Crystal growth and defects
Crystal growth and defects
Crystal growth and defects
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
� G<br />
*<br />
� Gn<br />
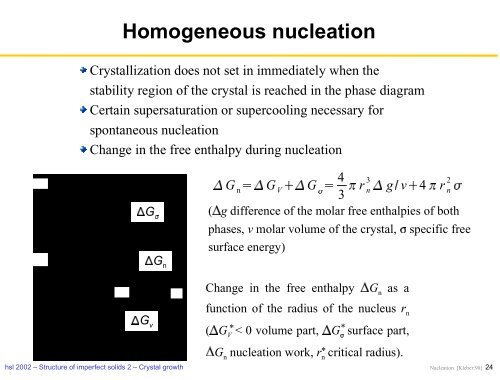
Homogeneous nucleation<br />
<strong>Crystal</strong>lization does not set in immediately when the<br />
stability region of the crystal is reached in the phase diagram<br />
Certain supersaturation or supercooling necessary for<br />
spontaneous nucleation<br />
Change in the free enthalpy during nucleation<br />
r* n<br />
� Gv<br />
� G �� Gn<br />
r n<br />
Change in the free enthalpy<br />
� Gn as a<br />
function of the radius of the nucleus r n<br />
(<br />
(<br />
� G n<br />
� g difference of the molar free enthalpies of both<br />
phases, v molar volume of the crystal, � specific free<br />
surface energy)<br />
� GV < 0 volume part,<br />
� G � surface part,<br />
� Gn nucleation work, rn critical radius).<br />
hsl 2002 – Structure of imperfect solids 2 – <strong>Crystal</strong> <strong>growth</strong> Nucleation [Kleber:90] 24<br />
�<br />
� G V<br />
�<br />
� G �<br />
�<br />
4<br />
3<br />
* *<br />
*<br />
� r n<br />
3 � g<br />
� v<br />
� 4<br />
� r n<br />
2 