Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
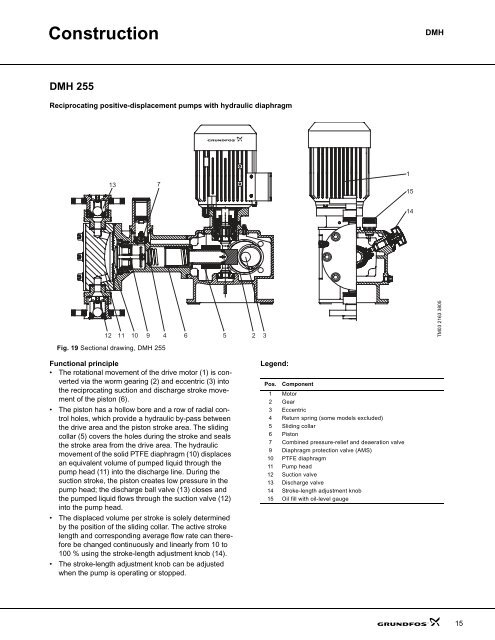
ConstructionDMHDMH 255Reciprocating positive-displacement pumps with hydraulic diaphragm1371151412 11 10 9 4 65 2 3Fig. 19 Sectional drawing, DMH 255TM03 2163 3805Functional principle• The rotational movement of the drive motor (1) is convertedvia the worm gearing (2) and eccentric (3) intothe reciprocating suction and discharge stroke movementof the piston (6).• The piston has a hollow bore and a row of radial controlholes, which provide a hydraulic by-pass betweenthe drive area and the piston stroke area. The slidingcollar (5) covers the holes during the stroke and sealsthe stroke area from the drive area. The hydraulicmovement of the solid PTFE diaphragm (10) displacesan equivalent volume of pumped liquid through thepump head (11) into the discharge line. During thesuction stroke, the piston creates low pressure in thepump head; the discharge ball valve (13) closes andthe pumped liquid flows through the suction valve (12)into the pump head.• The displaced volume per stroke is solely determinedby the position of the sliding collar. The active strokelength and corresponding average flow rate can thereforebe changed continuously and linearly from 10 to100 % using the stroke-length adjustment knob (14).• The stroke-length adjustment knob can be adjustedwhen the pump is operating or stopped.Legend:Pos. Component1 Motor2 Gear3 Eccentric4 Return spring (some models excluded)5 Sliding collar6 Piston7 Combined pressure-relief and deaeration valve9 Diaphragm protection valve (AMS)10 PTFE diaphragm11 Pump head12 Suction valve13 Discharge valve14 Stroke-length adjustment knob15 Oil fill with oil-level gauge15