Course Handout - Student Welfare Division - BITS Pilani
Course Handout - Student Welfare Division - BITS Pilani
Course Handout - Student Welfare Division - BITS Pilani
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
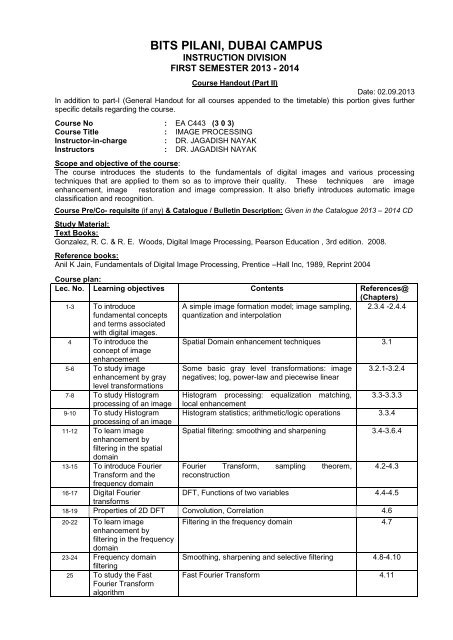
<strong>BITS</strong> PILANI, DUBAI CAMPUSINSTRUCTION DIVISIONFIRST SEMESTER 2013 - 2014<strong>Course</strong> <strong>Handout</strong> (Part II)Date: 02.09.2013In addition to part-I (General <strong>Handout</strong> for all courses appended to the timetable) this portion gives furtherspecific details regarding the course.<strong>Course</strong> No : EA C443 (3 0 3)<strong>Course</strong> Title : IMAGE PROCESSINGInstructor-in-charge : DR. JAGADISH NAYAKInstructors : DR. JAGADISH NAYAKScope and objective of the course:The course introduces the students to the fundamentals of digital images and various processingtechniques that are applied to them so as to improve their quality. These techniques are imageenhancement, image restoration and image compression. It also briefly introduces automatic imageclassification and recognition.<strong>Course</strong> Pre/Co- requisite (if any) & Catalogue / Bulletin Description: Given in the Catalogue 2013 – 2014 CDStudy Material:Text Books:Gonzalez, R. C. & R. E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, Pearson Education , 3rd edition. 2008.Reference books:Anil K Jain, Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing, Prentice –Hall Inc, 1989, Reprint 2004<strong>Course</strong> plan:Lec. No. Learning objectives Contents References@(Chapters)1-3 To introducefundamental conceptsand terms associatedwith digital images.4 To introduce theconcept of imageenhancement5-6 To study imageenhancement by graylevel transformations7-8 To study Histogramprocessing of an image9-10 To study Histogramprocessing of an image11-12 To learn imageenhancement byfiltering in the spatialdomain13-15 To introduce FourierTransform and thefrequency domainA simple image formation model; image sampling,quantization and interpolation2.3.4 -2.4.4Spatial Domain enhancement techniques 3.1Some basic gray level transformations: imagenegatives; log, power-law and piecewise linear3.2.1-3.2.4Histogram processing: equalization matching, 3.3-3.3.3local enhancementHistogram statistics; arithmetic/logic operations 3.3.4Spatial filtering: smoothing and sharpening 3.4-3.6.4Fourier Transform, sampling theorem,reconstruction4.2-4.316-17 Digital FourierDFT, Functions of two variables 4.4-4.5transforms18-19 Properties of 2D DFT Convolution, Correlation 4.620-22 To learn imageenhancement byfiltering in the frequencydomain23-24 Frequency domainfiltering25 To study the FastFourier TransformalgorithmFiltering in the frequency domain 4.7Smoothing, sharpening and selective filtering 4.8-4.10Fast Fourier Transform 4.11
26-27 Image degradation Image degradation model, 5.1-5.227-28 Degradation Estimating the degradation 5.629 To learn inversefiltering30-31 To introduce thefundamentals of imagecompression32-34 Basic Compressionmethods35-36 Basic Compressionmethods37-38 A brief introduction tosegmentationtechniques39-40 To study Imagereconstruction from theprojections41-42 To understandautomatic imagerecognition43 To learn where theimage processingInverse filtering 5.7Fundamentals of image compression 8.1Huffman, arithmetic and LZW coding. 