had kenyal tidak dilebihi.Nyatakan hukum ini.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) On the graph in Diagram 8, mark ' X ' at the elastic limit for each spring.Pada graf dalam Rajah 8, tandakan ' X ' pada had kenyal setiap spring.[2 marks]
papercollection(b) The spring stores energy when it is extended.Spring itu menyimpan tenaga apabila diregang.(i) Name the energy stored in the spring when it is extended.Namakan tenaga yang disimpan dalam spring yang diregang.18…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) Calculate the energy stored in spring R when its extension is 8.0 cm.Hitung tenaga yang disimpan dalam spring R apabila pemanjangannya8.0 cm.[3 marks](c)The springs are to be used in a Newton balance to measure a maximum load ofmass 8 kg.Spring-spring tersebut akan digunakan di dalam neraca Newton untuk mengukurbeban maksimum berjisim 8 kg.(i) What is the maximum weight of the load?Berapakah berat maksimum beban itu?…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii)Based on Diagram 8, choose two springs which are suitable to be used in theNewton balance specified above.Berdasarkan Rajah 8, pilih dua spring yang sesuai untuk digunakan didalam neraca Newton tersebut di atas.…......................................................................................................................[2 marks](iii) Which spring is the most suitable to be used in the Newton balance? Explainyour answer.Spring yang manakah paling sesuai untuk digunakan di dalam neracaNewton itu. Terangkan jawapan anda.…......................................................................................................................…......................................................................................................................[2 marks]
papercollection19Section BBahagian B[20 marks]Answer any one question from this section.Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini.9 Diagram 9.1 shows a stationary pistol on a smooth surface.Diagram 9.2 shows the pistol and bullet after the pistol has been fired by remotecontrol.Rajah 9.1 menunjukkan sebuah pistol pegun di atas permukaan licin.Rajah 9.2 menunjukkan pistol dan peluru selepas tembakan dilepaskan secara kawalanjauh.Stationary pistolPistol pegunDiagram 9.1 / Rajah 9.1Pistol recoils at lowerspeedPistol tersentak denganlaju yang lebih rendahBullet moves at high speedPeluru bergerak denganlaju tinggi(a) (i)Diagram 9.2 / Rajah 9.2What is the meaning of momentum?Apakah maksud dengan momentum?[1 mark](ii) State the total momentum of the pistol and bullet in Diagram 9.1Using Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2, compare the total momentum beforeand after the bullet is fired.Using Diagram 9.2, compare the magnitude and direction of the momentumof the bullet and pistol.Name the physics principle that can be applied to the motion of the bulletand pistol.
papercollection20Menggunakan Rajah 9.1 dan Rajah 9.2, bandingkan jumlah momentumsebelum dan selepas peluru itu ditembak.Menggunakan Rajah 9.2, bandingkan magnitud dan arah momentum pelurudan pistol.Nyatakan prinsip fizik yang boleh diaplikasi kepada gerakan peluru danpistol itu.[5 marks](b) Describe, in terms of momentum, the propulsion of a rocket engine.Terangkan, dalam sebutan momentum, rejangan sebuah enjin roket.[4 marks](c)Diagram 9.3 shows a the structure of a jet engine for a small jet plane.Rajah 9.3 menunjukkan struktur sebuah enjin jet bagi sebuah kapal terbang jetyang kecil.Compression bladesBilah pemampatCombustion chamberKebuk pembakaranTurbine bladesBilah turbinNozzleNozelFuel injectorPemancut bahan apiDiagram 9.3 / Rajah 9.3You are required to give some suggestions to improve the design of the jet engineso that it can be used on a larger jet plane that travels at a higher speed.Using the knowledge on forces and motion and the properties of materials, explainthe suggestions based on the aspects labeled on Diagram 9.3Anda dikehendaki memberi beberapa cadangan untuk membaiki reka bentuk enjinjet itu supaya enjin jet itu boleh digunakan pada sebuah kapal terbang jet yanglebih besar dan bergerak lebih laju.Menggunakan pengetahuan tentang gerakan, daya dan sifat-sifat bahanterangkan cadangan itu yang merangkumi aspek-aspek yang dilabel pada Rajah9.3.[10 marks]
papercollection2110 Diagram 10.1 shows a tuning fork vibrating near a microphone. The sound wavesdetected by the microphone are displayed on a cathode-ray oscilloscope.Rajah 10.1 menunjukkan sebuah tala bunyi bergetar berhampiran dengan sebuahmikrofon. Gelombang bunyi yang dikesan oleh mikrofon itu dipaparkan pada sebuahosiloskop sinar katod.When the tuning fork is struck harder, the sound produced is louder and the soundwaves produced are as shown in Diagram 10.2.Apabila tala bunyi itu diketuk dengan lebih kuat, bunyi yang dihasilkan adalah lebihnyaring dan gelombang bunyi yang dihasilkan adalah seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah10.2.a 2a 1Tuning forkTala bunyiDiagram 10.1 / Rajah 10.1 Diagram 10.2 / Rajah 10.2(a) (i) What is the meaning of longitudinal waves?Apakah maksud gelombang membujur?(ii)Explain how a tuning fork produces sound waves.Jelaskan bagaimana tala bunyi menghasilkan gelombang bunyi.[1 mark][4 marks]
