Modeling Hydra Behavior Using Methods Founded in Behavior-Based Robotics
Modeling Hydra Behavior Using Methods Founded in ... - SAIS
Modeling Hydra Behavior Using Methods Founded in ... - SAIS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
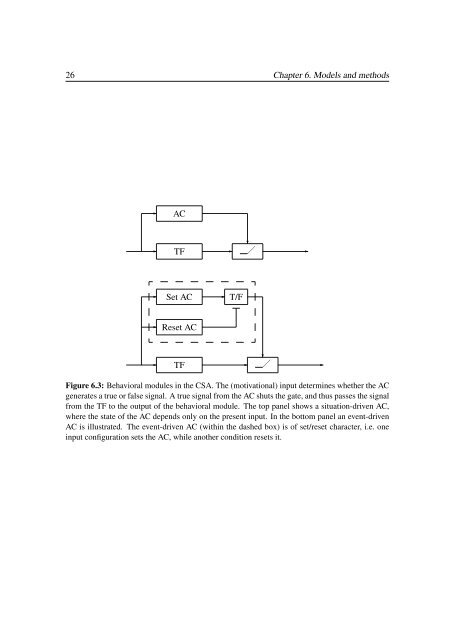
26 Chapter 6. Models and methods✲AC❄✲ TF ✲ ✲✲Set AC✲ T/F✲Reset AC❄✲ TF ✲ ✲Figure 6.3: <strong>Behavior</strong>al modules <strong>in</strong> the CSA. The (motivational) <strong>in</strong>put determ<strong>in</strong>es whether the ACgenerates a true or false signal. A true signal from the AC shuts the gate, and thus passes the signalfrom the TF to the output of the behavioral module. The top panel shows a situation-driven AC,where the state of the AC depends only on the present <strong>in</strong>put. In the bottom panel an event-drivenAC is illustrated. The event-driven AC (with<strong>in</strong> the dashed box) is of set/reset character, i.e. one<strong>in</strong>put configuration sets the AC, while another condition resets it.