A Scalar Homotopy Method for Solving an Over ... - TechScience
A Scalar Homotopy Method for Solving an Over ... - TechScience
A Scalar Homotopy Method for Solving an Over ... - TechScience
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
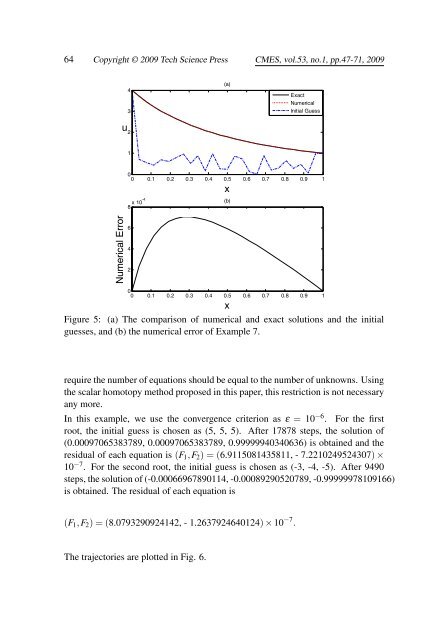
64 Copyright © 2009 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.53, no.1, pp.47-71, 2009u432(a)ExactNumericalInitial Guess100 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1x(b)8 x 10-4 xNumerical Error64200 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1Figure 5: (a) The comparison of numerical <strong>an</strong>d exact solutions <strong>an</strong>d the initialguesses, <strong>an</strong>d (b) the numerical error of Example 7.require the number of equations should be equal to the number of unknowns. Usingthe scalar homotopy method proposed in this paper, this restriction is not necessary<strong>an</strong>y more.In this example, we use the convergence criterion as ε = 10 −6 . For the firstroot, the initial guess is chosen as (5, 5, 5). After 17878 steps, the solution of(0.00097065383789, 0.00097065383789, 0.99999940340636) is obtained <strong>an</strong>d theresidual of each equation is (F 1 ,F 2 ) = (6.9115081435811, - 7.2210249524307) ×10 −7 . For the second root, the initial guess is chosen as (-3, -4, -5). After 9490steps, the solution of (-0.00066967890114, -0.00089290520789, -0.99999978109166)is obtained. The residual of each equation is(F 1 ,F 2 ) = (8.0793290924142, - 1.2637924640124) × 10 −7 .The trajectories are plotted in Fig. 6.