papercollection22(b) Using Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2,Berdasarkan Rajah 10.1 dan Rajah 10.2,(i)Compare the amplitudes of vibration of the tuning forks.Banding amplitud getaran tala bunyi itu.(ii) Compare the peak values, a 1 and a 2 , of the waves displayed by theoscilloscope.Banding nilai puncak, a 1 dan a 2 , bagi gelombang yang dipaparkan padaosiloskop.(iii) Relate the peak values displayed by the oscilloscope to the amplitude of thesound wave.Hubungkan nilai-nilai puncak yang dipapar pada osiloskop denganamplitud gelombang bunyi.(iv) Relate the peak value to the loudness of the sound produced.Hubungkan nilai puncak dengan kenyaringan bunyi yang dihasilkan.(v)Hence, deduce the relationship between the loudness of the sound and theamplitude of the wave.Seterusnya, deduksikan hubungan antara kenyaringan bunyi denganamplitud gelombang itu.[5 marks]
papercollection23(c)Diagram 10.3 shows a boat using sound waves to measure the depth of the sea.Rajah 10.3 menunjukkan sebuah bot menggunakan gelombang bunyi untukmengukur kedalaman laut.Reflected soundBunyi terpantulTransmitted soundBunyi terpancarDiagram 10.3 / Rajah 10.3(i)Using your knowledge of the nature and phenomena of waves, explain howthe following aspects of the wave affects the results obtained.Menggunakan pengetahuan anda tentang sifat dan fenomena gelombang,terangkan bagaimana aspek gelombang yang berikut mempengaruhikeputusan yang diperoleh.· Frequency of the wavesFrekuensi gelombang· Energy of the wavesTenaga gelombang(ii) List the equipment needed for the measurement.Senaraikan peralatan yang diperlukan untuk pengukuran itu.(iii) Explain how the depth of the sea is determined.Terangkan bagaimana kedalaman laut ditentukan.[4 marks][4 marks][2 marks]
papercollection24Section CBahagian C[20 marks]Answer any one question from this section.Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini.11 Diagram 11.1 shows the basic components and four processes in a refrigerator.Rajah 11.1 menunjukkan komponen asas dan empat proses dalam sebuah peti sejuk.Process 1 / Proses 1The compressor compressesthe coolant gasPemampat memampat gasbahan penyejukProcess 2 / Proses 2Heat is removed and the gaschanges into a liquidHaba dikeluarkan dan gasbertukar menjadi cecairProcess 4 / Proses 4The coolant absorbs heat fromthe interior of the refrigeratorBahan penyejuk menyerap habadari bahagian dalam peti sejukProcess 3 / Proses 3The coolant expands andchanges from a liquid to a gasBahan penyejuk mengembangdan bertukar dari cecair ke gasDiagram 11 / Rajah 11(a) (i) Explain, using the kinetic theory, how the coolant changes from a gas to aliquid in Process 2.Jelaskan, dengan menggunakan teori kinetik, bagaimana bahan penyejuk itubertukar menjadi cecair dalam Proses 2.[3 marks](ii) Explain, in terms of latent heat, how the coolant removes heat in Process 3and Process 4.Jelaskan, dalam sebutan haba pendam, bagaimana bahan penyejuk itumengeluarkan haba dalam Proses 3 dan Proses 4.[2 marks]
papercollection25(b)Table11.1 and Table 11.2 show some characteristics of the coolants and the pipesthat carry the coolant in the refrigerator.Jadual 11.1 dan Jadual 11.2 menunjukkan beberapa ciri bahan penyejuk dansaluran yang membawa bahan penyejuk dalam peti sejuk itu.CoolantBahan penyejukSpecific latent heat of vapourisationHaba pendam tentu pengewapanJ kg -1Boiling pointTakat didiho CP 1.5 × 10 5 35Q 7.6 × 10 5 10R 4.5 × 10 5 -10PipeSaluranTable 11.1 / Jadual 11.1Specific heat capacityMuatan haba tentuJ kg –1 o C –1DiameterDiameterX 220 Big / BesarY 350 Small / KecilZ 180 Big / BesarTable 11.2 / Jadual 11.2(c)Explain the suitability of each characteristic of the coolant and that of the pipe sothat the refrigerator can work efficiently.State which coolant and which pipe should be chosen.Terangkan kesesuaian setiap ciri bahan penyejuk dan saluran supaya peti sejukitu boleh berfungsi dengan cekap.Nyatakan bahan penyejuk dan saluran manakah patut dipilih.[10 marks]500 g of water at 30 o C is placed in the freezer of a refrigerator.500 g air pada 30 o C diletakkan ke dalam peti pembeku sebuah peti sejuk.[Specific latent heat of fusion of ice /Haba pendam tentu perlakuran ais = 3.34 × 10 5 J kg –1 ,Specific heat capacity of water / Muatan haba tentu air = 4 200 J kg –1 o C –1 ](i) Explain the meaning “specific heat capacity of water is 4 200 J kg –1 o C –1”Terangkan maksud “muatan haba tentu air = 4 200 J kg –1 o C –1 ”[1 mark](ii) Calculate the heat removed when the water is cooled to 0 o C.Hitungkan haba yang dikeluarkan apabila air itu disejukkan hingga ke 0 o C.[2 marks](iii) Calculate the heat removed when the water at 0 o C is frozen into ice at 0 o C.Hitungkan haba yang dikeluarkan apabila air pada 0 o C dibekukan menjadiais pada 0 o C.[2 marks]
papercollection12 (a) Diagram 12.1 shows a magnet being used to induce a current in a coil.Rajah 12.1 menunjukkan sebatang magnet digunakan untuk mengaruh arus didalam suatu gegelung.26XNSGMagnet moved towards coilMagnet digerakkan ke arah gegelungDiagram 12.1 / Rajah 12.1(i) State Lenz's law.Nyatakan hukum Lenz.[1 mark](ii) Explain how current is induced in the coil. State the pole at X.Terangkan bagaimana arus diaruh di dalam gegelung itu. Nyatakan kutubdi X.[4 marks]
