6th - Public Schools of Robeson County
6th - Public Schools of Robeson County
6th - Public Schools of Robeson County
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
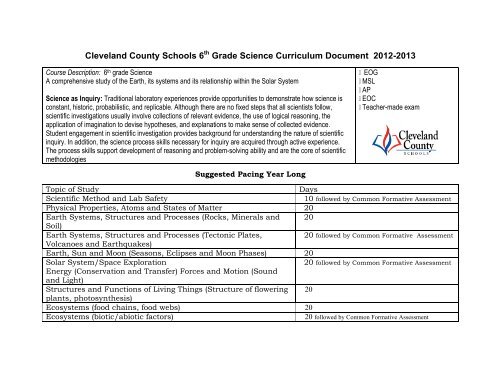
Cleveland <strong>County</strong> <strong>Schools</strong> 6 th Grade Science Curriculum Document 2012-2013Course Description: 6 th grade ScienceA comprehensive study <strong>of</strong> the Earth, its systems and its relationship within the Solar SystemScience as Inquiry: Traditional laboratory experiences provide opportunities to demonstrate how science isconstant, historic, probabilistic, and replicable. Although there are no fixed steps that all scientists follow,scientific investigations usually involve collections <strong>of</strong> relevant evidence, the use <strong>of</strong> logical reasoning, theapplication <strong>of</strong> imagination to devise hypotheses, and explanations to make sense <strong>of</strong> collected evidence.Student engagement in scientific investigation provides background for understanding the nature <strong>of</strong> scientificinquiry. In addition, the science process skills necessary for inquiry are acquired through active experience.The process skills support development <strong>of</strong> reasoning and problem-solving ability and are the core <strong>of</strong> scientificmethodologiesEOGMSLAPEOCTeacher-made examSuggested Pacing Year LongTopic <strong>of</strong> StudyDaysScientific Method and Lab SafetyPhysical Properties, Atoms and States <strong>of</strong> Matter 20Earth Systems, Structures and Processes (Rocks, Minerals and 20Soil)Earth Systems, Structures and Processes (Tectonic Plates,Volcanoes and Earthquakes)Earth, Sun and Moon (Seasons, Eclipses and Moon Phases) 20Solar System/Space ExplorationEnergy (Conservation and Transfer) Forces and Motion (Soundand Light)Structures and Functions <strong>of</strong> Living Things (Structure <strong>of</strong> flowering 20plants, photosynthesis)Ecosystems (food chains, food webs) 20Ecosystems (biotic/abiotic factors)20 followed by Common Formative Assessment10 followed by Common Formative Assessment20 followed by Common Formative Assessment20 followed by Common Formative Assessment
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesPhysical Science P1: Understand the properties <strong>of</strong> waves and the wavelike properties <strong>of</strong> waves and the wavelike property <strong>of</strong> energy inearthquakes, light, and sound.5 days 6.P.1.1primary waves, secondary • http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/earth/anatomy-tsunami.htmlCompare the properties <strong>of</strong> waves to waves, surface waves,the wavelike property <strong>of</strong> energy in epicenter, focus, fault • http://www.kettering.edu/physics/drussell/Demos/wavesintro/waves-intro.htmlearthquakes, light and sound. magnitude,Essential Questions:electromagnetic1. What are the characteristicsspectrum, Richter scale, • http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/waves.htm<strong>of</strong> a wave?2. How are waves created?earthquake, seismic,3. What is sound?waves, seismograph,4. What is light?Seismic waves,• http://www.kettering.edu/physics/drussell/Demos/waves/wav5. What is a seismic wave? longitudinal waves,emotion.html6. What are the basiccharacteristics <strong>of</strong> atransverse waves,potential energy, kinetic • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/aqa_pretransverse wave?energy, vibrations, sound _2011/radiation/anintroductiontowavesrev1.shtml7. What are the basic waves, light waves, light,characteristics <strong>of</strong> a wave length, trough,longitudinal wave?crest, amplitude, pitch, • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/aqa_pre6.P.1.2refraction, reflection,_2011/radiation/anintroductiontowavesact.shtmlExplain the relationship among10 days visible light, the electromagnetic compression, frequency,spectrum, and sight.disturbance, Doppler, • http://www.ngflcymru.org.uk/vtc/16022007/sound_travels/lesson.htmlEssential Questions:sound, parts <strong>of</strong> eye, color,1. What part <strong>of</strong> theReflection,electromagnetic spectrum isvisible light?electromagnetic spectrum(EMS), opaque,• www.pppst.com (PowerPoint)2. What causes light to appear translucent, visible light,as different colors? transparent, ultraviolet3. What type <strong>of</strong> a wave does rays, radiation, light color • United Streaming: Smash Lab, Earthquake Pro<strong>of</strong> Houselight travel as?
