Physics Study Guides.pdf - James M. Hill Memorial High School
Physics Study Guides.pdf - James M. Hill Memorial High School
Physics Study Guides.pdf - James M. Hill Memorial High School
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
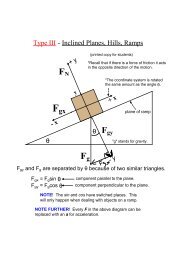
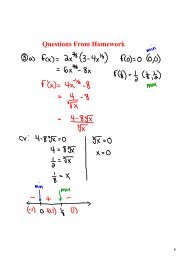
Newton’s Laws Problem GuideImportant EquationsF = maf = μNExampleF - forcef - force of frictionm - massμ - coefficient of frictiona - accelerationN - normal force<strong>Physics</strong>Equilibrium problems (where there is no net force) are the most common type of problem involving Newton’s laws.ExampleA block of mass m is at rest on an incline of angle θ. Solve for the the coefficient of static friction (μ) in terms of m,g, and θ.SolutionThe first step in any problem involving Newton’s laws is to draw anFBD of the situation and carefully label all the forces involved. TheFBD on the right shows all the forces all drawn from a single pointinstead of from where they’re acting so that it’s easier to visualizethe axes. In these sort of problems it is best to angle the coordinatesystem so that the x-axis is parallel to the incline. This forces us tobreak the weight vector into its components. Since the object is inequilibrium, the weight vector’s components can be matched to thenormal force and friction.Here is the mathematical process to solve this problem:start with the equation for frictionsubstitute the y-component of the weight vector (mg cos θ) for Nsubstitute the x-component of the weight vector (mg sin θ) for fsolve for μsimplify the resultNotesPage 3 of 3