papercollection27(b) Diagram 12.2 shows an alternating current generator which will be used to supplya large direct current to an electrical component R.Rajah 12.2 menunjukkan sebuah penjana arus ulangalik yang digunakan untukmembekal suatu arus terus yang besar kepada sebuah komponen elektrik R.Rotation / PutaranRectification circuitLitar rektifikasiRDiagram 12.2 / Rajah 12.2Table 12.1 shows the characteristics of four alternating current generators, W, X,Y and Z.Jadual 12.1 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi empat penjana arus ulangalik W, X, Yand Z.GeneratorPenjanaNumber of turns of coilBilangan lilitan gegelungStrength of magnetsKekuatan magnetW 6 000 High / TinggiX 10 000 Medium / SederhanaY 9 000 High / TinggiZ 5000 Medium / SederhanaTable 12.1 / Jadual 12.1
papercollection28Table 12.2 shows the characteristics of four rectification circuits, A, B, C and D tobe used with one of the generators.Jadual 12.2 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi empat litar rektifikasi, A, B, C dan D yangakan digunakan bersama satu daripada penjana ituRectification circuitLitar rektifikasiArrangement of componentsSusunan komponenCapacitance of CKapasitans bagi COne diode / Satu diodACRLargeBesarOne diode / Satu diodBCRSmallKecilFour diodes / Empat diodCLargeBesarCRFour diodes / Empat diodDSmallKecilCRTable 12.2 / Jadual 12.2
papercollection29(c)You are asked to investigate the characteristics of the four generators shown inTable 12.1 and the four rectification circuits shown in Table 12.2.Study the specifications of all the four generators and four rectification circuitsfrom the following aspects:– Number of turns of coil in the generator– Strength of the magnets in the generator– Arrangement of components in the rectification circuit– Capacitance of the capacitor in the rectification circuit.Explain the suitability of the aspects.State the most suitable generator and the most suitable rectification circuit to beused.Anda dikehendaki menyiasat ciri-ciri bagi empat penjana dalam Jadual 12.1 danempat litar rektifikasi dalam Jadual 12.2.Kaji spesifikasi bagi empat penjana dan empat litar rektifikasi dari aspek berikut:– Bilangan lilitan bagi gegelung penjana– Kekuatan magnet bagi penjana– Susunan komponen dalam litar rektifikasi– Kapasitans bagi kapasitor dalam litar rektifikasiJelaskan aspek-aspek tersebut.Nyatakan penjana yang paling sesuai dan litar rektifikasi yang paling sesuaidigunakan.[10 marks]Diagram 12.3 shows a transformer with a bulb at its output terminals. The bulblights up at normal brightness.Rajah 12.3 menunjukkan sebuah transformer dengan sebuah mentol di terminaloutputnya. Mentol itu menyala dengan kecerahan normal.I P = 0.125 A240 V12 V 24 W(i)Diagram 12.3 / Rajah 12.3State the type of transformer.Nyatakan jenis transformer itu.N P N S = 150[1 mark](ii) Determine the value of N P .Tentukan nilai N P . [2 marks](iii) Calculate the efficiency of the transformer.Hitung kecekapan transformer itu.[2 marks]END OF QUESTION PAPERKERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
papercollection30INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATESMAKLUMAT UNTUK CALON1. This question paper consists of three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.Kertas soalan ini mengandungi tiga bahagian: Bahagian A, Bahagian B danBahagian C.2. Answer all questions in Section A. Write your answers for Section A in the spacesprovided in the question paper.Jawab semua soalan dalam Bahagian A. Jawapan anda bagi Bahagian A hendaklahditulis pada ruang yang disediakan dalam kertas soalan ini.3. Answer one question from Section B and one question from Section C. Write youranswers for Section B and Section C on your own writing paper.Jawab satu soalan daripada Bahagian B dan satu soalan daripada Bahagian C.Jawapan anda bagi Bahagian B dan Bahagian C hendaklah ditulis dalam kertas tulisanda sendiri.4. Show your working, it may help you to get marks.Tunjukkan kerja mengira, ini membantu anda mendapatkan markah.5. If you wish to change your answer, cross out the answer that you have done. Then writedown the new answer.Jika anda hendak menukar sesuatu jawapan, batalkan jawapan yang telah dibuat.Kemudian tulis jawapan yang baru.6. The diagrams in the questions provided are not drawn to scale unless stated.Rajah yang mengiringi soalan tidak dilukis mengikut skala kecuali dinyatakan.7. A list of formulae is provided on page 2.Satu senarai formula disediakan di halaman 2.8. The marks allocated for each question or part question are shown in brackets.Markah yang diperuntukkan bagi setiap soalan atau ceraian soalan ditunjukan dalamkurungan.9. You are advised to spend 90 minutes to answer questions in Section A, 30 minutes forSection B and 30 minutes for Section C.Anda dinasihati supaya mengambil masa 90 minit untuk menjawab soalan dalamBahagian A, 30 minit untuk Bahagian B dan 30 minit untuk Bahagian C.10. You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator.Anda dibenarkan menggunakan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh diprogram.
