September 2004 - bcps
September 2004 - bcps
September 2004 - bcps
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
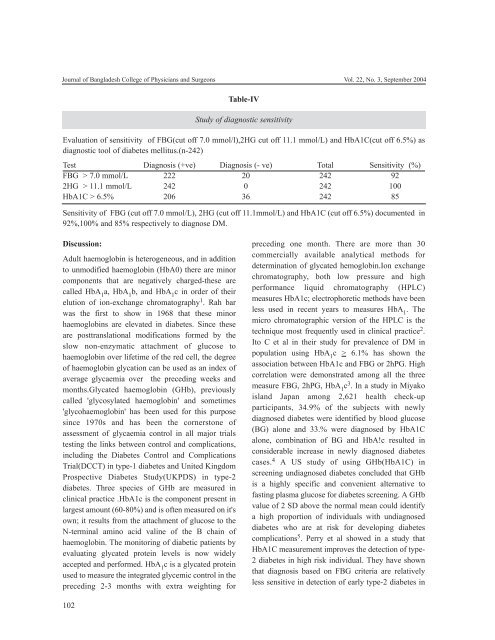
Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 22, No. 3, <strong>September</strong> <strong>2004</strong>Table-IVStudy of diagnostic sensitivityEvaluation of sensitivity of FBG(cut off 7.0 mmol/l),2HG cut off 11.1 mmol/L) and HbA1C(cut off 6.5%) asdiagnostic tool of diabetes mellitus.(n-242)Test Diagnosis (+ve) Diagnosis (- ve) Total Sensitivity (%)FBG > 7.0 mmol/L 222 20 242 922HG > 11.1 mmol/L 242 0 242 100HbA1C > 6.5% 206 36 242 85Sensitivity of FBG (cut off 7.0 mmol/L), 2HG (cut off 11.1mmol/L) and HbA1C (cut off 6.5%) documented in92%,100% and 85% respectively to diagnose DM.Discussion:Adult haemoglobin is heterogeneous, and in additionto unmodified haemoglobin (HbA0) there are minorcomponents that are negatively charged-these arecalled HbA 1a, HbA 1b, and HbA 1c in order of theirelution of ion-exchange chromatography 1 . Rah barwas the first to show in 1968 that these minorhaemoglobins are elevated in diabetes. Since theseare posttranslational modifications formed by theslow non-enzymatic attachment of glucose tohaemoglobin over lifetime of the red cell, the degreeof haemoglobin glycation can be used as an index ofaverage glycaemia over the preceding weeks andmonths.Glycated haemoglobin (GHb), previouslycalled 'glycosylated haemoglobin' and sometimes'glycohaemoglobin' has been used for this purposesince 1970s and has been the cornerstone ofassessment of glycaemia control in all major trialstesting the links between control and complications,including the Diabetes Control and ComplicationsTrial(DCCT) in type-1 diabetes and United KingdomProspective Diabetes Study(UKPDS) in type-2diabetes. Three species of GHb are measured inclinical practice .HbA1c is the component present inlargest amount (60-80%) and is often measured on it'sown; it results from the attachment of glucose to theN-terminal amino acid valine of the B chain ofhaemoglobin. The monitoring of diabetic patients byevaluating glycated protein levels is now widelyaccepted and performed. HbA 1c is a glycated proteinused to measure the integrated glycemic control in thepreceding 2-3 months with extra weighting forpreceding one month. There are more than 30commercially available analytical methods fordetermination of glycated hemoglobin.Ion exchangechromatography, both low pressure and highperformance liquid chromatography (HPLC)measures HbA1c; electrophoretic methods have beenless used in recent years to measures HbA 1. Themicro chromatographic version of the HPLC is thetechnique most frequently used in clinical practice 2 .Ito C et al in their study for prevalence of DM inpopulation using HbA 1c > 6.1% has shown theassociation between HbA1c and FBG or 2hPG. Highcorrelation were demonstrated among all the threemeasure FBG, 2hPG, HbA 1c 3 . In a study in Miyakoisland Japan among 2,621 health check-upparticipants, 34.9% of the subjects with newlydiagnosed diabetes were identified by blood glucose(BG) alone and 33.% were diagnosed by HbA1Calone, combination of BG and HbA!c resulted inconsiderable increase in newly diagnosed diabetescases. 4 A US study of using GHb(HbA1C) inscreening undiagnosed diabetes concluded that GHbis a highly specific and convenient alternative tofasting plasma glucose for diabetes screening. A GHbvalue of 2 SD above the normal mean could identifya high proportion of individuals with undiagnoseddiabetes who are at risk for developing diabetescomplications 5 . Perry et al showed in a study thatHbA1C measurement improves the detection of type-2 diabetes in high risk individual. They have shownthat diagnosis based on FBG criteria are relativelyless sensitive in detection of early type-2 diabetes in102