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources5 days4. What are the characteristics<strong>of</strong> light?5. How does the structure <strong>of</strong>the human eye detect light?6.P.1.3Explain the relationship among therate <strong>of</strong> vibration, the medium throughwhich vibrations travel, sound andhearing.Essential Questions:1. What are the characteristics<strong>of</strong> sound waves thatdetermine the properties <strong>of</strong>sound?2. How does sound travelthrough the mediums <strong>of</strong>solid, liquids, and gases?3. How is the human eardesigned to receive soundwaves?4. How do the vocal cordswork to produce sound?vs. pigment color, sounds,vocal cords, frequency,parts <strong>of</strong> the ear, function& structure <strong>of</strong> the ear,affect hearing, doppler,amplitude, pitch, matter,loudness• www.physicsclassroom.com• www.frontiernet.net/~imaging/play_apiano.html• www.freemosquitoringtone.org/• Waves foldables• Video <strong>of</strong> siren to show Doppler effect• www.brainpop.com• www.exploratorium.edu/exibits/mix n match/
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameReflections:ClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesLiteracy component:Writing Standard 2 – Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration <strong>of</strong> historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technicalprocesses.(show less)1. Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories as appropriate toachieving purpose; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension.2. Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples.3. Use appropriate and varied transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts.4. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic.5. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone.6. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented.Ex. How do waves carry energy? What are waves? The Nature <strong>of</strong> Sound – Summarizing Activity, Light and Color – Summarizing ActivityReading Standard 2 - Determine the central ideas or conclusions <strong>of</strong> a text; provide an accurate summary <strong>of</strong> the text distinct from prior knowledge oropinions.Technology:Physical Science P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties <strong>of</strong> matter.5 days 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is Atom, element, periodic • Refer to periodic table
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources5 daysmade up <strong>of</strong> atoms and atoms <strong>of</strong>the same element are all alike, butare different from the atoms<strong>of</strong> other elements.Essential questions:1. Distinguish among phases<strong>of</strong> matter and describeproperties <strong>of</strong> each phase.2. Investigate how particlesmove when heat energy isapplied.6.P.2.2 Explain the effect <strong>of</strong> heat onthe motion <strong>of</strong> atoms through adescription <strong>of</strong> what happens toparticles during a change inphase.table, matterThermal energy, density,heat energyBoiling point, meltingpoint, solubility, solvent,density• www.pppst.com• http://ww2.unime.it/weblab/mirror/ExplrSci/dswmedia/density.htm• http://ww2.unime.it/weblab/mirror/ExplrSci/dswmedia/density.htmEssential questions:1. What are the four phases <strong>of</strong>matter?2. What are the characteristics<strong>of</strong> each phase <strong>of</strong> matter?3. How does heat energy affectthe motion <strong>of</strong> atoms?4. What happens to particlesduring each phase change?