papercollection1SULITNO. KAD PENGENALANANGKA GILIRANNAMA: …….…………......…….............……..………. TINGKATAN: …….....………PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUASEKOLAH MENENGAHNEGERI KEDAH DARUL AMANPEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM 2009 4531/3<strong>PHYSICS</strong>Kertas 311 jam Satu jam tiga puluh minit2JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU1. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalam dwibahasa.Untuk Kegunaan Pemeriksa2. Soalan dalam bahasa Inggeris mendahuluisoalan yang sepadan dalam bahasaMelayu.3. Calon dibenarkan menjawab keseluruhanatau sebahagian soalan sama ada dalambahasa Inggeris atau bahasa Melayu.4. Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat dihalaman belakang kertas soalan ini.BahagianABSoalanJumlahMarkahpenuh1 162 123 124 12MarkahdiperolehKertas soalan ini mengandungi 15 halaman bercetakSULIT
papercollection2Section ABahagian A[28 marks]Answer all questions in this section.Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini.1 A student carries out an experiment to study the relationship between the angle ofincidence, i, and the angle of refraction, r, when a light ray passes from air to asemicircular glass block. The apparatus set-up for this experiment is shown in Diagram1.1.Seorang murid menjalankan satu eksperimen untuk mengkaji hubungan antara suduttuju, i, dan sudut biasan, r, apabila sinar cahaya merambat dari udara ke blok kacasemibulatan. Susunan radas bagi eksperimen ini ditunjukkan pada Rajah 1.1.Semi-circular glass blockBlok kaca semibulatanRefracted raySinar biasanrIncident raySinar tujuiTo power supplyKe bekalan kuasaRay boxKotak sinarDiagram 1.1 / Rajah 1.1The ray box is adjusted so that a ray of light enters the semicircular glass block at anangle of incidence, i = 15 o .The angle of refraction, r, is measured with a protractor.The experiment is repeated with angles of incidence, i = 30 o , 45 o , 60 o and 75 o .The corresponding measurements made by the protractor are shown in Diagrams 1.2,1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6.Kotak sinar dilaraskan supaya satu sinar cahaya memasuki blok kaca semibulatanpada sudut tuju, i = 15 o .Sudut biasan, r, diukur oleh sebuah protraktor.Pengukuran sepadan yang dibuat oleh protraktor ditunjukkan pada Rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5 dan 1.6.
papercollection3i = 15 osin i = …………r = ……….sin r = …………15 oDiagram 1.2 / Rajah 1.2i = 30 osin i = …………r = ……….sin r = …………30 oDiagram 1.3 / Rajah 1.3
papercollection4i = 45 osin i = …………r = ……….sin r = …………45 oDiagram 1.4 / Rajah 1.4i = 60 osin i = …………r = ……….sin r = …………60 oDiagram 1.5 / Rajah 1.5
i = 75 osin i = …………r = ……….sin r = …………575 o papercollectionDiagram 1.6 / Rajah 1.6(a)For the experiment described on page 2, identify:Bagi eksperimen yang diterangkan di halaman 2, kenal pasti:(i) The manipulated variablePembolehubah dimanipulasikan.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) The responding variablePembolehubah bergerak balas.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](iii) The constant variablePembolehubah dimalarkan.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection6(b)For this part of the question, write your answers in the spaces provided in thecorresponding diagrams.Untuk bahagian soalan ini, tulis jawapan anda dalam ruang yang disediakandalam rajah-rajah yang sepadan.Based on Diagrams 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6:Berdasarkan Rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 dan 1.6:(i)Record the readings, r, of the protractor.Catat bacaan, r, protraktor itu.[2 marks](ii) For each value of i, calculate and record the value of sin i.Bagi setiap nilai i, hitung dan catat nilai sin i.[1 mark](iii) Calculate sin r for each value of r in 1(b)(i).Record the value of sin r.Hitung sin r untuk setiap nilai r di 1(b)(i).Catat nilai sin r.[2 marks](c) Tabulate your results for all values of i, sin i and sin r in the space below.Jadualkan keputusan anda bagi semua nilai i, sin i dan sin r dalam ruang dibawah.(d) On the graph paper provided, plot a graph of sin i against sin r.Pada kertas graf yang disediakan, lukis graf sin i melawan sin r.[2 marks][5 marks](e) Based on your graph in 1(d), state the relationship between sin i and sin r.Berdasarkan graf anda di 1(d), nyatakan hubungan antara sin i dan sin r.....................................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection7Graph of sin i against sin rGraf sin i melawan sin r
papercollection82 A student carries out an experiment to investigate the relationship between the collectorcurrent, I C , and the base current, I B , for a transistor.Seorang pelajar menjalankan eksperimen untuk mencari hubungan antara aruspengumpul dengan arus tapak bagi suatu transistor.The result of this experiment is shown in the graph of I C against I B in Diagram 2.Keputusan eksperimen itu ditunjukkan oleh graf I C melawan I B pada Rajah 2.I C / mAGraph of I C against I BGraf I C melawan I B120100806040200 100 200 300 400 500 600I B / μADiagram 2 / Rajah 2
papercollection9(a) Based on the graph in Diagram 2,Berdasarkan graf pada Rajah 2,(i) State the relationship between I C and I B .Nyatakan hubungan antara I C dan I B ..…......................................................................................................................[1 mark](ii) Determine the value of I B when I C = 100 mA.Show on the graph, how you determine the value of I B .Tentukan nilai I B apabila I C = 100 mA.Tunjukkan pada graf bagaimana anda menentukan nilai I B ..…......................................................................................................................[3 marks](b) (i) Calculate the gradient, m, of the graph.Show on the graph how you determine the gradient m.Hitung kecerunan, m, bagi graf itu.Tunjukkan pada graf bagaimana anda menentukan kecerunan m.m = …………………………[3 marks](ii) The gradient of the graph represents amplification factor of the transistor.What is meant by amplification factor?Kecerunan graf mewakili faktor amplifikasi suatu transistor.Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan faktor amplifikasi?.…......................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection10(c) The emitter current, I E , is related to the base current, I B , and collector current, I Cthrough the formula;Arus pengeluar, I E , ada hubungan dengan arus tapak, I B , dan arus pengumpul, I Cmelalui formula;I E = I B + I CDetermine the emitter current, I E, , when the base current, I B = 350 μA.Show on the graph, how you determine the value of collector current, I C .Tentukan arus pengeluar apabila arus tapak, I B = 350 μA. Tunjukkan pada grafbagaimana anda mendapatkan nilai arus pengumpul, I C .[3 marks](d)State one precaution that should be taken during the experiment.Nyatakan satu langkah berjaga-jaga yang perlu diambil semasa eksperimendijalankan.....................................................................................................................................[1 mark]
papercollection11Section BBahagian B[12 marks]Answer any one question from this section.Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini.3 Diagram 3 shows two pails, R and S, with R containing more water than S. Both thepails are exposed to sunlight. After a few hours it was observed that the water in pail Sis hotter than the water in pail R.Rajah 3 menunjukkan dua baldi, R dan S, dengan R mengandungi lebih banyak airdaripada baldi S. Kedua-dua baldi didedahkan kepada cahaya matahari. Selepasbeberapa jam diperhatikan air dalam baldi S lebih panas daripada air dalam baldi R.SunlightSinar matahariSunlightSinar matahariRSDiagram 3 / Rajah 3Based on the information and observation:Berdasarkan maklumat dan pemerhatian tersebut:(a)State one suitable inference.Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai.[1 mark](b) State one suitable hypothesis.Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang sesuai.[1 mark](c)With the use of apparatus such as beaker, thermometer, immersion heater andother apparatus, describe one experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in3(b).Dengan menggunakan radas seperti bikar, termometer, pemanas rendam danradas lain, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat hipotesis yang dinyatakandi 3(b).
