Guidelines for Usage of Digital Signatures in e-Governance
Guidelines for Usage of Digital Signatures in e-Governance - DOIT & C
Guidelines for Usage of Digital Signatures in e-Governance - DOIT & C
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
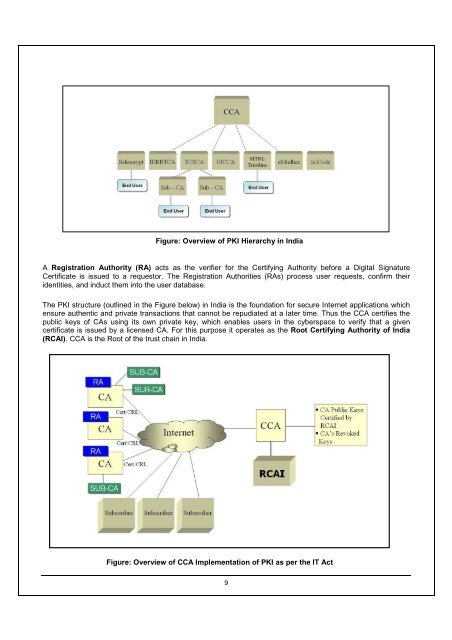
Figure: Overview <strong>of</strong> PKI Hierarchy <strong>in</strong> India<br />
A Registration Authority (RA) acts as the verifier <strong>for</strong> the Certify<strong>in</strong>g Authority be<strong>for</strong>e a <strong>Digital</strong> Signature<br />
Certificate is issued to a requestor. The Registration Authorities (RAs) process user requests, confirm their<br />
identities, and <strong>in</strong>duct them <strong>in</strong>to the user database.<br />
The PKI structure (outl<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> the Figure below) <strong>in</strong> India is the foundation <strong>for</strong> secure Internet applications which<br />
ensure authentic and private transactions that cannot be repudiated at a later time. Thus the CCA certifies the<br />
public keys <strong>of</strong> CAs us<strong>in</strong>g its own private key, which enables users <strong>in</strong> the cyberspace to verify that a given<br />
certificate is issued by a licensed CA. For this purpose it operates as the Root Certify<strong>in</strong>g Authority <strong>of</strong> India<br />
(RCAI). CCA is the Root <strong>of</strong> the trust cha<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> India.<br />
Figure: Overview <strong>of</strong> CCA Implementation <strong>of</strong> PKI as per the IT Act<br />
9