8.2.1-8.2.4Run-Length, symbol based, Bit plane and 8.2.5-8.2.9predictive coding JPEGImage segmentation 10Image reconstruction from projections, Principle ofcomputer tomography (CT), Projection and RadonTransform, The Fourier slice theorem,Reconstruction Using Parallel-Beam FilteredBackprojections..Object recognition, Pattern and Pattern classes,Image recognition based on Decision-TheoreticMethods.Image Processing Applications such as Characterrecognition, Bio-medical application, Remotesensing.5.1112.1-12.2On-linematerialstechniques are applied* The lectures may be slightly diverge from aforesaid plan based on students ‘background & interest in the topic, whichmay perhaps include special lectures and discussions that would be planned and schedule notified accordingly.Evaluation Scheme:EC No Components Duration Weightage% Date & Time Venue1 QUIZ 1 20 Mins 7 [TBA] To be2 TEST 1 (Closed Book) 50 Mins 20 02-10-20133 ASSIGNMENT (MATLAB) 3 MONTHS 8 [TBA]4 TEST 2 (OPEN BOOK) 50 Mins 25 06-11-2013COMPREHENSIVE (Closed5book)* Only prescribed text book(s) and hand written notes are permitted.3 Hours 40 05.01.14 ANannouncedin therespectiveyear noticeboards* Assignment / Practical / Field / Case Studies: The Assignment / Practical will be given / conductedon either some or all of the above mentioned topics. Case studies, interpretation of data and then analysis,will form a part of all evaluation components. Assignments(s) may include seminar presentation and viva.Details will be intimated through a separate notification or announced in the class and the deadlines wouldbe indicated therein. However all assignments/reports would be completed by 2 nd week of December,2013. It is necessary that all students stick to time schedule and do not postpone submission ofassignments/reports. This will prevent extra load during last two weeks of class work. No make-ups wouldbe allowed for submission of assignments / practical reports.Reading Assignments: <strong>Student</strong>s are advised to read, collect additional information on the above mentioned topicsas per given schedule. In addition, awareness w.r.t. latest developments in the area would be an added advantage*The field indicated in blue is applicable only for those who conduct the evaluation components mentionedtherein.Mid-sem Grading:Mid-sem grading will be displayed after two evaluation components or earlier when- ever about 40 % ofevaluation components are completed.Note: A student will be likely to get “NC”, if he / she doesn’t appear / appear for the sake ofappearing for the evaluation components / scoring zero in pre-compre total.
Makeup and Attendance policies:Make-ups are not given as a routine. It is solely dependent upon the genuineness of the circumstancesunder which a student fails to appear in a scheduled evaluation component. In such circumstances, priorpermission should be obtained from the Instructor-in-Charge (I/C).The decision of the I/C in the abovematter will be final.Attendance: Every student is expected to be responsible for regularity of his/her attendance in classrooms and laboratories, to appear in scheduled tests and examinations and fulfill all other tasks assignedto him/her in every course. A student should have a minimum of 50% of attendance in a course to beeligible to appear for the Comprehensive Examination in that course. For the students under the purview ofAcademic Counseling Board (ACB), the Board shall prescribe the minimum attendance requirement on acase-to-case basis. Attendance in the course will be a deciding factor in judging the seriousness of astudent which may be directly / indirectly related to grading.General timings for consultation:Each instructor will specify his / her chamber consultation hours duringwhich the student can contact him / her in his / her chamber for consultation. (For details see part II)General instructions:<strong>Student</strong>s should come prepared for classes and carry the text book(s) or material(s) as prescribed by the<strong>Course</strong> Faculty to the class.Notices:All notices concerning the course will be displayed on the respective Notice Boards.Contact detailsDr. Jagadish Nayak Assistant ProfessorContact details: Chamber No:330 (Inside Communication Systems Lab, 3 rd Floor B wing)Contact No: +9714 4200700 Ext. 436 email: jagadishnayak@dubai.bits-pilani.ac.inMobile No: 055 4907979Instructor-in-ChargeDr. Jagadish Nayak