papercollection12In your description, state clearly the following:Dalam penerangan anda , nyatakan dengan jelas perkara berikut:(i)(ii)The aim of the experiment.Tujuan eksperimen.The variables in the experiment.Pembolehubah dalam eksperimen.(iii) The list of apparatus and materials.Senarai radas dan bahan.(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus.Susunan radas.(v)The procedure of the experiment which should include one method ofcontrolling the manipulated variable and one method of measuring theresponding variable.Prosedur eksperimen yang mesti termasuk satu kaedah mengawalpembolehubah dimanipulasi dan satu kaedah mengukur pembolehubahbergerak balas.(vi) The way you tabulate the data.Cara anda menjadualkan data.(vii) The way you analyse the data.Cara anda menganalisis data.[10 marks]
papercollection4 A student who moves his ear near a vibrating tuning fork hears loud and soft soundsalternately.Diagram 4.1 shows the positions of loud sounds are closer together.Diagram 4.2 shows the positions of loud sound are further apart.13Seorang pelajar yang menggerakkan telinganya dekat dengan tala bunyi yang bergetarmendengar bunyi kuat dan lemah secara berselang-seli.Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan kedudukan bunyi-bunyi kuat lebih rapat.Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan kedudukan bunyi-bunyi kuat lebih jauh daripada satu samalain.Ear of studentTelinga pelajarEar of studentTelinga pelajarL L L L L L LLArm of tuning forkLengan tala bunyiL : Loud sound heardL : Bunyi kuat didengarTuning fork : arms further apartTala bunyi : jarak antara lenganlebih jauhTuning fork : arms nearerTala bunyi : jarak antara lenganlebih rapatDiagram 4.1 / Rajah 4.1 Diagram 4.2 / Rajah 4.2Based on the information and observation:Berdasarkan maklumat dan pemerhatian tersebut:(a) State one suitable inference.Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai.(b) State one suitable hypothesis.Nyatakan satu hipotesis yang sesuai.[1 mark][1 mark]
papercollection14(c)With the use of apparatus such as two loudspeakers, signal generator and otherapparatus, describe one experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in 4(b).Dengan menggunakan radas seperti dua pembesar suara, penjana isyarat danradas lain, terangkan satu eksperimen untuk menyiasat hipotesis yang dinyatakandi 4(b).In your description, state clearly the following:Dalam penerangan anda, nyatakan dengan jelas perkara berikut:(i)The aim of the experiment.Tujuan eksperimen.(ii) The variables in the experiment.Pembolehubah dalam eksperimen.(iii) The list of apparatus and materials.Senarai radas dan bahan.(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus.Susunan radas.(v)The procedure of the experiment which should include one method ofcontrolling the manipulated variable and one method of measuring theresponding variable.Prosedur eksperimen yang mesti termasuk satu kaedah mengawalpembolehuhah dimanipulasikan dan satu kaedah mengukur pembolehubahbergerak balas.(vi) The way you tabulate the data.Cara anda menjadualkan data.(vii) The way you analyse the data.Cara anda menganalisis data.[10 marks]END OF QUESTION PAPERKERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
papercollection15INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATESMAKLUMAT UNTUK CALON1. This question paper consists of two sections: Section A and Section B.Kertas soalan ini mengandungi dua bahagian: Bahagian A dan Bahagian B.2. Answer all questions in Section A. Write your answers for Section A in the spaceprovided in this question paper.Jawab semua soalan dalam Bahagian A. Jawapan anda bagi Bahagian A hendaklahditulis pada ruang yang disediakan dalam kertas soalan ini.3. Answer one question from Section B. Write your answers for Section B on your ownwriting paper. You may use equations, diagram, tables, graphs and other suitablemethods to explain your answers.Jawab satu soalan daripada Bahagian B. Tulis jawapan bagi Bahagian B pada kertastulis anda sendiri. Anda boleh menggunakan persamaan, rajah, jadual, graf dan caralain yang sesuai untuk menjelaskan jawapan anda.4. Show your working, it may help you to get marks.Tunjukkan kerja mengira, ini membantu anda mendapatkan markah.5. The diagrams in the questions are not drawn to scale unless stated.Rajah yang mengiringi soalan tidak dilukis mengikut skala kecuali dinyatakan.6. The marks allocated for each question or sub-part of a question are shown in brackets.Markah yang diperuntukkan bagi setiap soalan atau ceraian soalan ditunjukkan dalamkurungan.7. If you wish to change your answer, cross out the answer that you have done. Then writedown the new answer.Jika anda hendak menukar jawapan, batalkan jawapan yang telah dibuat. Kemudiantulis jawapan yang baru.8. You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator.Anda dibenarkan menggunakan kalkulator saintifik yang tidak boleh diprogram.9. You are advised to spend 60 minutes to answer questions in Section A and 30 minutesfor Section B.Anda dinasihati supaya mengambil masa 60 minit untuk menjawab soalan dalamBahagian A dan 30 minit untuk Bahagian B.
