Organic Farming in the Tropics and Subtropics: Peanuts - Naturland
Organic Farming in the Tropics and Subtropics: Peanuts - Naturland
Organic Farming in the Tropics and Subtropics: Peanuts - Naturland
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
II Special section: <strong>Organic</strong> Peanut Cultivation<br />
2.6. Biological methods of plant protection<br />
Many forms of resistance by peanuts aga<strong>in</strong>st pests <strong>and</strong> diseases are already<br />
known, <strong>and</strong> new, resistant stra<strong>in</strong>s are cont<strong>in</strong>ually be<strong>in</strong>g developed. The <strong>in</strong>ternational<br />
research <strong>in</strong>stitute ICRISAT Centre is devoted to this topic, <strong>and</strong> regularly publishes<br />
its results, as well as those of various o<strong>the</strong>r countries 17 .<br />
2.6.1. Diseases<br />
The most important ways of avoid<strong>in</strong>g diseases are:<br />
Crop rotation<br />
Choos<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> right variety<br />
Sufficient supply of nutrients<br />
Uproot<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>fest<strong>in</strong>g plants to stop <strong>the</strong> disease spread<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Destruction of any <strong>in</strong>fested plant parts after <strong>the</strong> harvest<br />
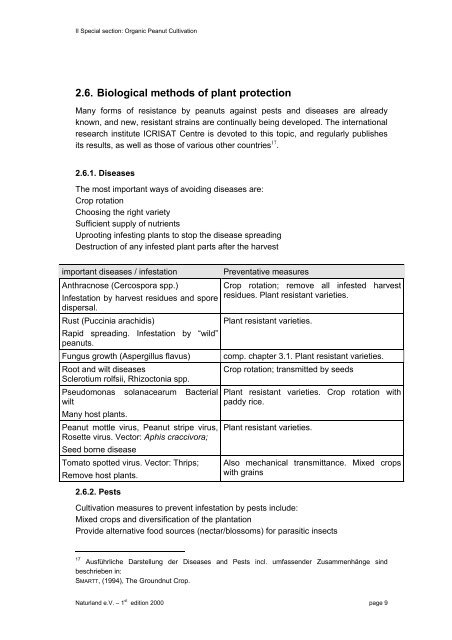
important diseases / <strong>in</strong>festation Preventative measures<br />
Anthracnose (Cercospora spp.)<br />
Infestation by harvest residues <strong>and</strong> spore<br />
dispersal.<br />
Rust (Pucc<strong>in</strong>ia arachidis)<br />
Rapid spread<strong>in</strong>g. Infestation by “wild”<br />
peanuts.<br />
Crop rotation; remove all <strong>in</strong>fested harvest<br />
residues. Plant resistant varieties.<br />
Plant resistant varieties.<br />
Fungus growth (Aspergillus flavus) comp. chapter 3.1. Plant resistant varieties.<br />
Root <strong>and</strong> wilt diseases<br />
Sclerotium rolfsii, Rhizoctonia spp.<br />
Pseudomonas solanacearum Bacterial<br />
wilt<br />
Many host plants.<br />
Peanut mottle virus, Peanut stripe virus,<br />
Rosette virus. Vector: Aphis craccivora;<br />
Seed borne disease<br />
Tomato spotted virus. Vector: Thrips;<br />
Remove host plants.<br />
2.6.2. Pests<br />
Crop rotation; transmitted by seeds<br />
Plant resistant varieties. Crop rotation with<br />
paddy rice.<br />
Plant resistant varieties.<br />
Also mechanical transmittance. Mixed crops<br />
with gra<strong>in</strong>s<br />
Cultivation measures to prevent <strong>in</strong>festation by pests <strong>in</strong>clude:<br />
Mixed crops <strong>and</strong> diversification of <strong>the</strong> plantation<br />
Provide alternative food sources (nectar/blossoms) for parasitic <strong>in</strong>sects<br />
17 Ausführliche Darstellung der Diseases <strong>and</strong> Pests <strong>in</strong>cl. umfassender Zusammenhänge s<strong>in</strong>d<br />
beschrieben <strong>in</strong>:<br />
SMARTT, (1994), The Groundnut Crop.<br />
Naturl<strong>and</strong> e.V. – 1 st edition 2000 page 9