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources5 days6.P.2.3 Compare the physicalproperties <strong>of</strong> pure substances thatareindependent <strong>of</strong> the amount <strong>of</strong> matterpresent including density,melting point, boiling point, andsolubility to properties thatare dependent on the amount <strong>of</strong>matter present to includevolume, mass and weight.Essential Questions:1. What are the different waysthat energy can betransferred?2. How does the temperature<strong>of</strong> an object affect themovement <strong>of</strong> thermalenergy?3. What happens to thermalenergy during conduction,convection, and radiation?4. What are the similarities anddifferences between thedifferent forms <strong>of</strong> thermalenergy transfer?Reflections:
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesLiteracy Component:Writing Standard 2 – Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration <strong>of</strong> historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technicalprocesses.Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories as appropriate to achievingpurpose; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension.1. Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples.2. Use appropriate and varied transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts.3. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic.4. Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone.5. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented.Technology:
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesPhysical Science P.3 Understand characteristics <strong>of</strong> energy transfer and interactions <strong>of</strong> matter and energy.5 days 6.P.3.1Energy transfer,• www.discoveryIllustrate the transfer <strong>of</strong> heat energy heat transfer, radiation,from warmer objects to cooler ones convection, conductionusing examples <strong>of</strong> conduction,• www.education.comradiation and convection and theeffects that may result.5 days6.P.3.2Explain the effects <strong>of</strong>electromagnetic waves on variousmaterials to include absorption,scattering, and change intemperature.Essential Questions:1. How does light influence thetemperature <strong>of</strong> an object?2. How can you differentiatedbetween the different types <strong>of</strong>electromagnetic waves?3. How does the sun’s energy arriveas light?4. How can you distinguish white lightfrom the other colors <strong>of</strong> the visiblespectrum?5. What are the effects <strong>of</strong> the differentwavelengths <strong>of</strong> light?Electromagnetic waves,light, refracted andreflected, visiblespectrum, ultraviolet,infrared
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources6. How does light absorb or scattermatter?5 days6.P.3.3Explain the suitability <strong>of</strong> materials foruse in technologicaldesign based on a response to heat(to include conduction, expansion,and contraction) and electrical energy(conductors and insulators).Essential Questions:1. How is thermal energytransferred and converted into light?2. What are the similarities anddifferences between thermalconductors and insulators?3. What are examples <strong>of</strong>thermal conductors and insulators?4. How does change intemperature cause expansion andcontraction?5. How does electrical energymove through conductors andinsulators?6. How can you determine thebest material for use in atechnological design based on itsresponse to heat?Earth In the Universe
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesReflections:Literacy component:Reading Standard 9 - Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources withthat gained from reading a text on the same topic.Writing Standard 6 - Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and present the relationships betweeninformation and ideas clearly and efficientlyTechnology:
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesEarth Science E.1 Understand the earth/moon/sun system, and the properties, structures, and predictable motions <strong>of</strong> celestial bodies in theUniverse.6.E.1.1axis, craters, eclipse, • www.spacejpl.nasa.gov10 days Explain how the relative motion and equinox, lunar eclipse,relative position <strong>of</strong> themaria, solar eclipse, • Moon and Planet appsun, Earth and moon affect the meteoroid, moon phases,seasons, tides, phases <strong>of</strong> theneap tide, spring tide, • www.kidsastronomy.commoon, and eclipses.Newton’s lawEssential Questions:1. How does the rotation and <strong>of</strong> universal gravitation. • Moon and Planet apprevolution <strong>of</strong> the Earth affect units <strong>of</strong> orbit, penumbra, umbra,time on Earth?revolution, rotation,2. Why do we have seasons? solstice, waning, waxing3. How does the gravitationalpull and location <strong>of</strong> the sun, moon,and Earth affect ocean tides?4. How do the phases <strong>of</strong> themoon change as it revolves aroundEarth?5. What are the positions <strong>of</strong> thesun, moon, and Earth during a solarand lunar eclipse?6. How do the objects in oursolar system interact to createseasons? Tides? Moon phases?Eclipses?7. How does the rotation andrevolution <strong>of</strong> the Earth affect units <strong>of</strong>time on Earth?
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources8. Why do we have seasons?9. How does the gravitationalpull and location <strong>of</strong> the sun, moon,and Earth affect ocean tides?10. How do the phases <strong>of</strong> themoon change as it revolves aroundEarth?11. What are the positions <strong>of</strong> thesun, moon, and Earth during a solarand lunar eclipse?12. How do the objects in oursolar system interact to createseasons? Tides? Moon phases?Eclipses?10 days6.E.1.2Explain why Earth sustains life whileother planets do notbased on their properties (includingtypes <strong>of</strong> surface,atmosphere and gravitational force)and location to the Sun.Essential Questions:1. What are the conditionsneeded for living organisms tosurvive on planet Earth?2. What are the majordifferences between the inner andouter planets?3. What conditions on Earthmake it a suitable planet forsustaining life?