papercollection4531PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUASEKOLAH MENENGAHNEGERI KEDAH DARUL AMANPEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM 2009<strong>PHYSICS</strong>PERATURAN PEMARKAHANPeraturan pemarkahan ini mengandungi 16 halaman bercetak4531
papercollection2PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SPM 2009KEDAH DARUL AMANPERATURAN PEMARKAHAN<strong>PHYSICS</strong>PAPERMARKS<strong>Paper</strong> 1 50<strong>Paper</strong> 2 100<strong>Paper</strong> 3 40Total 190Jumlah markah diskalakan kepada 100%<strong>PHYSICS</strong><strong>Paper</strong> 11 C 26 B2 D 27 B3 D 28 A4 B 29 C5 D 30 A6 A 31 C7 B 32 B8 A 33 C9 D 34 D10 C 35 A11 B 36 D12 D 37 B13 C 38 A14 C 39 A15 A 40 A16 D 41 D17 A 42 B18 D 43 A19 C 44 B20 D 45 B21 B 46 B22 A 47 A23 A 48 C24 C 49 B25 B 50 A
papercollection3<strong>PHYSICS</strong><strong>Paper</strong> 2SECTION AMARKNO.MARKING CRITERIASUB TOTAL1 (a) (i) State the physical quantity correctly 1- Voltage/potential difference(ii) State the error correctly 1- Zero error//systematic error(b) (i) State the instrument correctly 1- Y/micrometer(ii) State the reason correctly 1- The scale has a smaller division 42(a) (i) State the explanation correctly 1- energy is used to break the bonds//change the state of matter(ii) State the explanation correctly 1- energy is used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules(b) Correct substitution 1- 0.2 x 3.36 x 10 5Correct answer and correct unit 1- 6.72 x 10 4 J(c) Mark on the box correctly 1- There is no net transfer of energy between the water and thesurroundings53(a) State the unit correctly 1- N m —2 // kg m —1 s —2(b) State one factor correctly 1- depth//density(c) (i) Correct substitution 1- 1010 x 2.5 x 10Correct answer and correct unit 1- 25250 N(ii) Show the substitution correctly 1- 125000 - 25250Correct answer and correct unit 1- 99750 N6
papercollection4NO.MARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL4(a) Name component T correctly 1- Thermistor//heat sensitive resistor(b)Underline the words correctly- resistance decreases- I B increases11(c) (i) Correct answer and correct unit 1- 0.08 s(ii) Correct substitution 11-0.08Correct answer and correct unit 1- 12.5 Hz(iii) Sketch the trace correctly 1- Sinusoidal with four complete cycles 75(a) (i) Compare the speed of light correctly 1- Speed of light is higher in air(ii) Compare the speed of light correctly 1- Speed of light is higher in air(iii) State the relationship correctly 1- If the speed of light decreases, then the light ray will bendtowards the normal(iv) State the phenomenon correctly 1- refraction(b) (i) Draw the light rays correctly- At least one light ray from point P bend away from the normalafter emerging into the air- Extrapolate the ray to point Q11(ii) Correct substitution 11.6-1.2Correct answer with no unit in decimal 1- 1.33 8
papercollection5NO.MARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL6(a) State the meaning correctly 1- Time for the activity of the radioactive substance to become halfof the original activity // Time taken for half of the mass ofradioactive substance to decay(b) (i) State the half life correctly- X : 10 minutes- Y : 5 minutes11(ii)State the answer correctly- X : 50 %- Y : 25 %11(c) State the comparison correctly 1- The decay rates for substance X is slower//vice versaState the relationship correctly 1- The shorter the half life, the higher the decay rate(d) Give the reason correctly 1- Background radiation 87(a) State the energy changes correctly 1- electrical energy to (gravitational) potential energy(b) (i) Correct substitution 1- 1.7 x 10Correct answer and correct unit- 17 W1(ii) Correct substitution 12x10x1.5-2.5Correct answer with correct unit- 12 W 1(iii) Correct substitution 112x100%17Correct answer with correct unit- 70.6 %1(c) State the change on the ammeter correctly 1- ammeter reading decreasesGive explanation correctly 1- less work done // less power required(d)Give one suggestion correctly- lubricate the moving parts to reduce friction 1 10
papercollection6NO.MARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL8(a) (i) Name the law correctly 1- Hooke’s Law(ii) Mark a cross on each line correctly 1 + 1- All correct (2 marks)- 1 or 2 correct (1 mark)(b) (i) State the energy correctly 1- Elastic potential energy(ii) Determine the force correctly 1- From the graph, F = 60 NCorrect substitution- ½ (60)(8)// ½ (60)(0.08)1Correct answer with correct unit 1- 240 N cm // 2.4 J // 2.4 N m(c) (i) State the maximum weight correctly 1- 80 N(ii) Name the two springs correctly 1 + 1- Spring P- Spring Q(iii) Give the choice correctly 1- Spring QGive the explanation correctly 1- More sensitive//smaller force constant 12
papercollection7SECTION BMARKNOMARKING CRITERIASUB TOTAL9(a) State the meaning correctly 1- Product of mass and velocity / /momentum = mass x velocity 1(ii)State the total momentum in Diagram 9.1 correctly- ZeroCompare the total momentum correctly- Total momentum before the bullet is fired = total momentumafter the bullet is fired.Compare the magnitude of the momentum of the bullet andpistol correctly- EqualCompare the direction of the momentum of the bullet andpistol correctly- Opposite1111Name the physics principle correctly- Principle of Conservation of Momentum15(b)Describe the propulsion of a rocket engine correctly- Liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen/fuel is pump into thecombustion chamber for combustion- The exhaust gas is ejected out of the rocket nozzle at high speed.- The ejected exhaust gas at high speed has a large momentum.- According to the Principle of Conservation of Momentum, therocket acquires a large momentum forward1111 4(c) State aspect of blade correctly 1- Using bigger blades/increase the number of blades/increase thespeed of bladeState reason for aspect of forces and motion correctly- Increase the air intakeState aspect of material of blade correctly- Blade made of strong materialState reason for aspect of material of blade correctly- Can withstand strong pressure/it will not break easilyState aspect of fuel injector correctly- Increase the number of fuel injectors//add more fuel injectorsState reason for aspect of fuel injector correctly- More fuel to be burnt to produce greater thrust11111
