A GP-AHP method for solving group decision-making fuzzy AHP ...
A GP-AHP method for solving group decision-making fuzzy AHP ...
A GP-AHP method for solving group decision-making fuzzy AHP ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1984 C.-S. Yu / Computers & Operations Research 29 (2002) 1969–2001<br />
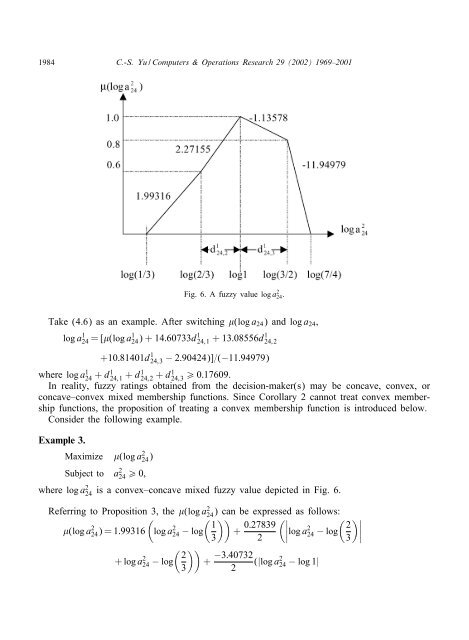
Fig. 6. A<strong>fuzzy</strong> value log a 2 24.<br />
Take (4.6) as an example. After switching (log a24) and log a24,<br />
log a 1 24 =[ (log a 1 24)+14:60733d 1 24;1 +13:08556d 1 24;2<br />
+10:81401d1 24;3 − 2:90424)]=(−11:94979)<br />
where log a1 24 + d124;1 + d124;2 + d124;3 ¿ 0:17609.<br />
In reality, <strong>fuzzy</strong> ratings obtained from the <strong>decision</strong>-maker(s) may be concave, convex, or<br />
concave–convex mixed membership functions. Since Corollary 2 cannot treat convex membership<br />
functions, the proposition of treating a convex membership function is introduced below.<br />
Consider the following example.<br />
Example 3.<br />
Maximize (log a 2 24)<br />
Subject to a 2 24 ¿ 0;<br />
where log a 2 24<br />
is a convex–concave mixed <strong>fuzzy</strong> value depicted in Fig. 6.<br />
) can be expressed as follows:<br />
(log a2 �<br />
24)=1:99316 log a2 � ��<br />
1<br />
24 − log +<br />
3<br />
0:27839<br />
��<br />
���<br />
log a<br />
2<br />
2 � ��<br />
2 ���<br />
24 − log<br />
3<br />
� ��<br />
2<br />
Referring to Proposition 3, the (log a 2 24<br />
+ log a 2 24 − log<br />
3<br />
+ −3:40732<br />
(|log a<br />
2<br />
2 24 − log 1|