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources4. What conditions on otherplanets keep them from beingsuitable for sustaining life?5 days6.E.1.3Summarize space exploration andthe understandings gainedfrom them.Essential Questions:5. What early theories anddiscoveries helped us gainknowledge about planets?6. How do we use the datagained by space exploration?7. What instruments are usedto collect data from space?8. What discoveries made byspace instruments help us betterunderstand the universe?9. What are the risks andbenefits <strong>of</strong> the International SpaceShuttle?10. How have the technologiesdeveloped in space enhanced ourdaily lives?Reflections:
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesLiteracy Component:Writing Standard 1 - Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content.Introduce claim(s) about a topic or issue, acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons andevidence logically.1. Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant, accurate data and evidence that demonstrate an understanding <strong>of</strong> the topic or text,using credible sources.2. Use words, phrases, and clauses to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence.3. Establish and maintain a formal style.4. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented.Ex. What are the effects <strong>of</strong> the movements <strong>of</strong> the Earth and the Moon? – Summarizing Activity What are the characteristics <strong>of</strong> Earth’s Sun andMoon? – Summarizing ActivityWriting Standard 8 - Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility andaccuracy <strong>of</strong> each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions <strong>of</strong> others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format forcitation.
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameEx. Research PlanetsClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesReading Standard 2 - Determine the central ideas or conclusions <strong>of</strong> a text; provide an accurate summary <strong>of</strong> the text distinct from prior knowledge oropinions.Technology:Earth Science 6.E.2 Understand the structure <strong>of</strong> the earth and how interactions <strong>of</strong> constructive and destructive forces have resultedin changes in the surface <strong>of</strong> the earth over time and the effects <strong>of</strong> the lithosphere on humans.4 days 6.E.2.1 Summarize the structure <strong>of</strong>the earth, including the layers, themantle and core based on the relativeposition, compositionand density.••http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.htmlhttp://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/index.htmlEssential Questions:What are the layers <strong>of</strong> the Earth?What materials/elements make upeach layer <strong>of</strong> the Earth?What position, from outer to inner,geology, lithosphere,erosion, deposition,compaction, cementation,plate tectonics, mid oceanridge, rift valley, sea floorspreading, subductionzone, convergentboundaries, divergentboundaries, transformboundaries, shearing• http://urbanext.illinois.edu/earth/85.cfm• http://tlc.discovery.com/convergence/quakes/interactives/makeaquake.html• http://teacher.scholastic.com/scholasticnews/magazines/ass
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources7 daysare the Earth’s layers found?6.E.2.2 Explain how crustal platesand ocean basins are formed, moveand interact using earthquakes, heatflow and volcanoes toreflect forces within the earth.Essential Questions:1. What is the theory <strong>of</strong> platetectonics?2. What is the relationshipbetween plate boundaries and majorgeological events?3. How are the four types <strong>of</strong>plate boundaries similar anddifferent?4. What is seismology?tension, compressioninner core, outer core,magma, volcano, crust,mantle, metamorphic,rock cycle, sediment,Pangaea, asthenosphereets/sn_ts_022211_diagram.html• http://www.channelone.com/news/volcano/• http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/earth/anatomy-nyiragongovolcano.html• http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/natural-disasters/forces-<strong>of</strong>-nature/?section=v• http://kids.discovery.com/games/build-play/volcano-explorer• http://www.amnh.org/ology/features/plates/5 days6.E.2.3 Explain how the formation <strong>of</strong>soil is related to the parent rocktype and the environment in which itdevelops.Essential Questions:What are the characteristics <strong>of</strong>minerals?How are rocks different thanminerals?What are the phases <strong>of</strong> the rockcycle?6.E.2.4 Conclude that the goodhealth <strong>of</strong> humans requires:
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources4 daysmonitoring the lithosphere,maintaining soil quality andstewardship.Essential Questions:1. Why is it important tomonitor the quality <strong>of</strong> our soil as wellas our water and air?2. How have humans affectedthe environment to include the quality<strong>of</strong> our soil?3. What are some things thatwe can do to improve the quality <strong>of</strong>the pedosphere?Reflections:Literacy Component:Writing Standard 3 - Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, well-chosen details and wellstructuredevent sequences.Reading Standard 1 - Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis <strong>of</strong> science and technical texts.