papercollection8State aspect of combustion chamber correctly- Increase the size of the combustion chamberState reason for aspect of combustion chamber correctly- More space for the fuel to be burntState aspect of nozzle correctly- Decrease the diameter of the nozzle111State reason for aspect of nozzle correctly- Exhaust gas ejected at higher velocity/higher momentum1 1020
papercollection9MARKNOMARKING CRITERIASUB TOTAL10(a) (i) State the meaning correctly 1- A wave in which the vibration of particles in the medium isparallel to the direction of propagation of the wave. 1(ii)Explain the production of sound waves correctly- When a tuning fork vibrates, layers of air vibrate- The particles of air undergo s series of compression andrarefaction- Sound energy is propagated through the air in the form ofwaves1111 4(b) (i) Compare the amplitudes of the wave form correctly- The amplitude in Diagram 10.2 is higher1(ii)(iii)(iv)(v)Compare the peak values of the wave form correctly- The peak value in Diagram 10.2 is higherState the relationship between amplitude and peak valuecorrectly- The higher the amplitude, the higher the peak valueState the relationship between the peak value and loudnesscorrectly- The higher the peak value, the louder is the sound.State the relationship between the loudness and the amplitudecorrectly- The higher the amplitude, the louder is the sound1111 5(c) (i) Suggest the type of frequency correctly 1- The boat must use high frequency sound wavesGive the reason correctly- Smaller wavelength, less diffractedSuggest the type of energy correctly- High energy wavesGive the reason correctly- High penetrating power1114(ii)Suggest the list of equipments needed for the measurementTransmitterReceiverSound generatorCRO[Any of the three above] 3(iii)State the method of measuring the time- The time taken, t from the transmitter to the receiver is recordedby the CRO- The speed of the sound wave, v in water is given- The depth of the sea, d = 2vt111320
papercollection10SECTION CNOMARKING CRITERIA11(a) (i) State the explanation correctly- Temperature of the coolant decreases- Speed of the molecules decreases- Distance between molecules decreasesMARKSUB TOTAL111 3(ii)State the explanation correctly- When coolant changes from a liquid to a gas, latent heat isrequired.- Latent heat is obtained from the interior of the refrigerator.11 2(b)State the specific latent heat of vaporisation and reasoncorrectly1 High specific latent heat of vaporization2 Rate of heat removed is faster1+1State the boiling point and reason correctly 1+13 Coolant with low boiling point4 Easily can to vapour/gasState the specific heat capacity and reason correctly 1+15 Low specific heat capacity6 Can be heat up (cool down) fasterState the diameter and reason correctly 1+17 Big diameter8 Can carry more coolantState most suitable choice of coolant and justification correctly 1QLow specific latent heat of vaporization and low boiling pointState most suitable pipe and justification correctly 1ZLow specific heat capacity and big diameter10(c) (i)State the meaning correctlyThe quantities of heat required to change the temperature of 1 kgof water by 1 o C is 4200 J.1(ii)Correct substitution0.5 x 4200 x 30 1Correct answer and correct unit63 000 J 1(iii)Correct substitution0.5 x 3.34.x 10 5 1Correct answer and correct unit1.67 x 10 5 J 1 520
papercollectionNO12(a) (i)(ii)(b)11MARKING CRITERIAState Lenz’s Law correctly- The direction of the induced current is such as to oppose thechange causing it.State the explanation correctly- The solenoid experiences a change in the magnetic flux/magneticfield (lines)- According to Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction- An e.m.f. is induced in the coil- X is north poleState the suitable number of turns of coil in the generator andreason correctly- High number of turns of coil- Larger force acting on the coil / higher electromagnetic fieldstrengthState the suitable strength of the magnets in the generator andreason correctly- High strength magnets- Larger force acting on the coilState the suitable arrangement of components in therectification circuit- Using 4 diodes and a capacitor- 4 diodes to produce full-wave rectification and capacitor as asmootherState the suitable capacitance of the capacitor in therectification circuit- Large capacitance- To produce a constant output voltageState most suitable choice of generator and justificationcorrectly- Y and high number of turns of coil and high strength of magnetsState most suitable choice rectification circuit and justificationcorrectly- C, 4 diodes and a capacitor with high capacitanceMARKSUB TOTAL111111+11+11+11+111(c) (i) State the type of transformer correctly- Step-down transformer(ii) Correct substitution 1(240)(150)12Correct answer and no unit 13000(iii) Correct substitution241´ 100(0.125)(240)Correct answer with unit 180% // 0.8 5201
