(PE) Pipe Performance in Potable Water Distribution Systems
(PE) Pipe Performance in Potable Water Distribution Systems
(PE) Pipe Performance in Potable Water Distribution Systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
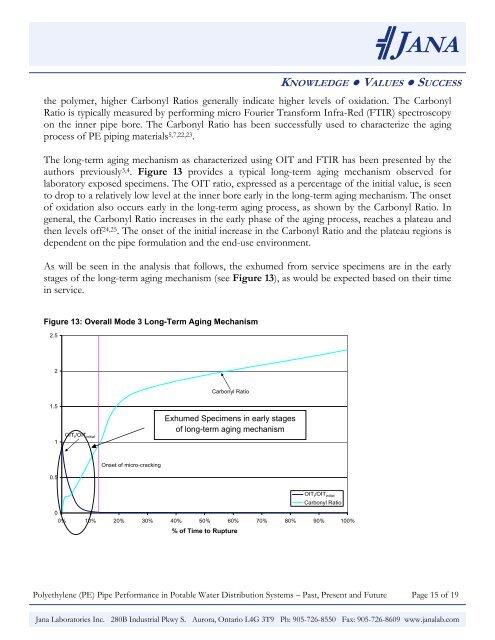
╣JANAKNOWLEDGE ● VALUES ● SUCCESSthe polymer, higher Carbonyl Ratios generally <strong>in</strong>dicate higher levels of oxidation. The CarbonylRatio is typically measured by perform<strong>in</strong>g micro Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) spectroscopyon the <strong>in</strong>ner pipe bore. The Carbonyl Ratio has been successfully used to characterize the ag<strong>in</strong>gprocess of <strong>PE</strong> pip<strong>in</strong>g materials 5,7,22,23 .The long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g mechanism as characterized us<strong>in</strong>g OIT and FTIR has been presented by theauthors previously 3,4 . Figure 13 provides a typical long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g mechanism observed forlaboratory exposed specimens. The OIT ratio, expressed as a percentage of the <strong>in</strong>itial value, is seento drop to a relatively low level at the <strong>in</strong>ner bore early <strong>in</strong> the long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g mechanism. The onsetof oxidation also occurs early <strong>in</strong> the long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g process, as shown by the Carbonyl Ratio. Ingeneral, the Carbonyl Ratio <strong>in</strong>creases <strong>in</strong> the early phase of the ag<strong>in</strong>g process, reaches a plateau andthen levels off 24,25 . The onset of the <strong>in</strong>itial <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> the Carbonyl Ratio and the plateau regions isdependent on the pipe formulation and the end-use environment.As will be seen <strong>in</strong> the analysis that follows, the exhumed from service specimens are <strong>in</strong> the earlystages of the long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g mechanism (see Figure 13), as would be expected based on their time<strong>in</strong> service.Figure 13: Overall Mode 3 Long-Term Ag<strong>in</strong>g Mechanism2.52Carbonyl Ratio1.51OIT t /OIT <strong>in</strong>itialExhumed Specimens <strong>in</strong> early stagesof long-term ag<strong>in</strong>g mechanismOnset of micro-crack<strong>in</strong>g0.500% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%% of Time to RuptureOITt/OIT<strong>in</strong>itialt Carbonyl RatioPolyethylene (<strong>PE</strong>) <strong>Pipe</strong> <strong>Performance</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Potable</strong> <strong>Water</strong> <strong>Distribution</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> – Past, Present and Future Page 15 of 19Jana Laboratories Inc. 280B Industrial Pkwy S. Aurora, Ontario L4G 3T9 Ph: 905-726-8550 Fax: 905-726-8609 www.janalab.com