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesTechnology:Life Science 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors <strong>of</strong> plants that enable them to survive and reproduce.10 days 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic• http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biologyii/nutrition/photosynthesis-activities.phpstructures and functions <strong>of</strong> floweringplants required for survival,reproduction and defense.Essential Questions:• http://www.nclark.net/PhotoRespiration1. What are the basicstructures <strong>of</strong> flowering plants?• http://filebox.vt.edu/users/dwilhelm/portfolio/biounitplan.pdf2. What purpose does each <strong>of</strong>these structures serve?10 days6.L.1.2 Explain the significance <strong>of</strong>the processes <strong>of</strong> photosynthesis,respiration, and transpiration to thesurvival <strong>of</strong> green plantsand other organisms.Essential Questions:3. What is the process <strong>of</strong>photosynthesis?4. What is the process <strong>of</strong>respiration?5. What is the process <strong>of</strong>transpiration?6. How do photosynthesis,Humus, decomposers,photosynthesis,chlorophyll, chloroplasts,angiosperm, pollen,sunlight, sugar, roots,pollination, seedling,stamen, ovary, anther,Fertilization, light energy,stomata, xylem, phloem,osmotic pressure, cellularrespiration, transpiration
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesrespiration and transpiration all worktogether to keep green plants alive?11. What are food chains andfood webs?12. What are the roles <strong>of</strong>each <strong>of</strong> the following: Producers,consumers and decomposers?13. How are oxygen, water,nitrogen and carbon dioxidecycled between living and nonlivingthings?KeyConceptsResourcesReflections:Literacy component:Reading Standard 9 - Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gainedfrom reading a text on the same topic.Ex. Read The Lorax, or Video, Science TextbookWriting Standard 10 - Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a dayor two) for a range <strong>of</strong> discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.Ex. Science Journal <strong>of</strong> effects <strong>of</strong> tropism
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResourcesTechnology:Life Science 6.L.2 Understand the flow <strong>of</strong> energy through ecosystems and the responses <strong>of</strong> populations to the biotic and abiotic factorsin their environment.5 days 6.L.2.2• http://plantsinmotion.bio.indiana.edu/plantmotion/movementExplain how plants respond toexternal stimuli (includings/tropism/tropisms.htmldormancy and forms <strong>of</strong> tropism) toenhance survival in an• http://leavingbio.net/plant%20responses.htmenvironment.Essential Questions:• http://www.biology-online.org/6/3_abiotic_factors.htm1. How do plants adapt toenvironmental conditions?• http://sciencereviewgames.com/srg/games/hs.php?id=812. What are dormancy andtropism?10 days6.L.2.3Summarize how the abiotic factors(such as temperature,water, sunlight, and soil quality) <strong>of</strong>biomes (freshwater,marine, forest, grasslands, desert,Producer, consumer,herbivore, carnivore,omnivore, decomposerfood web, scavenger,food chain, energypyramid, transmission,absorption, reflection,photosynthesis, estuary,perennial, dormancy,bulbs, positive tropism,environment, stimulus,gravity, temperature,biome, canopy, desert,grassland, savanna,deciduous, coniferous,permafrost, biotic, abiotic,rainforest, tundra• http://jklsciencelab.weebly.com/biotic-and-abioticfactors.html• http://exchange.smarttech.com/search.html?q=%20abiotic%20factors.%20biotic%20factors• http://www.fi.edu/tfi/units/life/habitat/habitat.html
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesTundra) affect the ability <strong>of</strong>organisms to grow, survive and/orcreate their own foodthrough photosynthesis.Essential Questions:3. How do physicalconditions such as temperature,water, sun light and soil quality indifferent biomes affect the ability<strong>of</strong> plants to grow and surviveKeyConceptsResources• http://www.geography4kids.com/files/land_ecosystem.html• http://www.thesciencequeen.net/Warm Ups: Sciencespot.netOther Resources: Spigot ScienceScience Queen• http://www.stcms.si.edu/stcms.htm• http://www.madsci.org/libs/MAD_libs.html• http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Graph-For-Students-to-Self-Monitor-Grades• http://www.superlativescience.com/2012/07/sciencenotebooks.html#comment-form• http://moneysavingmom.com/2012/05/free-ebookfascinating-science-for-kids.html
6 th grade ScienceTimeFrameClarifyingObjectivesKeyConceptsResources• http://sciencenotebooking.blogspot.com/search?updatedmin=2008-01-01T00%3A00%3A00-05%3A00&updatedmax=2009-01-01T00%3A00%3A00-05%3A00&maxresults=24• http://www.ateacherstreasure.com/p/tutorials.html