papercollectionNO12<strong>PHYSICS</strong><strong>Paper</strong> 3SECTION AMARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL1(a) (i) State the manipulated variable correctlyAngle of incidence / i 1 1(ii)(iii)State the responding variable correctlyAngle of refraction / r // sin r 1 1State the constant variable correctlyGlass block // Semicircular glass block // Refractive index 1 1(b) (i) Record the readings of r correctlyDiagram 1.2 : 11 o2 2Diagram 1.6 : 41 oDiagram 1.3 : 20 oDiagram 1.4 : 29 oDiagram 1.5 : 36 oNote : 1. All 5 values correct – 2 marks2. 3 or 4 values correct – 1 mark(ii)(iii)State the values of sin i correctlyDiagram 1.2 : 0.2588Diagram 1.3 : 0.5000Diagram 1.4 : 0.7071Diagram 1.5 : 0.8660Diagram 1.6 : 0.9659Note : 1. Accept e.c.f. from (b)(i)2. All 5 values correct – 2 marks3. 3 or 4 values correct – 1 mark4. Not necessary to have consistent number of d.p.State the values of sin r correctlyAll 5 values of sin r correctDiagram 1.2 : 0.1908Diagram 1.3 : 0.3420Diagram 1.4 : 0.4848Diagram 1.5 : 0.5878Diagram 1.6 : 0.6561Note : 1. Accept e.c.f. from (b)(i)2. All 5 values correct – 2 marks3. 3 or 4 values correct – 1 mark4. Not necessary to have consistent number of d.p.1 12 2
papercollection13(c)Tabulate the results for i, sin i, r and sin r correctlyi sin i r sin r15 o 0.2588 11 o 0.190830 o 0.5000 20 o 0.342045 o 0.7071 29 o 0.484860 o 0.8660 36 o 0.587875 o 0.9659 41 o 0.6561Table with 4 columns correctly labelledsin i and sin r consistent to 2, 3 or 4 decimal places11 2(d)Draw a complete graph of sin i against sin rGive a tick (ü) based on the following:A • sin i at the y-axis, sin r at the x-axisB • Uniform scale at both axesC • 5 points plotted correctly[Note : 4 points plotted correctly : ü]D • Straight line of best fit is drawnE • Minimum size of graph 5 x 4 big squares(Big square : 2 cm x 2 cm)(From the origin to the last point)üüüüüüMarks awarded :(e)Number of ü Marks6 ü 54 – 5 ü 43 ü 32 ü 21 ü 1State the correct relationship between sin i and sin rsin i is directly proportional to sin r 1 11655
papercollectionNO14MARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL2(a) (i) State the correct relationshipI C increases linearly with I B // I C is directly proportional to I B 1 1(ii)Determine the value of I B correctlyI B = 500 μA 1Draw the extrapolation line to the point (500, 100) or beyond 1Draw the lines I C = 100 mA and I B = 500 μA 1 3(b) (i) Calculate the gradient of the graph, m, and state the value of m- Draw a sufficiently large triangle 1- Correct substitution (Follow candidate’s triangle) 1- State the correct value200 1 3(ii)State the correct meaningThe ratio of the change in I C to the change in I B //DIC1 1DIB(c)Determine the value of I E and state the correct value of I E- Intrapolation line from I B = 350 μA to the given line and from thegiven line to the I C – axis 1- State the correct value of I CI C = 70 mA // 70 000 μA 1- State the correct value of I E70.35 mA // 70 350 μA 1 3(d)State one correct precaution- Position of the eyes such that line of sight is perpendicular to thescale of the meter to avoid parallax error1- Current is switched off after readings are taken1Max1112
papercollectionNO15SECTION BMARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL3 (a) State a suitable inferenceThe mass // volume affects the rise in temperature // temperature 1 1(b) State a relevant hypothesisThe greater the mass // volume, the smaller the rise in temperature// temperature 1 1(c) Describe a complete and suitable experimental framework(i)(ii)State the aim of experimentTo investigate the relationship between the mass and rise intemperature (of water) 1State the manipulated variable and the responding variableManipulated variable : MassResponding variable : Increase in temperature1State the constant variableConstant variable : Heat supplied // Time of heating //Power of the heater //1(iii)(iv)(v)(vi)List out the important apparatus and materialsBeaker, water, thermometer, immersion heater, stopwatch, balance 1for measuring massDraw or describe a functionable arrangement of the apparatus1State the method of controlling the manipulated variablePut a mass of 100 g of water in a beaker 1State the method of measuring the responding variableSwitch on the heater for 5 minutes and record the temperature rise. 1(vii)(viii)State how the procedure is repeated to obtain at least 5 sets ofresultsRepeat the experiment with 150 g, 200 g, 250 g, 300 g and 350 gof water.Tabulate the data1(ix)Mass of water / g Temperature rise / o C100150200250300350 1State how data will be analysedThe graph of temperature rise against mass is drawn 1 10Note : Mark accordingly if the manipulated variable is volume. 12
papercollectionNO.16MARKING CRITERIAMARKSUB TOTAL4 (a) State a suitable inferenceThe distance / separation between the arms affect the distance /separation between the loud sounds 1 1(b)(c)State a relevant hypothesisThe smaller the distance / separation between the arms, the greateris the distance / separation between the loud sounds 1 1Describe a complete and suitable experimental framework(i)State the aim of experimentTo investigate the relationship between the separation betweentwo loudspeakers and the distance between the position of theloud sounds 1(ii)State the manipulated variable and the responding variableManipulated variable : separation between loudspeakersResponding variable : distance between position of loud soundsState the constant variableConstant variable : Frequency of the sound // wavelength ofthe sound // Distance of the line ofobservation to the loudspeakers11(iii)List out the important apparatus and materialsTwo loudspeakers, signal generator, metre rule / measuring tape,(microphone, cathode ray oscilloscope) 1(iv) Draw or describe a functionable arrangement of the apparatus 1(v)(vi)(vii)State the method of controlling the manipulated variableThe two loudspeakers are placed at a distance, a = 0.4 m apart. 1State the method of measuring the responding variableThe positions of two successive loud sounds is determined and thedistance, x, between them is measured with a metre rule 1State how the procedure is repeated to obtain at least 5 sets ofresultsThe procedure is repeated for the values of a = 0.8 m, 1.2 m, 1.6m, 2.0 m and 2.4 m 1(viii) Tabulate the dataa / mx / m0.40.81.21.62.02.4 1(ix)State how data will be analyzedA graph of x against a is drawn 1 1012