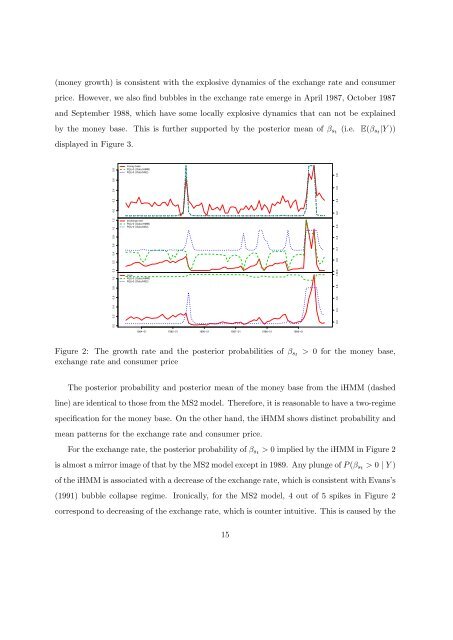
4 Empirical Application: Argentina HyperinflationIn this section, we apply the iHMM approach to the money base, exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate <strong>an</strong>d consumerprice in Argentina from J<strong>an</strong>uary 1983 to November 1989. The money base is used as a proxyfor market fundamental <strong>an</strong>d the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate data series is to capture fundamentally determinedbubble-like behavior. The purpose is to investigate whether there is evidence of bubblebehaviors in the consumer price.These three data series are also examined in HPS <strong>an</strong>d Shi (2010). Both HPS <strong>an</strong>d Shi (2010)conduct a two-regime <strong>Markov</strong>-switching ADF (MSADF) test (<strong>with</strong> different specifications inthe error vari<strong>an</strong>ce) on these three data series <strong>an</strong>d conclude no evidence of bubbles in theconsumer price. The two-regime <strong>Markov</strong>-switching (MS2) models of HPS <strong>an</strong>d Shi (2010) areboth estimated by MLE.As a benchmark, we estimate a MS2 model using the Bayesi<strong>an</strong> approach, which is 16∆y t | s t = j, Y 1,t−1 ∼ N(ϕ j0 + β j y t−1 + ϕ j1 ∆y t−1 + · · · + ϕ j4 ∆y t−4 , σ 2 j ) (18)Pr(s t = j | s t−1 = j) = p jj (19)<strong>with</strong> j = 1, 2. The prior of self-tr<strong>an</strong>sition probabilities p 11 <strong>an</strong>d p 22 is Beta(9, 1) <strong>an</strong>d the priorof (ϕ j , σ j ) is a normal-gamma distribution, namely σ −2jThe prior me<strong>an</strong> <strong>an</strong>d vari<strong>an</strong>ce of precision σ −2j∼ G(1, 1) <strong>an</strong>d ϕ j | σ j ∼ N(0, σ 2 I).are unity. The infinite hidden <strong>Markov</strong> model,(11)-(16) is estimated by setting L = 5 <strong>an</strong>d <strong>with</strong> priors ϕ, H ∼ NW(0, 1, 0.2I, 5), χ ∼ G(1, 1)<strong>an</strong>d ν ∼ Exp(1). 17 We set this prior in order to make the prior parameters of the MS2 modelequal to the me<strong>an</strong> of the hierarchical prior of the iHMM.Figure 2 illustrates the posterior probabilities of β st> 0 (i.e P (β st > 0|Y )) for the logarithmicmoney base, exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate <strong>an</strong>d consumer price. From the MS2 model (dotted line),we c<strong>an</strong> see that the posterior probability exceeds the 0.5 in June 1985 <strong>an</strong>d July 1989 for allthree data series, which suggests the existence of explosive behaviors. Me<strong>an</strong>while, since thespikes appear simult<strong>an</strong>eous in these two periods, the explosive behavior of market fundamentals16 The lag order is the same as that in HPS <strong>an</strong>d Shi (2010).17 Larger Ls produce the same results in bubble detection.14
(money growth) is consistent <strong>with</strong> the explosive dynamics of the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate <strong>an</strong>d consumerprice. However, we also find bubbles in the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate emerge in April 1987, October 1987<strong>an</strong>d September 1988, which have some locally explosive dynamics that c<strong>an</strong> not be explainedby the money base. This is further supported by the posterior me<strong>an</strong> of β st (i.e. E(β st |Y ))displayed in Figure 3.0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8money baseP(βt>0 | Data,IHMM)P(βt>0 | Data,MS2)0.2 0.4 0.6 0.80.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.20.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0exch<strong>an</strong>ge rateP(βt>0 | Data,IHMM)P(βt>0 | Data,MS2)priceP(βt>0 | Data,IHMM)P(βt>0 | Data,MS2)0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.91984−01 1985−01 1986−01 1987−01 1988−01 1989−01Figure 2: The growth rate <strong>an</strong>d the posterior probabilities of β stexch<strong>an</strong>ge rate <strong>an</strong>d consumer price> 0 for the money base,The posterior probability <strong>an</strong>d posterior me<strong>an</strong> of the money base from the iHMM (dashedline) are identical to those from the MS2 model. Therefore, it is reasonable to have a two-regimespecification for the money base. On the other h<strong>an</strong>d, the iHMM shows distinct probability <strong>an</strong>dme<strong>an</strong> patterns for the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate <strong>an</strong>d consumer price.For the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate, the posterior probability of β st > 0 implied by the iHMM in Figure 2is almost a mirror image of that by the MS2 model except in 1989. Any plunge of P (β st > 0 | Y )of the iHMM is associated <strong>with</strong> a decrease of the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate, which is consistent <strong>with</strong> Ev<strong>an</strong>s’s(1991) bubble collapse regime. Ironically, for the MS2 model, 4 out of 5 spikes in Figure 2correspond to decreasing of the exch<strong>an</strong>ge rate, which is counter intuitive. This is caused by the15