Biochemie-Zentrum der Universität Heidelberg (BZH)
Biochemie-Zentrum der Universität Heidelberg (BZH)
Biochemie-Zentrum der Universität Heidelberg (BZH)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
8<br />
pool of inactive transcription factor. Inactivation<br />
of WCC requires the continuous activity of FRQ,<br />
since FRQ-dependent phosphorylation is antag-<br />
onized by PP2A-dependent dephosphorylation<br />
and reactivation of WCC.<br />
Fig. 3: The activity of the WCC is regulated by phosphorylation.<br />
Hyperphosphorylated WCC is inactive. It is<br />
activated by PP2A-dependent dephosphorylation. Dephosphorylated<br />
WCC binds to the frq promoter and activates<br />
transcription. When FRQ protein is synthesized, it<br />
recruits CK1a and inactivates the WCC by promoting its<br />
phosphorylation.<br />
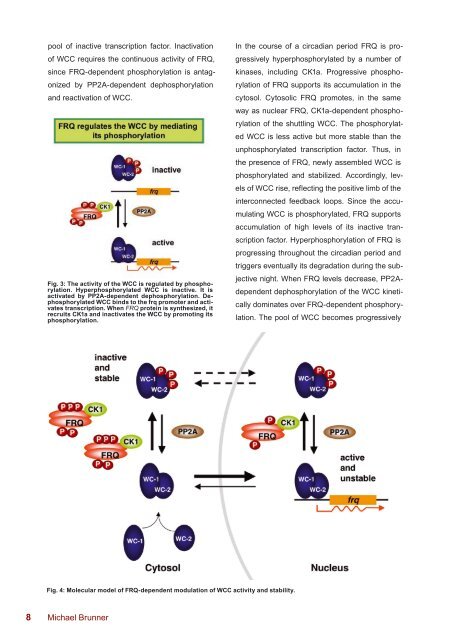
Fig. 4: Molecular model of FRQ-dependent modulation of WCC activity and stability.<br />
Michael Brunner<br />
In the course of a circadian period FRQ is pro-<br />
gressively hyperphosphorylated by a number of<br />
kinases, including CK1a. Progressive phospho-<br />
rylation of FRQ supports its accumulation in the<br />
cytosol. Cytosolic FRQ promotes, in the same<br />
way as nuclear FRQ, CK1a-dependent phospho-<br />
rylation of the shuttling WCC. The phosphorylat-<br />
ed WCC is less active but more stable than the<br />
unphosphorylated transcription factor. Thus, in<br />
the presence of FRQ, newly assembled WCC is<br />
phosphorylated and stabilized. Accordingly, lev-<br />
els of WCC rise, reflecting the positive limb of the<br />
interconnected feedback loops. Since the accu-<br />
mulating WCC is phosphorylated, FRQ supports<br />
accumulation of high levels of its inactive tran-<br />
scription factor. Hyperphosphorylation of FRQ is<br />
progressing throughout the circadian period and<br />
triggers eventually its degradation during the sub-<br />
jective night. When FRQ levels decrease, PP2A-<br />
dependent dephosphorylation of the WCC kineti-<br />
cally dominates over FRQ-dependent phosphory-<br />
lation. The pool of WCC becomes progressively