ENG Chapter 1 - Biodiversity Skills
ENG Chapter 1 - Biodiversity Skills
ENG Chapter 1 - Biodiversity Skills
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
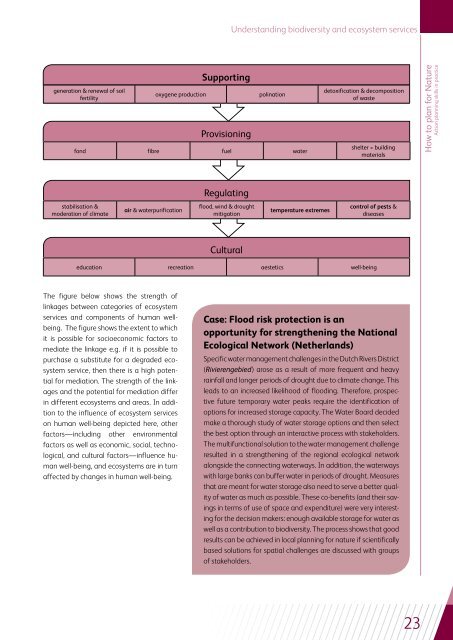
Understanding biodiversity and ecosystem servicesgeneration & renewal of soilfertilityoxygene productionSupportingProvisioningpolinationfond fibre fuel waterdetoxification & decompositionof wasteshelter = buildingmaterialsHow to plan for NatureAction planning skills in practiceRegulatingstabilisation &moderation of climateair & waterpurificationflood, wind & droughtmitigationtemperature extremescontrol of pests &diseasesCulturaleducation recreation aestetics well-beingThe figure below shows the strength oflinkages between categories of ecosystemservices and components of human wellbeing.The figure shows the extent to whichit is possible for socioeconomic factors tomediate the linkage e.g. if it is possible topurchase a substitute for a degraded ecosystemservice, then there is a high potentialfor mediation. The strength of the linkagesand the potential for mediation differin different ecosystems and areas. In additionto the influence of ecosystem serviceson human well-being depicted here, otherfactors—including other environmentalfactors as well as economic, social, technological,and cultural factors—influence humanwell-being, and ecosystems are in turnaffected by changes in human well-being.Case: Flood risk protection is anopportunity for strengthening the NationalEcological Network (Netherlands)Specific water management challenges in the Dutch Rivers District(Rivierengebied) arose as a result of more frequent and heavyrainfall and longer periods of drought due to climate change. Thisleads to an increased likelihood of flooding. Therefore, prospectivefuture temporary water peaks require the identification ofoptions for increased storage capacity. The Water Board decidedmake a thorough study of water storage options and then selectthe best option through an interactive process with stakeholders.The multifunctional solution to the water management challengeresulted in a strengthening of the regional ecological networkalongside the connecting waterways. In addition, the waterwayswith large banks can buffer water in periods of drought. Measuresthat are meant for water storage also need to serve a better qualityof water as much as possible. These co-benefits (and their savingsin terms of use of space and expenditure) were very interestingfor the decision makers: enough available storage for water aswell as a contribution to biodiversity. The process shows that goodresults can be achieved in local planning for nature if scientificallybased solutions for spatial challenges are discussed with groupsof stakeholders.23