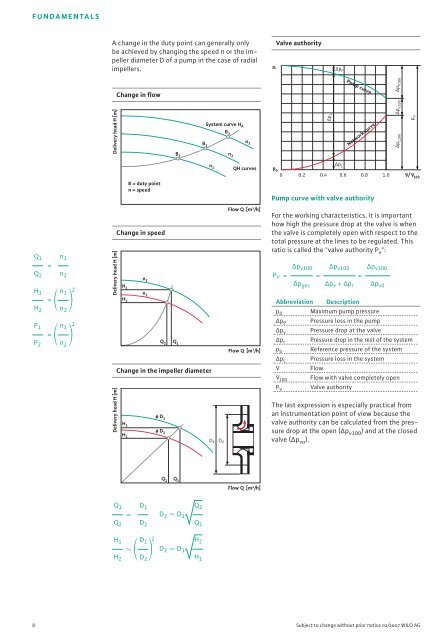
PLH_KKK_U2_31.QXP 25.05.2007 11:01 Uhr Seite 8FUNDAMENTALSA change in the duty point can generally onlybe achieved by changing the speed n or the impellerdiameter D of a pump in the case of radialimpellers.pValve authority∆p PQ 1 n 1=Q 2 n 2 H 2 n 2H 1 n 12= P 2 n 2P 1 n 12=Delivery head H [m]Delivery head H [m]Delivery head H [m]Change in flowChange in speedH 1n 1n 2H 2Q 1H 1B = duty pointn = speedQ 2Change in the impeller diameterø D 1ø D 2H 2Q 1Q 2Q 1 D 1 D 2 D 1Q 2 D 2 H 2 D 2H 1 D 12 D 2 D 1System curve H AB 1B 2B 3n 1n 2n 3D 1 D 2Q 2Q 1H 2H 1QH curvesFlow Q [m³/h]Flow Q [m 3 /h]Flow Q [m³/h]p 0Pump curve with valve authorityFor the working characteristics, it is importanthow high the pressure drop at the valve is whenthe valve is completely open with respect to thetotal pressure at the lines to be regulated. Thisratio is called the "valve authority P v ":∆p v100 ∆p v100P V = ==∆p ges ∆p v + ∆p rAbbreviationp 0∆p P∆p v∆p rp b∆p LV˙V˙100P VDescriptionMaximum pump pressurePressure loss in the pumpPressure drop at the valvePressure drop in the rest of the systemReference pressure of the systemPressure loss in the systemFlow∆p LFlow with valve completely openValve authorityPump curveNetwork curve0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0∆p v100∆p v0V˙/V˙100The last expression is especially practical froman instrumentation point of view because thevalve authority can be calculated from the pressuredrop at the open (∆p v100 ) <strong>and</strong> at the closedvalve (∆p vo ).p 0∆p v100 ∆p P100∆p L100∆p v8 Subject to change without prior notice 02/2007 WILO AG
PLH_KKK_U2_31.QXP 25.05.2007 11:01 Uhr Seite 9FUNDAMENTALSSuction behaviour of the centrifugal pumpGeneralThe cause of pump suction is the pressure appliedto the liquid level in the suction tank,so in the case of an open tank, this is the atmospheric<strong>air</strong> pressure. Its mean value at sea level isp b = 101320 N/m 2 (= 1.0132 bar) <strong>and</strong> is equivalentto the pressure of a water column 10.33 m high at4 °C. Thus, normal <strong>air</strong> pressure must allow thepump to be able to pump water from a depth ofabout 10 m. The actually reachable geodeticsuction head H S geo is considerably less, however.The reasons for this are:• Fluids evaporate when the temperature-dependentvapour pressure p D N/m 2 is reached.The pressure can then only drop to this value atthe highest point of the suctioned fluid column.• Pump head losses occur in the suction line as aresult of speed generation – v S 2 /2 g [m] –, aswell as due to fluid friction, direction changes<strong>and</strong> changes in cross-section H VS [m].A further pump head loss is caused by friction<strong>and</strong> speed changes when the fluid enters theblade channels. To avoid vapour formation, thetotal head (static pump head plus the velocityhead v S 2 /2g) in the entry cross-section of thepump must therefore be greater than the vapourpressure head of the pumped fluid by a certainamount. This energy difference is referred toas NPSH [m], the abbreviation for "net positivesuction head", <strong>and</strong> is identical with the previouslycommon term "maintained pressure headH H ".When the pump is installed above the suctionwater level, <strong>and</strong> the shaft is horizontal <strong>and</strong> thesuction tank open, the head difference H S geomay not be greater thanp b P DH S geo = - - H VS - NPSH [m]g · ρ g · ρwith gravitational acceleration g in m/s 2 <strong>and</strong>the density ρ in kg/m 3 . If the suction tank isclosed, then the absolute pump head in thetank (p I + p b )/g · ρ appears for p b /g · ρ, wherebyp I st<strong>and</strong>s for the overpressure in the tank.With the pressure units in bar, the density ρin kg/dm 3 <strong>and</strong> g = 9.81 m/s 2 , the equation takeson the following generally valid form:10.2 · (p b + p l - P D )H S geo = - H VS - NPSH [m]ρIn the case of underpressure in the suction tank,p I has a negative sign.Required NPSH (NPSHR)The smallest value of the NPSH at which thepump can be continuously operated under thegiven working conditions (speed, flow, deliveryhead, pumped fluid) can be determined fromthe pump curves in the catalogues. The NPSHdefined this way is also called NPSHR (NPSHrequired). It is not a constant value, but stronglyincreases with increasing flow. If one comparescentrifugal pumps having different specificspeeds, one can see that the NPSH value growswith increasing specific speed. The suction thendecreases. Pumps which run very fast can thereforeoften only overcome low suction heads oreven only be operated at inlet head, even withcold water. Improvement is possible by selectinga lower operating speed, but this at the cost ofeconomic efficiency.Available NPSH (NPSHA)For an existing or planned system, the NPSHAavailable at the entry cross-section of the pumpcan be determined by solving the equation forNPSH:10.2 · (p b + p l - P D )NPSHA = - H VS - H S geo [m]ρIf the fluid level is above the pump, instead ofH s geo the geodetic inlet head H z geo is pluggedin <strong>and</strong> the equation becomes:10.2 · (p b + p l - P D )NPSHA = - H VS + H S geo [m]ρ• When planning a pump system, it is recommendedthat a pump be selected which hasan NPSHR at least 0.5 m lower than the availableNPSHA.• For a pump in operation, by measuring the pressurep1 at the suction flange of the pump, theNPSHA can be calculated from the equation10.2 · (p b + p l - P D ) v 2 1NPSHA = + - H S geo [m]ρ2 · gwith the previously given units for the pressure<strong>and</strong> density. If this is an underpressure, p 1 isgiven a negative sign. The quantity v 1 is theaverage flowrate in the entry cross-section A 1of the pump, v 1 = Q/A 1 with Q in m 3 /s <strong>and</strong> A 1in m 2 .Wilo Planning Guide - <strong>Refrigeration</strong>, <strong>air</strong>-<strong>conditioning</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>cooling</strong> <strong>technology</strong> 02/2007 9